Summary:
- Apple’s Services revenue hit $25 billion in Q4 FY2024, growing 12% YoY with industry-leading 74% gross margins.
- The iPhone generated $46.2 billion (49% of revenue) in Q4 FY2024, growing 6% YoY, supported by record installations.
- Revenue growth remains uneven, with stagnation in China offset by strong performances in Europe (+11%) and emerging markets.
- Apple maintained a 46.2% gross margin, with $26.8 billion in operating cash flow and $29 billion in shareholder payouts.
- AI-powered Apple Intelligence and Vision Pro showcase Apple’s ability to monetize its ecosystem and sustain long-term growth.
kaczka/iStock Unreleased via Getty Images
Investment Thesis
Following our latest coverage, Apple’s performance has remained muted, with growth driven primarily by its robust ecosystem and high-margin Services segment. Services generated $25 billion in Q4 FY2024, reflecting 12% YoY growth and gross margins of 74%. This segment exemplifies Apple’s ability to leverage its 2 billion+ active device base for recurring revenue, enabling monetization through upselling innovations like Apple Intelligence and Vision Pro. These pillars position Apple for sustained long-term growth.
Revenue Hits 6% Growth Led by Services and iPhone
Apple’s Q4 fiscal 2024 revenue of $94.9 billion holds an annual growth of 6% based on gains across iPhone, iPad, and Mac categories. The product revenue combined with a high contribution from the Services segment hit an all-time revenue of $25 billion (+12% YoY). The company’s topline is also uplifted by the diverse revenue records achieved in regions like the Americas, Europe, and Rest of Asia Pacific. After a stagnation in the top-line for 4 years, 2025 and 2026 analysts estimates are marking an emergence of growth in the midterm.
seekingalpha.com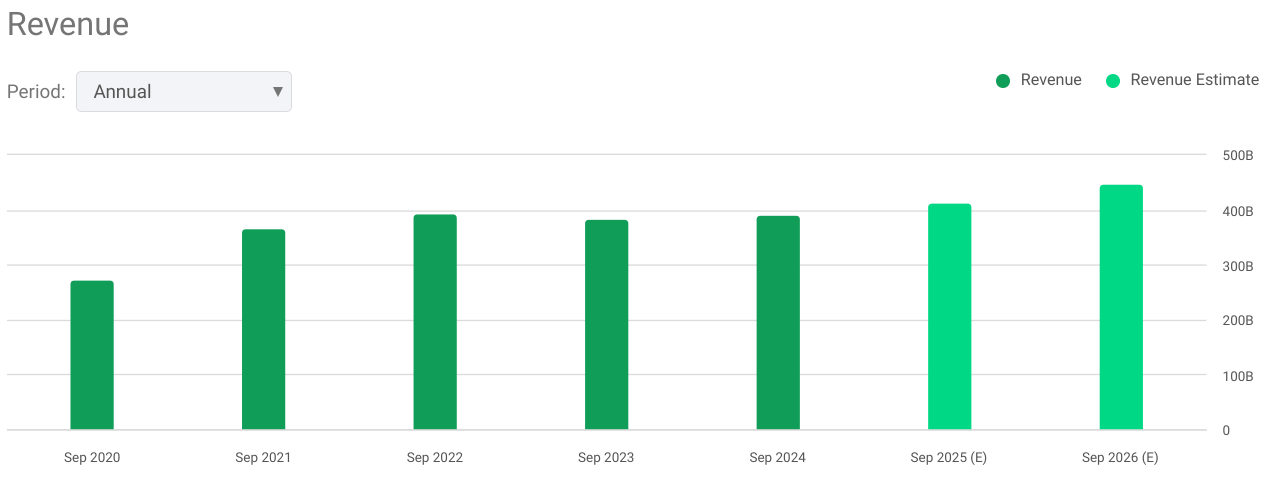
On the product side, the iPhone segment generated $46.2 billion with a 6% YoY growth and a September quarter record. This growth extended across all geographic segments based on the iPhone 16-series. The iPhone’s 49% revenue dominance reflects its lead as Apple’s core product that may continue to be supported by its continually growing active installed base. The base attained new highs and stable 17.7% market share (smartphone shipments) in the September quarter, with a high satisfaction level of 98% in the US.
