Summary:
- Nvidia is a leading provider of graphics cards for computing and Data Center AI.
- The company is facing headwinds due to lower gaming demand, but the industry tends to be cyclical.
- Its Data center AI business is growing strong and its products have been adopted by all major hyperscalers such as AWS, Azure and Google Cloud.
Justin Sullivan
The Artificial Intelligence industry is now at a major tipping point towards mass adoption, as computing technology has improved and costs have plummeted. Therefore it is no surprise that the AI industry was valued at $387.45 billion in 2022 and is forecasted to grow at a rapid 20.1% compounded annual growth rate, reaching a value of $1.39 trillion by 2029. Picking a winner in the AI industry is challenging, so when there is a gold rush, why not sell shovels by investing in a company like Nvidia which has developed the backbone infrastructure through its revolutionary chips. In this post, I’m going to break down Nvidia’s AI advantage, its financials, and valuation, let’s dive in.
What is AI?
AI basically uses software models to create a human-like intelligence capable of completing tasks. Recently, the OpenAI institute, which is backed by Elon Musk and Y Combinator’s Sam Altman, has released a series of free AI tools, which have gone viral. These tools include DALL-E, an AI image generator, which enables you to write any words into the search box and get a custom image generated. For example, I asked the platform to create me random images of a monkey wearing a hat and playing basketball which it did.
Monkey Wearing a Hat, playing basketball (Created by author with AI image generator)
I also created an image of ” Warren Buffett wearing an apron”, which you can see below. This tool may seem like a joke, but it has the potential to put many graphic designers and artists out of work.
Warren Buffett Apron (created by author with AI Image Generator)
Another popular tool announced is ChatGPT, which offers a human language interface that can be used to answer exam questions and even write software code. The reason this is interesting is Nvidia (NASDAQ:NVDA) has established a strong foothold as a leader in AI for enterprises, so if the aforementioned free tools look interesting, imagine what the world’s best supercomputers can accomplish, I will discuss that in the next section.
Artificial Intelligence and Nvidia
Nvidia is a semiconductor chip designer known for being a leader in high-performance graphic cards. If you have a high-powered PC, it will likely use an NVIDIA Graphical processing unit [GPU].
Nvidia also has a thriving Data Center focused Artificial Intelligence business. Oracle recently announced an extended partnership with Nvidia to help scale Artificial Intelligence for enterprises. Oracles Cloud Infrastructure [OCI] aims to make NVIDIA’s AI enterprise platform available to large organizations. As you can see on the chart below, Oracles cloud infrastructure utilizes 512 Nvidia GPUs per “cluster”. This equates to “tens of thousands” of Nvidia GPUs for Oracle’s entire infrastructure, this includes Nvidia’s A100 chips and new H100 GPUs.
Nvidia Oracle (Next Platform/Oracle)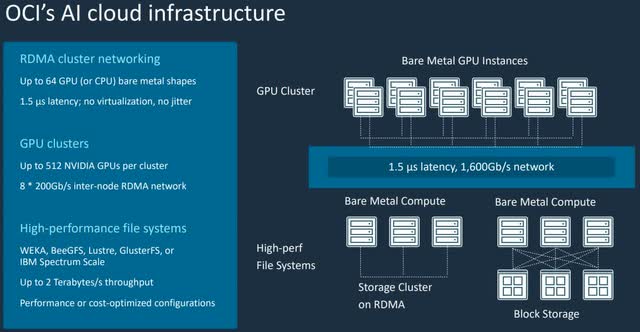
Nvidia’s H100 GPU is a technological breakthrough as it offers 7 times better performance than its A100 for specific accelerated computing tasks. These include Genome Sequencing, a rapidly growing industry. In addition to Fast Fourier Transform [FFT], a mathematical model with applications such as RADAR and signal processing.
