Summary:
- Chinese tech stocks are making a strong comeback with regulatory restrictions easing after more than two years.
- DiDi, since the delisting from NYSE, has not received the attention of growth investors for good reasons.
- DiDi stock has gained more than 200% since November, and this analysis tries to determine whether the rally will continue amid encouraging developments.
Haiqing Zhong
Chinese stocks are making a solid comeback amid signs that regulatory pressures will finally ease on the country’s booming tech sector. It would be an understatement to say that the last couple of years have been hard for investors with exposure to China’s tech sector. DiDi Global Inc. (OTCPK:DIDIY) investors have been at the thick of it with the company being forced to delist from the NYSE less than a year from its IPO in June 2021. Now trading over the counter, DIDIY stock hardly gets the attention of growth investors. However, investors might want to evaluate how the changing regulatory environment in China will impact DiDi and its market value on the back of a 200% increase in DiDi stock since last November.
The business
DiDi Global operates a ridesharing business in a few countries around the world, including Brazil, Mexico, Australia, New Zealand, Hong Kong, Taiwan, and Japan in addition to its home country of China. The company offers various services, including ride-hailing, car rental, and bike-sharing. DiDi Global has been expanding rapidly in recent years as it looks to compete with global ride-hailing giants such as Uber Technologies, Inc. (UBER). The company has also invested in new technologies and services, such as autonomous vehicles, to stay competitive and improve its services. DiDi quickly grew to outcompete Uber in the Chinese ride-sharing market. As a result, Uber China sold its operations to DiDi and became a minority shareholder. The company also invested $100 million in Lyft, Inc. (LYFT), forming a collaboration to share technologies and marketing expertise. However, in the last two years, DiDi has faced significant hurdles because of the pandemic and regulatory scrutiny from Chinese watchdogs.
The Impact Of The Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on ride-hailing companies as social distancing measures and lockdowns led to a decline in travel and transportation demand. Commuting to work and going out, in general, came to an abrupt stop, which resulted in a decline in ride requests for companies like DiDi. Additionally, ride-hailing companies had to implement new safety protocols, such as mandatory mask-wearing and increased cleaning, which added to their expenses. As a result, the industry leaders including Uber and Lyft reported significant losses in the first half of 2020.
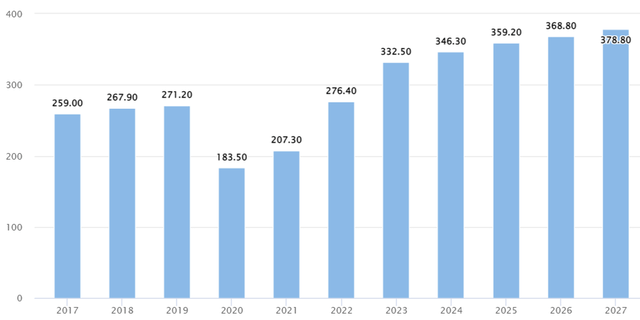
Exhibit 1: Worldwide revenue in the ridesharing and taxi market (USD billions)
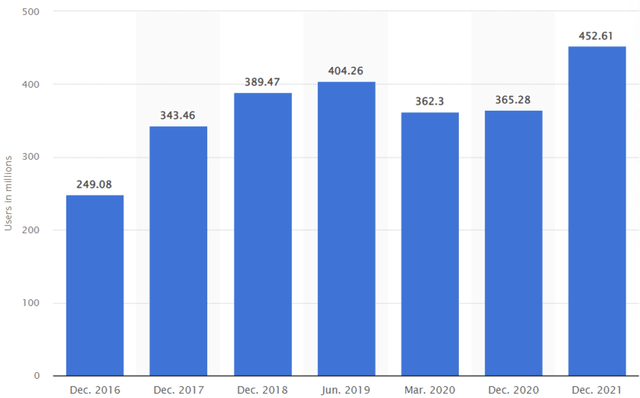
According to the chart above, global revenue for the ride-hailing market was significantly lower in 2020 and 2021. Because of continuous lockdowns, social distancing measures, and China’s Zero Covid policy, the number of online ride-hailing users in China declined sharply compared to many other countries.