Meanwhile, Services stood as an emerging growth component. The segment held a 12% YoY revenue increase to $25 billion. The expansion of paid subscriptions (2X over four years to over 1 billion) led to an increased engagement within Apple’s ecosystem. This segment’s gross margin of 74% (unchanged from the prior quarter) represents the highest profitability within Apple’s portfolio and the core driver of consolidated margin stability.
statista.com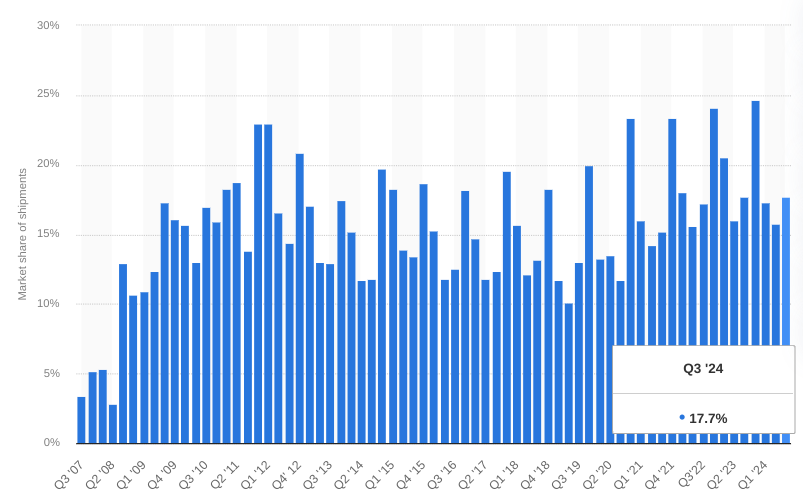
Further, the Mac segment’s revenue ($7.7 billion) reflects a 2% YoY increase from the introduction of the M4 family of chips and customer satisfaction level of 95% in the US. Here, nearly half of the Mac customers this quarter were new to the product, that points to Apple’s expanding market penetration. Similarly, iPad revenue grew by 8% YoY (totaling $7 billion). This growth was derived from the demand in both developed and emerging markets, with standout double-digit growth rates in regions such as Mexico, Brazil, and India. The iPad also benefits from customer satisfaction rates of 97% in the US that is driving engagement in Apple’s ecosystem, boosting Apple’s service revenue.
However, there is a contraction in revenue in the Wearables, Home, and Accessories segment (-3% YoY to $9 billion). Despite this dip, the Apple Watch’s installed base hit an all-time high, with over half of the new purchases being from first-time buyers. This segment holds a potential for recovery due to a direct integration into the expanding base of Apple’s products (like iPhone).
Considering the size of Apple’s operations, the core question here is whether this top-line growth is profitable. At the bottom line, Apple’s consolidated gross margin of 46.2% based on a stable operational framework supported by the products’ gross margins of 36.3% (+1%-points sequentially due to favorable product mix shifts) and services margins of 74%. In short, the company’s consolidated profitability has the capability to maintain sharp margins under adverse macro conditions (like high inflation and consumption behavior in the target market).
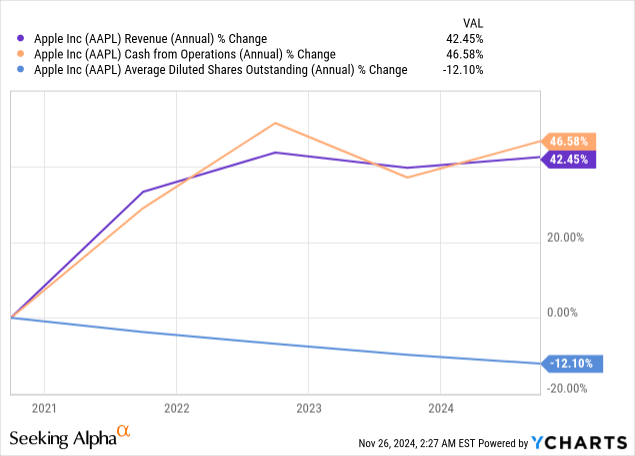
Interestingly, OpEx of $14.3 billion had a 6% YoY increase in line with the growth rate of revenue. Whereas, operating cash flow stood at $26.8 billion, with a new record for the September quarter. This constant operational management and preservation of cash flow led to a $29 billion payout to the stockholders, with $25 billion of buybacks. On a long-term basis (5Y), the company hit a top-line growth of 42% and with that 47% jump in operational cash flow. Then a sharp use of cash led to a drop of 12% in diluted shareholding.