Nvidia H100 performance (Nvidia)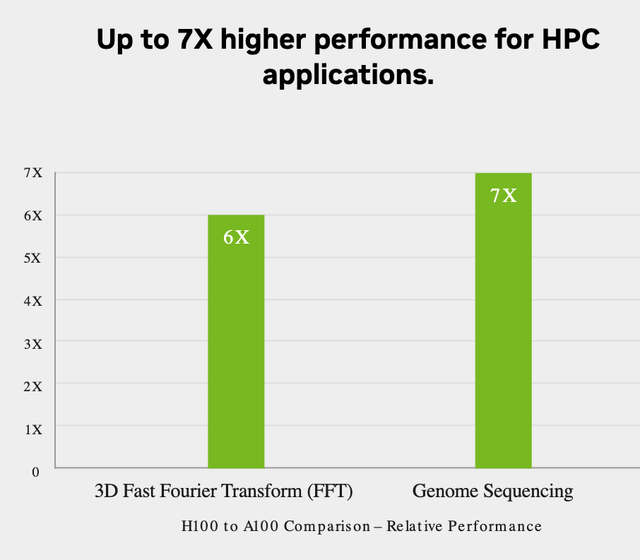
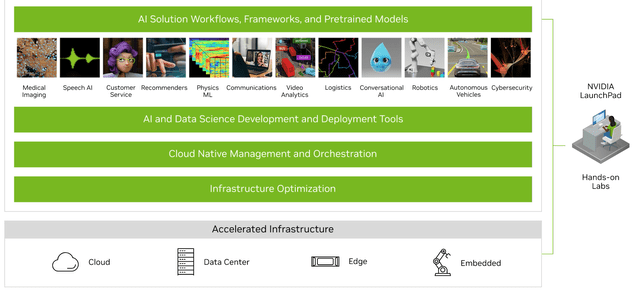
Nvidia’s AI platform enables organizations to develop AI solutions for their business. This includes all aspects of the process from data processing, to AI model training and scaled deployment. There are many applications that include “Conversational AI” bots, business process automation, computer vision technology and much more. A specific use case is Nvidia Clara, which uses AI and high-performance computing [HPC] for drug discovery, medical imaging, and even genomics.
Nvidia has also recently (December 7th) announced a partnership with Deutsche Bank to accelerate the use of AI in the financial services sector. The bank will utilize Nvidia’s Enterprise AI platform on its Google Cloud infrastructure for a variety of applications. This includes the use of real-time “risk valuation,” which usually is an overnight process, as it is so CPU intensive. In addition, the bank plans to use it for “Price discovery” and model backtesting. This means its traders can manage risk more effectively while also driving down energy costs with accelerated computing.
Deutsche Bank also aims to leverage Nvidia’s AI platform in order to create 3D virtual avatars. These are expected to be used for a variety of applications from customer service to the navigation of internal HR questions. The next stage after this will be “metaverse style’ experiences with its banking clients.
Nvidia Avatar of CEO Jenson (Nvidia)
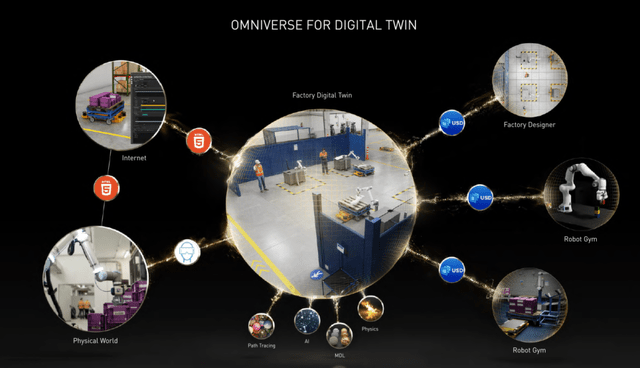
Nvidia has also scaled its AI-powered “Digital Twin” business, which can be used to create copies of manufacturing facilities. This can then be used to optimize production and better visualize improvements. Nvidia is even creating a “Digital Twin” of the entire earth, which can be used to track global warming and potential changes to emissions.
Financial Review
Nvidia reported mixed financial results for the third quarter of fiscal year 2023. Its revenue was $5.9 billion, which actually declined by 17% year over year, a positive is this metric still surpassed analyst estimates by $114.74 million.
The revenue decline was mainly driven by a substantial 51% decline in gaming segment revenue to $1.574 billion. This may seem terrible at first glance, it should be noted that the gaming industry has been cyclical historically and thus a demand pullback was expected after a major boom in 2020. In addition, many consumers purchased Nvidia graphics cards for Bitcoin mining in 2020, and with the decline in Bitcoin we are also experiencing a “crypto winter”.
