Summary:
- JPM’s strong balance sheet, diverse business model, and robust risk management framework support weathering any SVB contagion effect.
- Due to its strong liquidity management, I believe JPMorgan is well-positioned to weather unpredictable economic climates and drive growth.
- The bank is expected to benefit from a likely economic recovery and a stabilizing housing market.
- JPMorgan invests heavily in its digital transformation to enhance customer experiences and drive growth.
subman
Investment Thesis
Last week, bank shares significantly dropped when SVB Financial Group (SIVB) announced they must take several “strategic initiatives”. As a result, SVB is one of the first banks since the financial crisis of 2008 that has actually experienced a liquidity shortage, forcing it to reorganize the balance sheet and recognize losses on its securities portfolios aside from crypto-related meltdowns.
Unless you have a crystal ball, it is impossible to predict when these risks will materialize and the extent of the impact. Investors are now worried that other banks might experience problems similar to those at SVB, causing a contagion effect. Following the global financial crisis, larger banks’ regulations have been much tighter, and banks must undergo annual stress tests to demonstrate their resilience in various adverse economic scenarios.
Thus, large banks such as JPMorgan Chase & Co. (NYSE:JPM) are generally far more liquid than smaller ones, have much more capital, are likely much better at managing risk, and are subject to regulatory monitoring. As a result, following the sell-off, investors get a better entry point at JPM, a reputable bank that is well-capitalized to weather the storm.
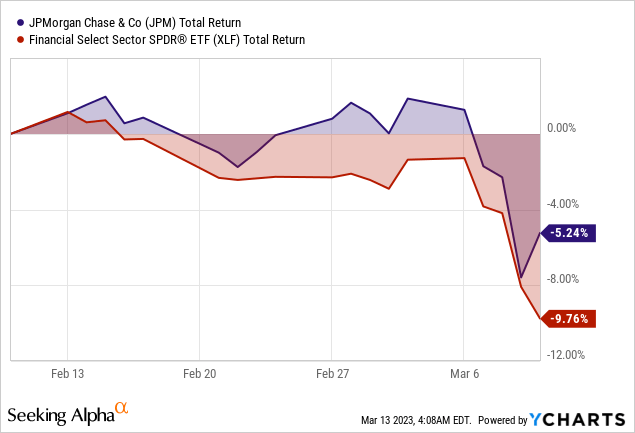
The SVB Meltdown Update
After announcing that SVB had realized a $1.8 billion loss after selling $21 billion of its “available-for-sale securities” from its portfolio, SIVB stock fell sharply. In addition, SVB announced that it was looking to raise $2.25 billion to make up for the loss.
Therefore, concerns have arisen about the impact on JPMorgan’s financial performance and market valuations due to the collapse of SVB and the subsequent sell-off in bank stocks. While JPMorgan is not directly exposed to SVB’s troubles, it is still vulnerable to the banking sector’s broader risks.
One of the main risks is the potential contagion effect from SVB’s failure, which could lead to deposit outflows and bond losses. In addition, the broad market pessimism could cause a further reduction in JPM’s market value as investors become more cautious about the prospects of the banking sector. Large banks will still experience some pain due to the current dynamics, but it won’t likely be as severe.
Favorably, following the fall of SVB, government officials rushed to allay concerns about the soundness of the US economy on Sunday, promising to guarantee all depositors’ money fully. They also pledged to provide banks needing funds with more forgiving terms on short-term loans. To increase public confidence in the banking system in the wake of SVB’s shutdown, the Treasury Department, Federal Reserve, and Federal Deposit Insurance Corp. collaborated to announce these plans.
Overall, while the collapse of SVB and broader risks facing the banking sector could impact JPMorgan’s financial performance and market valuation, the bank’s strong balance sheet, diverse business model, and robust risk management framework should help it weather these challenges. However, investors should monitor evolving economic, and market conditions as risks to JPMorgan and the broader banking sector could increase if conditions deteriorate further.
Macroeconomic Outlook & Trends
The economic outlook and trends could significantly impact JPMorgan’s financial performance and market valuations over the long term. As a large financial institution, JPMorgan’s business depends on the broader economy’s health and financial markets.
The deceleration in growth and moderate inflation could reduce demand for loans and other financial services, impacting JPMorgan’s revenue and earnings growth. In addition, the rapid monetary tightening and higher interest rates could increase the cost of capital for JPMorgan, reducing profitability. However, the impact of these factors on JPMorgan’s financial performance will depend on how effectively the company can manage risk and adjust its business strategies to the changing economic environment.