Looking forward, Apple’s focus on tech advancements (obviously AI) may boost its lead with a massive installed base. Fundamentally, Apple Intelligence integrates generative models with privacy-focused computing that are directly tied to products such as the iPhone 16’s enhanced capabilities and the M4-powered Mac lineup. This alignment may lead to Apple Intelligence’s rapid adoption in Apple’s products (say iPhone) that will make Apple’s AI highly relevant among enterprises too. This effect is the same as the Apple Vision Pro (a strategic push into spatial computing) with over 2,500 native spatial apps and significant enterprise adoption. Similarly, enhancements in health-related features across wearables, such as sleep apnea notifications on Apple Watch, add value to the ecosystem by targeting health-conscious consumers.
Yiazou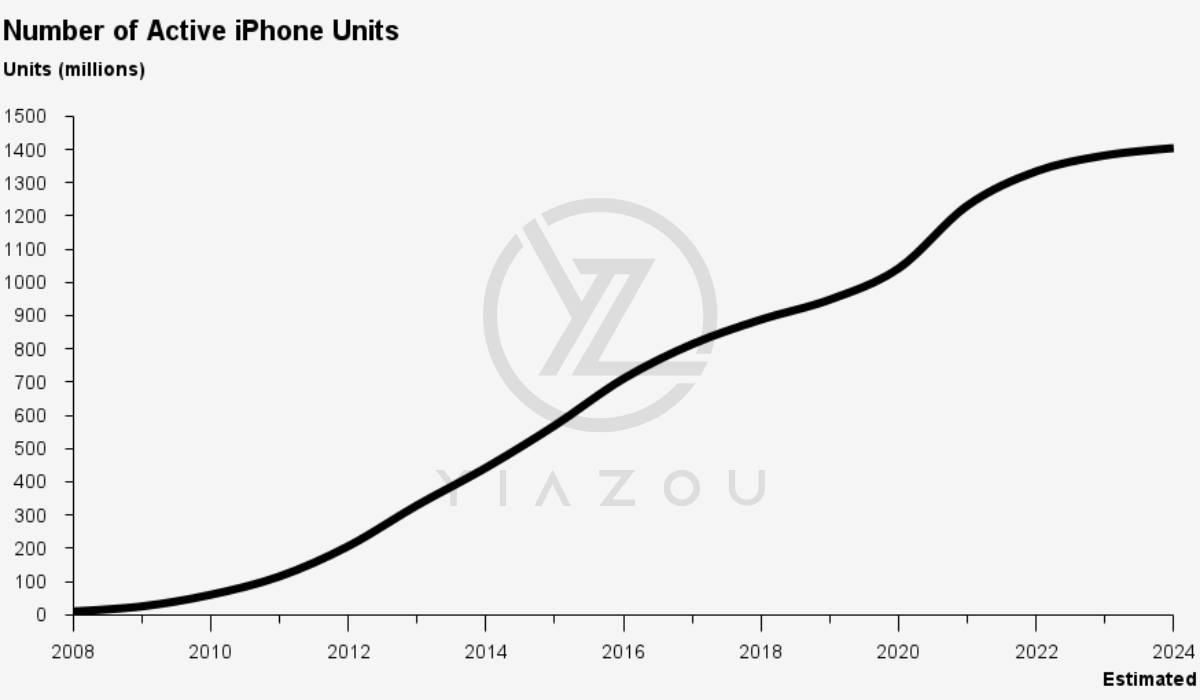
iPhone’s 50% Revenue Share, Gross Margins, and Regional Disparities Mark Downside Risks
On the downside, Apple’s financial standing remains tethered to the iPhone, which marks roughly half of consolidated revenue with the adoption rates for iOS 18.1 being twice as fast as those for 17.1 which signals short-term enthusiasm. It reflects that the iPhone is still the backbone of Apple’s business and any bump in incremental growth of iPhone shipments directly impacts Apple’s market expectations. Supply chain efficiencies have eliminated delays to seize robust demand in Q4 but short lead times may reflect tepid consumer interest rather than improved operational edge. The prolonged cyclicality in the iPhone shipments led to the absence of supply shortages and balanced inventory levels. There is no sequential consistency in shipment growth, and this suggests Apple is not experiencing a new demand outpacing the supply trend as seen in the last decade.