Nvidia Gaming Revenue (Q3,FY23 report)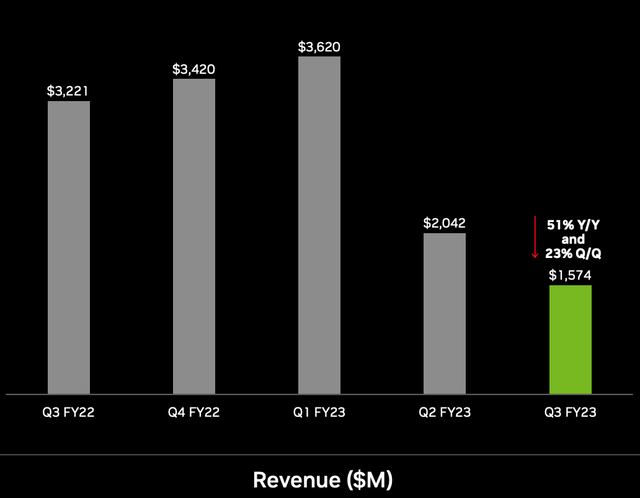
Data Center is the growth engine
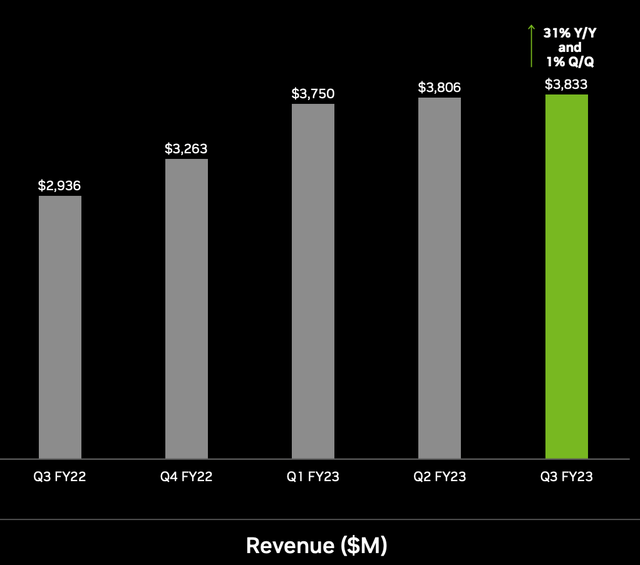
A positive for Nvidia is its Data Center business, which has continued to thrive, thanks to the aforementioned tailwinds in its AI chips. Its Data Center segment reported $3.83 billion in revenue, which increased by a rapid 31% year over year. A positive for Nvidia is this segment contributes ~64% of total revenue and thus the fact this is growing strong is a positive. This segment also continues to grow thanks to the ongoing “Digital Transformation” of Enterprises as companies move their I.T workloads to the cloud. The cloud industry was valued at $429.5 billion in 2021 and is forecasted to grow at a rapid 15.8% compounded annual growth rate up until 2028.
In the first quarter of 2023, Nvidia plans to supply its new H100 AI chips to all the major cloud infrastructure providers such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. In mid-November, the company reported a large partnership with Microsoft Azure, which aims to build a vast AI supercomputer for its enterprise customers.
Nvidia‘s automotive segment is also rapidly growing as it increased its revenue by an outstanding 86% year over year to $251 million. This is still a small section of Nvidia’s overall business but has huge potential.
Nvidia’s open AI car computing platform called “Nvidia DRIVE” is utilized by many automotive manufacturers such as Mercedes, Volvo, and Audi. The goal of the platform is to help enable self-driving technology at scale, as most automotive manufacturers have not developed this technology in-house (unlike Tesla).
Automotive Revenue (Q3,22 report)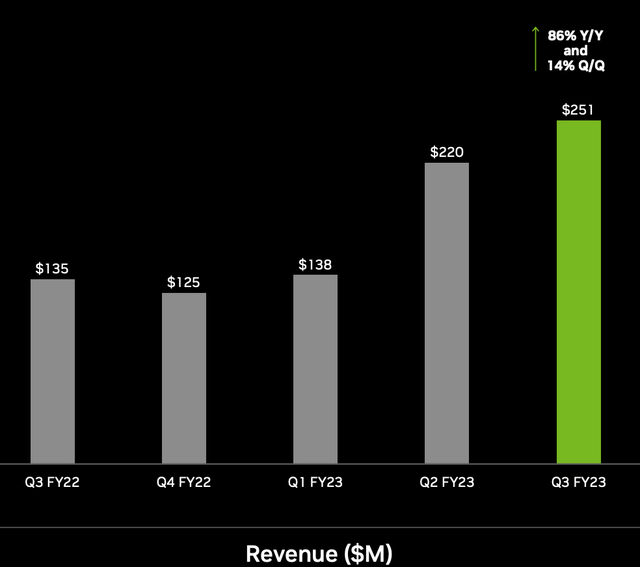
Profitability Challenges
Nvidia reported Operating Income of $601 million, which declined by a substantial 72% year over year. This was mainly driven by a 31% rise in operating expenses, which compounded the revenue decline, driven by the cyclical gaming demand. The good news is the majority of these expenses look to have been driven by a series of Data Center infrastructure expenses and increased headcount. Thus the company is really investing in itself and the Data Center expenses should really be considered as “Capital Expenses”, as a long-term benefit is forecasted.