Exhibit 2: Number of online ride-hailing users in China from December 2016 to December 2021 (in millions)
Although the pandemic had a negative impact on ride-hailing companies’ overall business, it did lead to an increase in demand for certain services, such as food and grocery delivery. Many restaurants and grocery stores, which were forced to close their doors or limit capacity, began to rely more heavily on delivery services offered by companies like Uber Eats and Lyft to reach customers. This led to an increase in delivery orders and revenue for those segments of these companies’ businesses. Additionally, ride-hailing companies quickly adapted to contactless payment systems to minimize the spread of the virus, which had a positive impact on the future of their services. With the lifting of pandemic restrictions, revenue in the ride-hailing & taxi segment is expected to reach $332.50 billion in 2023, with China accounting for the majority of revenue at $130.20 billion.
Tightened Regulations For Tech Companies
Chinese regulators have tightened regulations for tech companies in recent years for a few reasons. One major reason is to protect consumers’ data and privacy. In recent years, there have been several high-profile cases of data breaches and misuse of personal data by tech companies in China, which has led regulators to take a more active role in ensuring companies are properly protecting consumers’ information. Regulators have introduced new laws and regulations to protect consumers’ data and privacy, which include measures such as requiring companies to obtain explicit consent from users before collecting their data and implementing stricter security protocols for protecting personal information.
Another reason is to promote fair competition and prevent monopolistic practices. China has several large and powerful tech companies that dominate their respective industries. Regulators have sought to level the playing field for smaller companies and prevent these large companies from using their dominance to stifle competition. To promote fair competition and prevent monopolistic practices, regulators have been targeting companies that abuse their market dominance. They have been investigating and imposing fines on companies that engage in price fixing, exclusive dealing, and other anti-competitive behaviors.
Additionally, as Chinese tech companies have grown in size and influence, regulators have become increasingly concerned about the potential for these companies to influence politics and public opinion. As a result, regulators have sought to increase oversight and control over the activities of these companies, including through tighter regulations. Further, regulators have introduced new cybersecurity laws and regulations to protect consumers from cyberattacks and data breaches and to ensure that companies are properly protecting personal and sensitive information.
Lastly, Chinese regulators have been tightening regulations on online platforms, such as social media, to monitor and control the information that is being shared. This includes measures such as requiring platforms to remove content that is deemed to be false, defamatory, or harmful, and to take steps to prevent the spread of misinformation and hate speech. China also introduced new licensing requirements for certain types of online services, such as Internet finance and ride-hailing, to ensure that companies are operating in compliance with laws and regulations.
All these regulations are aimed at safeguarding Chinese residents and the country’s national interests but these decisions have weighed on tech companies including DiDi Global. China’s Cyberspace Administration took the unprecedented step of removing DiDi from app stores in 2021 citing the need for data protection, safety, and compliance with national laws and regulations. With its 25 mobile apps ordered removed from app stores, registration of new users was also halted, and the company was fined for data-security breaches.
According to Reuters, Chinese authorities are set to restore DiDi Global’s ride-hailing and other apps to domestic app stores as soon as next week, ending a two-year regulatory crackdown on the technology sector. The lifting of the ban on DiDi apps is part of Chinese policymakers’ plan to reestablish private sector confidence while allowing the tech industry to contribute to economic growth. As part of efforts to strengthen the economy, China’s Central Bank will increase its support for private firms while relaxing restrictions on technology firms. According to state-owned CCTV, Guo Shuqing, Communist Party chief of the People’s Bank of China, said that monetary policy in 2023 will focus on expanding demand, particularly personal consumption. DiDi may be able to resume normal operations as soon as next week now that regulations are being relaxed.
The Reopening Of The Chinese Economy
China’s Zero-Covid policy, which aimed to prevent the further spread of the virus, had a significant impact on travel demand and the Chinese economy even when the travel sectors of other countries were enjoying the pent-up demand for travel throughout 2022. The measures implemented as part of the Zero-Covid policy, such as mandatory mask-wearing, temperature checks, and contact tracing, as well as social distancing guidelines and lockdowns, led to a massive decline in travel and transportation demand last year. This has resulted in a decline in revenue for companies in the travel and tourism industry, including airlines, hotels, and other hospitality businesses.
In addition to the travel and tourism industry, the Zero-Covid policy has also impacted other sectors of the economy. For example, the restriction of movement and lockdowns have led to a decline in consumer spending and economic activity, as people were encouraged to stay at home and avoid non-essential travel. This has led to a decrease in revenue for businesses in sectors such as retail, entertainment, and leisure. The Zero-Covid policy has also led to a decline in foreign investment and trade, as travel restrictions and quarantine measures made it more difficult for businesses to operate and for people to travel for trade and investment purposes. The slowdown in overall economic activity in China impacted ride-hailing services such as DiDi in 2022, with COVID-19 measures increasing costs for ride-hailing companies because they had to invest in additional safety equipment and protocols, such as cleaning and disinfection.