On the list, another issue is the price sensitivity. Tim Cook sidestepped questions about trade-ups versus trade-downs during Q4 earnings call. This suggests a growing cohort of customers may be opting for lower-priced models, and this trend is adverse for Apple’s margins as NAND and DRAM prices are set to rise. While most commodities are projected to decrease in cost, memory components like NAND and DRAM have bucked this trend with prices rising during the September quarter and expected to continue increasing in the December quarter. With gross margins forecasted at 46%-47% for the December quarter (a historical high) any deviation in Q1 FY2025 earnings may confirm demand-side challenges in premium segments and may lead to a drop in the stock.
Finally, Apple’s geographic performance holds uneven growth. China presents an area of concern as Apple held the top two smartphone positions in urban China but overall revenue was ‘relatively flat.’ This flatness contrasts with stronger performance in regions like Europe’s 11%. The improvement in China is due to sequential forex benefits (an external factor) that is unrelated to product performance. Without this, growth in China may appear weaker against intensifying competition from local brands like Huawei and Xiaomi amid uncertainty regarding the effects of China’s stimulus plans.
Emerging markets’ (India and the Middle East) positive contributions hold smaller revenue bases that cannot offset stagnation in China. These top-line and gross margin issues may create a downside pressure on the AAPL’s price.
statista.com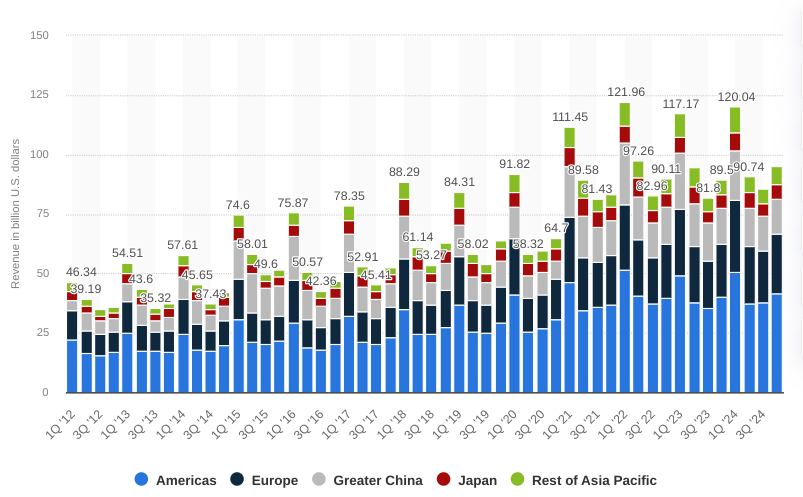
Takeaway
Apple’s ecosystem and high-margin Services segment continue to drive sustainable growth, with Services generating $25 billion in Q4 FY2024 at 74% margins. However, over-reliance on the iPhone, rising component costs, and uneven geographic performance, particularly in China, present challenges. While innovation and recurring revenues support long-term potential, near-term risks may pressure margins and growth expectations.
Analyst’s Disclosure: I/we have no stock, option or similar derivative position in any of the companies mentioned, and no plans to initiate any such positions within the next 72 hours. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
Seeking Alpha’s Disclosure: Past performance is no guarantee of future results. No recommendation or advice is being given as to whether any investment is suitable for a particular investor. Any views or opinions expressed above may not reflect those of Seeking Alpha as a whole. Seeking Alpha is not a licensed securities dealer, broker or US investment adviser or investment bank. Our analysts are third party authors that include both professional investors and individual investors who may not be licensed or certified by any institute or regulatory body.