JPM Economic Update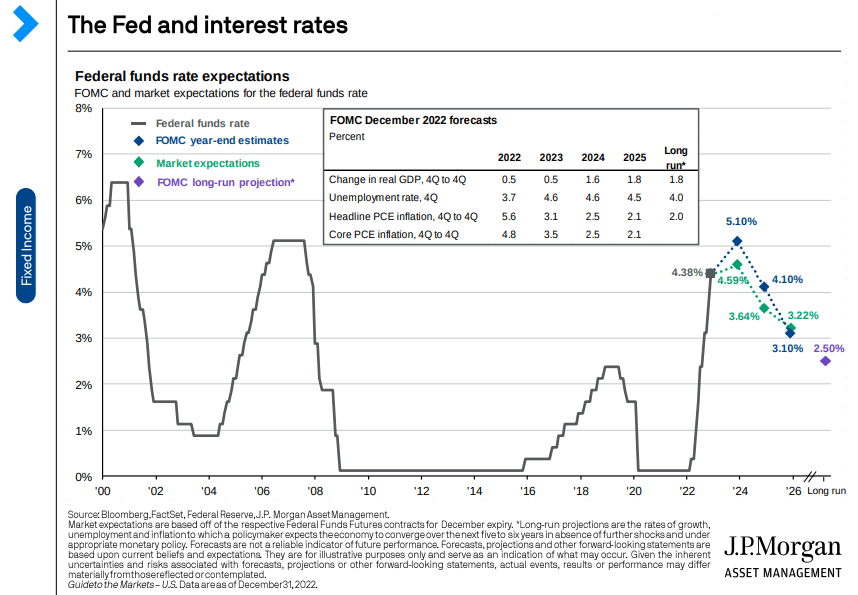
Additionally, The outlook for the US dollar and the performance of the bond and loan markets could also impact JPMorgan’s business. A strong dollar may make it more difficult for the bank to generate revenue from international operations. At the same time, broader high-yield bond and loan spreads could increase credit risk and lead to higher loan loss provisions. However, JPMorgan’s diversified business model and robust risk management practices may help mitigate these risks.
Moreover, the payment trends identified by JPMorgan are focused on optimizing core treasury management functions and preparing for ecosystem opportunities, which could provide growth opportunities for the bank. By leveraging payments-related innovations, JPMorgan can increase efficiencies and offer new services to clients, which could drive revenue growth.
Finally, the commercial real estate outlook may impact JPMorgan’s performance as the bank is a significant player in the commercial real estate lending market. The potential for a mild to moderate recession and the uncertainty surrounding the future of office space could lead to increased credit risk for JPMorgan’s commercial real estate portfolio. However, the bank’s focus on high-performing asset classes, such as multifamily and industrial properties, may help mitigate these risks.
Overall, the economic outlook and trends directly affect JPMorgan’s financial performance and market valuations over the long term. Accordingly, the bank’s ability to effectively manage risk and adapt its business strategies to the changing environment will be critical in determining its future success.
Favorable Interest Rate Environment
Net interest income, the profit banks make on loans after they cover the cost of funding those assets, is a core part of their business and is heavily influenced by interest rates. JPMorgan is dependent on market forces, and uncertain deposits reprice dynamics.
JPMorgan’s profits have been driven by higher interest rates, with net interest income up 28% in 2022. In addition, the Federal Reserve’s aggressive rate hikes to control inflation have allowed banks to charge more for loans, indicating a favorable outlook for JPM which continues expanding its profitability while offsetting the increasing operating cost pressures (i.e., higher labor costs).
Thus, the firmwide average cost of deposits remains uncertain, but JPMorgan expects net interest income excluding markets to be around $74 billion for 2023, maintaining the upward trajectory since late 2021.
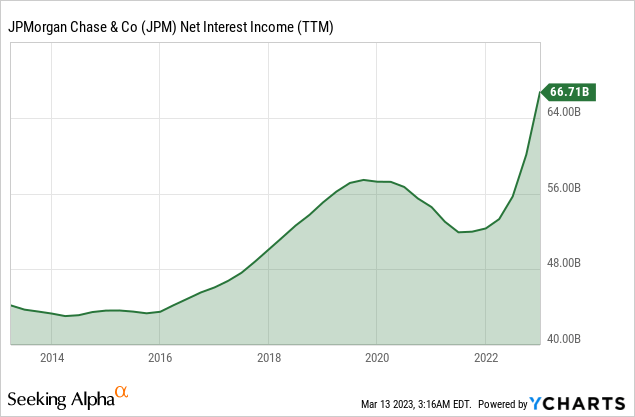
Additionally, JPMorgan’s strategy of hoarding cash, which it has followed since interest rates started to increase, is proving prudent amid the current unpredictable economic climate. While the bank could have deployed cash into higher-yielding shorter-term bonds, it has chosen to cover deposit outflows with cash, which is easier and less costly than selling bonds that might be trading at a loss. Lastly, JPMorgan has more cash to deploy into higher-yielding bonds if the Fed raises rates more than anticipated.