After three years of trying to keep COVID-19 cases to nearly zero, China is finally loosening its Zero-Covid rules in response to public outrage over the government’s stringent restrictions. The Zero-Covid policy included measures such as frequent testing for people seeking access to public areas, as well as forced quarantines and lockdowns in areas where cases were found. Chinese officials were concerned that the rules were putting too much strain on the economy. As a result, Beijing issued new rules in December that effectively phased out Zero-Covid, no longer requiring inbound travelers to quarantine since January 8. According to a National Health Commission statement, people arriving in China will only be required to obtain negative Covid test results within 48 hours of arrival, as opposed to eight days of isolation under the Zero-Covid policy.
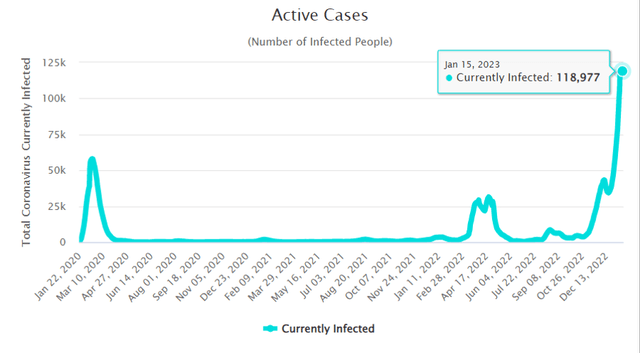
That being said, there is no sign of a strong economic recovery in the short run because people are still afraid of going out and becoming infected. Experts believe that with a weak vaccination program, a poor healthcare system, and only a small percentage of China’s population being exposed to Covid-19, the country will face a new wave of cases. This can have serious economic consequences, such as delayed investments and a further decline in economic activity. As a result, Citigroup economists maintained their 5.6% annual growth forecast for 2023 but reduced their fourth-quarter growth forecast to 3.7% from 4.4% previously.
Exhibit 3: Active Covid Cases in China Spiked following the reopening
Although the reopening of the economy and relaxing Covid rules are promising developments for DiDi, investors should be cautious of short-term challenges that could deteriorate the investor sentiment toward DiDi in 2023 before the company finally makes the most of these positive developments in the latter part of the year.
Takeaway
Because of the deteriorating economic situation and regulatory controls, Chinese companies have received a great deal of attention in recent years. As China moves to abandon the Zero Covid policy, cases continue to rise across the country, preventing people from going out. The increase in cases has also impacted a healthcare system that is woefully underprepared. The Chinese people are dangerously vulnerable, and experts believe that the abrupt shift away from Zero Covid might not speed up the economic recovery as expected. Furthermore, the country’s internal data is lacking, leaving local officials unsure of the number of COVID-19 cases.
Looking at the longer term, the easing regulatory scrutiny should pave the way for DiDi to resume its growth journey. However, investors should be cautious of investing in a company with little transparency of financial reporting now that DiDi is trading over the counter as opposed to a main US exchange.
Editor’s Note: This article discusses one or more securities that do not trade on a major U.S. exchange. Please be aware of the risks associated with these stocks.
Analyst’s Disclosure: I/we have a beneficial long position in the shares of UBER either through stock ownership, options, or other derivatives. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
Seeking Alpha’s Disclosure: Past performance is no guarantee of future results. No recommendation or advice is being given as to whether any investment is suitable for a particular investor. Any views or opinions expressed above may not reflect those of Seeking Alpha as a whole. Seeking Alpha is not a licensed securities dealer, broker or US investment adviser or investment bank. Our analysts are third party authors that include both professional investors and individual investors who may not be licensed or certified by any institute or regulatory body.

The unexpected moment is always sweeter
At Leads From Gurus, we strive to achieve sweet returns by predicting which companies would report unexpected earnings. Join us to discover the power of earnings surprises.
Your subscription includes access to:
- Weekly actionable ideas that would help you beat the market.
- In-depth research reports on stocks that are well-positioned to beat earnings estimates.
- Three model portfolios designed to help you beat the market.
- Educational articles discussing the strategies followed by gurus.
- An active community of like-minded investors to share your findings.
Act now to secure the launch discount!