The company also has a robust balance sheet with $13.1 billion in cash and marketable securities. The business does have $9.7 billion in long-term debt, but only $1.2 billion is current debt, which is manageable.
Advanced Valuation
In order to value Nvidia, I have plugged the latest financials into my discounted cash flow model. I have forecasted 10% revenue growth for next year and 26% revenue growth over the next 2 to 5 years. I forecast gaming demand to rebound and the Datacenter segment to continue to grow.
Nvidia stock valuation (created by author Ben at Motivation 2 invest)
To increase the accuracy of the valuation, I have capitalized R&D expenses, which has increased the operating margin to 33.25%. I have also forecasted a target pre-tax operating of ~45%. I forecast this to be driven by operating leverage in the data center segment and a rebound in gaming.
Nvidia stock valuation (created by author Ben at Motivation 2 Invest)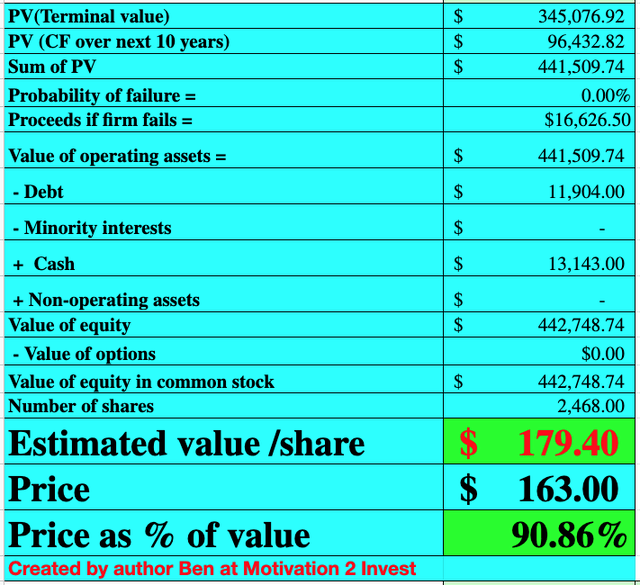
Given these factors I get a fair value of $179.40 per share, the stock is trading at $163 per share at the time of writing and thus is ~95 undervalued.
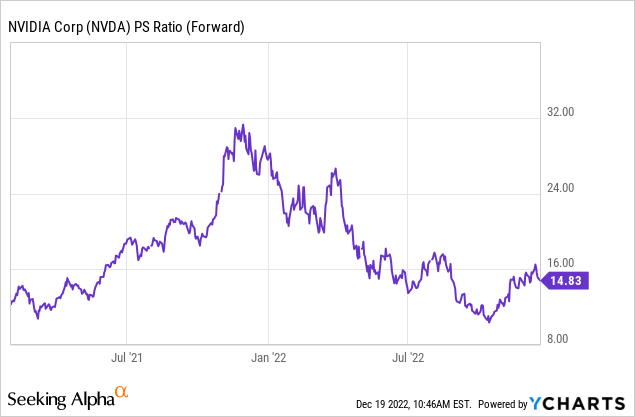
As an extra datapoint, Nvidia trades at a Price to Sales ratio = 14.49, which is ~14% cheaper than its 5-year average.
Risks
Recession/Gaming Demand
Many analysts are forecasting a recession, which may cause delayed consumer and business spending. Gaming demand may remain suppressed, while indirect revenue derived from crypto mining applications may never bounce back. Ethereum has moved from a proof of work to a proof of stake model, which is expected to impact this.
Final Thoughts
Nvidia is a technology powerhouse and true leader in data center hardware. The company is poised to benefit from the growth in the Artificial Intelligence industry and the cloud. It is currently facing a series of headwinds from low gaming demand, but given stock is undervalued intrinsically, it could be a great long-term investment.
Disclosure: I/we have a beneficial long position in the shares of NVDA either through stock ownership, options, or other derivatives. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.