Digital Transformation Remains Key
JPMorgan invests heavily in digital transformation to enhance customer experiences and drive growth. As a result, the bank is keeping its expenses flat while doubling its volumes, with total technology expenses expanding to $14.1 billion in 2022 at a CAGR of 6% from 2019 to 2022. In addition, across its business segments, JPMorgan is investing $4.1 billion in developing its products, platforms, and infrastructure.
The Consumer & Community Bank segment focuses on developing its Consumer and Small Business Payments platform, which supports $5 trillion in annual payments volume, and its personalization engine. The Corporate & Investment Bank segment is developing e-commerce capabilities and a real-time payment platform for clients.
With its AM Morgan Suite, the Asset & Wealth Management segment enables over $1 trillion in digital and self-service transactions. Finally, the Commercial Bank segment invests in sales enablement tools, data analytics for bankers, and a cloud-based, client-focused data platform.
Investor Day 2022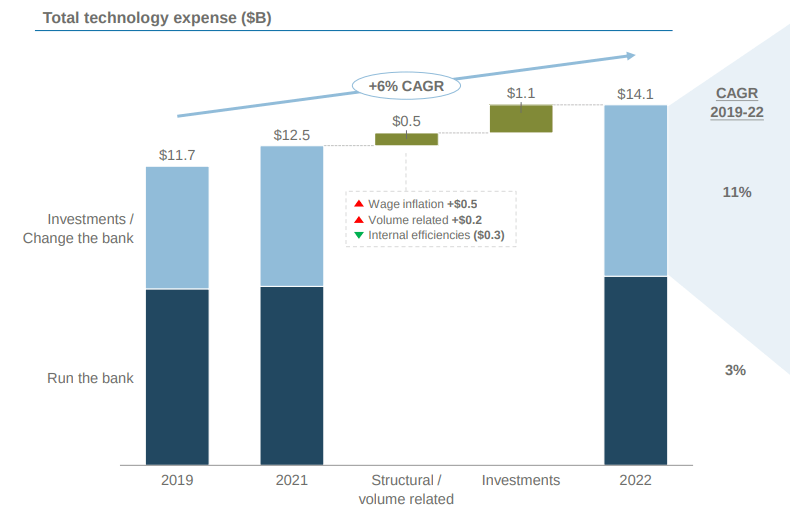
Moreover, JPMorgan is also modernizing its infrastructure and applications for speed, resilience, and cost efficiency. It is refactoring applications to optimize cloud adoption, replacing them with SaaS solutions, and building cloud-native core banking systems. It also enables a multi-cloud strategy, creates a highly secure private cloud platform, and consolidates its global data centers from 33 to 17 by 2025.
Interestingly, JPMorgan is investing in AI platforms to drive speed-to-market and enable adoption at scale. It has invested over $1 billion in business impact projected by 2023 and is achieving a 70% faster delivery of production AI models. In addition, the bank is adopting modern data practices and technologies to drive digital transformation, such as chatbots, social messaging payment apps, and banking-as-a-service.
Lastly, JPMorgan uses zero-trust security frameworks to lock down data at every point and embeds security precautions throughout the system. With its digital transformation investments, JPMorgan is well-positioned to differentiate itself with technology and drive returns.
Additional Risks To Consider
The lack of interest in early-stage or speculative businesses due to higher rates could lead to a slowdown in venture capital lending, affecting JPMorgan’s exposure to the tech sector. However, JPMorgan’s well-diversified loan portfolio and strong presence in other sectors, such as real estate and consumer lending, should offset any weakness in the tech sector.
Furthermore, rising corporate defaults are another potential risk, leading to increased credit losses for JPMorgan. However, the bank’s robust risk management framework and strong credit rating should help mitigate the impact of rising default rates.
Lastly, falling house prices could reduce demand for mortgages and home equity loans, affecting JPMorgan’s revenue growth and net interest margins. However, JPMorgan’s well-diversified loan portfolio, solid commercial lending, and asset management presence should offset any weakness of the real estate sector.
A Possible Valuation Rerating In 2023
JPMorgan expects a 6.5% increase in expenses in 2023, attributed to higher labor costs, additional hiring, and investments in technology, marketing, and building branches. However, despite revenue growth being outpaced by expense growth in 2022, JPMorgan’s efficiency ratio remained strong and generated significant returns.
JPMorgan is expected to benefit from a likely economic recovery and a stabilizing housing market. The Conference Board predicts 1.7% US Gross domestic product (GDP) growth in 2024, while JPMorgan expects between 0.5% and 1% growth in 2022 before normalizing at 1.8%. Bloomberg forecasts a consensus year-end price target of just above 4,000 for the S&P 500.
Operating Expenses Increase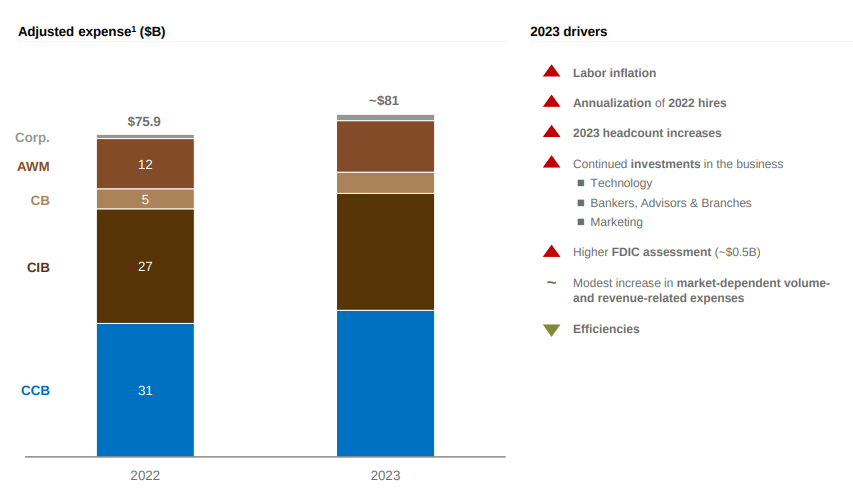
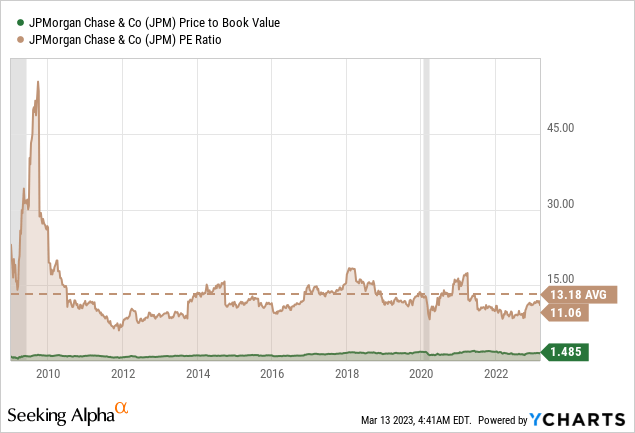
JPMorgan’s lending and investment banking should recover along with the economy, boosting its results. In addition, the stock is still modestly priced with a P/E ratio of around 11x and 10.5x forward earnings, and its dividend yields around 3%, making it attractive to investors. Although two straight years of large expense hikes may not have pleased investors, JPMorgan’s effective cost management, EPS expansion, and stabilization will lead to a possible market rerating to the upside in the foreseeable future in my view.
Concluding Thoughts
In conclusion, JPMorgan appears to be a solid investment option for long-term investors. The bank’s strong liquidity management, digital transformation initiatives, and progressive macroeconomic outlook provide a positive outlook for the future. While there may be some short-term expense hikes, the bank’s overall efficiency ratio remains strong, helping it generate significant returns. With a dividend yield of just under 3% and a modest valuation, JPMorgan’s position as the largest bank in many areas, continued investments, and forward-looking view make it an attractive blue-chip stock for investors in my opinion.
Disclosure: I/we have no stock, option or similar derivative position in any of the companies mentioned, and no plans to initiate any such positions within the next 72 hours. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
Author of Yiazou Capital Research
Unlock your investment potential through deep business analysis.
I am the founder of Yiazou Capital Research, a stock-market research platform designed to elevate your due diligence process through in-depth analysis of businesses.
I have previously worked for Deloitte and KPMG in external auditing, internal auditing, and consulting.
I am a Chartered Certified Accountant and an ACCA Global member, and I hold BSc and MSc degrees from leading UK business schools.
In addition to my research platform, I am also the founder of a private business.

