Summary:
- EV leaders NIO Inc. and Tesla, Inc. are concentrating on product portfolios and operational efficiencies to drive long-term success and edge out EV competition.
- Tesla’s investor day unveiled a next-generation platform to cut costs and support various vehicle types for an annual production of 20 million units with improved operator density and simplified manufacturing.
- NIO gears up for H1 2023 with five new models, while soft gross margin challenges persist due to rising operating expenses and promotional activities.
- Tesla’s buy rating is reaffirmed on substantial operational efficiencies through its Next-Gen Platform and positive delivery outlook.
- Since the start of 2023, NIO has been down 5.5%, and its suppressed valuation and positive outlook offer a more attractive risk/reward profile.
sefa ozel
Investment Thesis
Electric vehicles (EV) have emerged as a promising solution in a world where the demand for sustainable energy is rapidly increasing. With giants like Tesla, Inc. (NASDAQ:TSLA) and NIO Inc. (NYSE:NIO) leading the way in EV technology, the race to create efficient, affordable, high-performance electric cars has intensified. The article will take a closer look at their latest product lines and operational challenges.
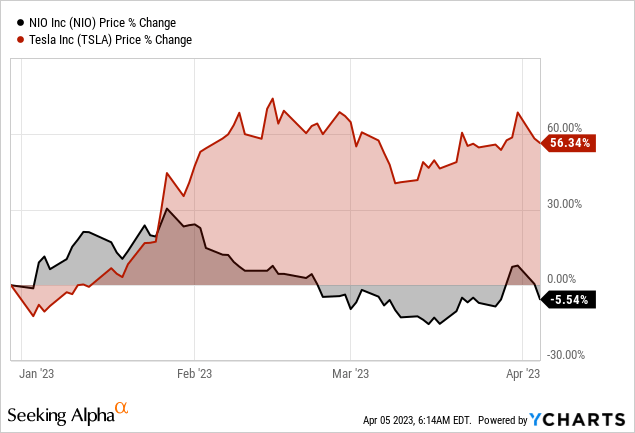
Since the start of the year, Tesla has had a strong bull run, rising by 56.3%, while NIO is down 5.5% for the same period. Despite the strong pullback in TSLA stock during 2022, there is much more upside for the stock accounting for the substantial operational efficiencies resulting from the Next-Gen Platform. On the contrary, NIO has remained flat due to operational challenges, but there is light at the end of the tunnel.
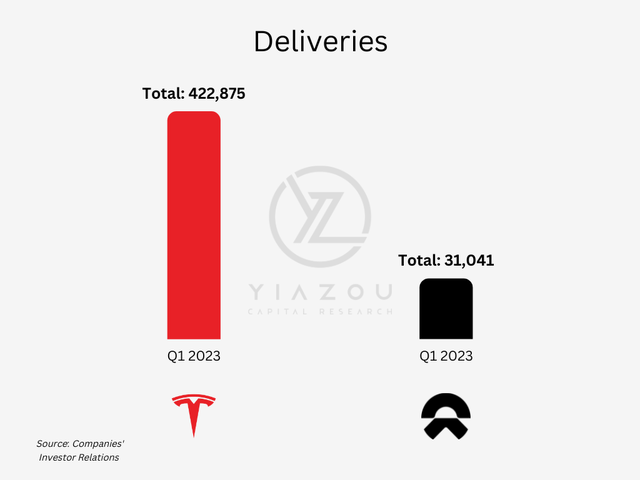
A Battlefield Of Deliveries
In the first three months of the year, Tesla delivered 422,875 cars, an increase of nearly 4% from the fourth quarter’s performance. Tesla has been ramping up production at two new plants since then, one close to Berlin and the other in Austin, Texas. So, even though Tesla produced over 440k automobiles and delivered over 422k during the first quarter, beating its previous record of 405k, Wall Street had high hopes for Tesla’s Q1 deliveries, which justifies the pullback in the stock price.
Despite the beating, my concern is the rising inventory, particularly for the Model S and Model X. Even though having nearly 9,000 Model S/X in stock at the end of the first quarter seems excessive, Tesla supports that many of those units are currently in transit to Europe. Nevertheless, despite the limited visibility at this point, Tesla’s target to produce 1.8 million vehicles in 2023 seems attainable, considering the probability of further price cuts.
Tesla repeatedly lowered its prices in the U.S., Europe, and China during the first quarter of 2023. In addition, a sizable portion of deliveries seemed to come from cars made at Tesla’s giga-factory in Shanghai. Thus, the automaker has been lowering prices, particularly in China, where the most recent reductions have sparked a bidding war among its rivals. As a result, although Tesla continues to lead other manufacturers in global EV sales, it is now up against more fierce competition from China.
NIO stock had increased by nearly 28% over the previous week from its March lows due to 31,041 deliveries at the low end of the range it anticipated one month earlier and lower than the 40,052 delivered in the prior quarter. Nevertheless, March’s deliveries were up 20.5% from the same period last year, supporting its momentum. Lastly, NIO will expand the battery-swapping network and install 1,000 Power Swap stations in 2023.
Tesla: A Next-Gen Platform To Attain Significant Operational Efficiency
The investor day for TSLA was focused heavily on manufacturing and its importance in reducing costs for the next-generation vehicle. Tesla emphasized the need for greater manufacturing efficiency by reducing steps in the process. For example, instead of conducting quality control at the end of the assembly, Tesla aims to balance parallel and serial production, allowing more people and robots to work on a vehicle simultaneously. This will significantly reduce manufacturing floor space by up to 40% and improve capital expenditures per unit.
Investor Day 2023 (Tesla)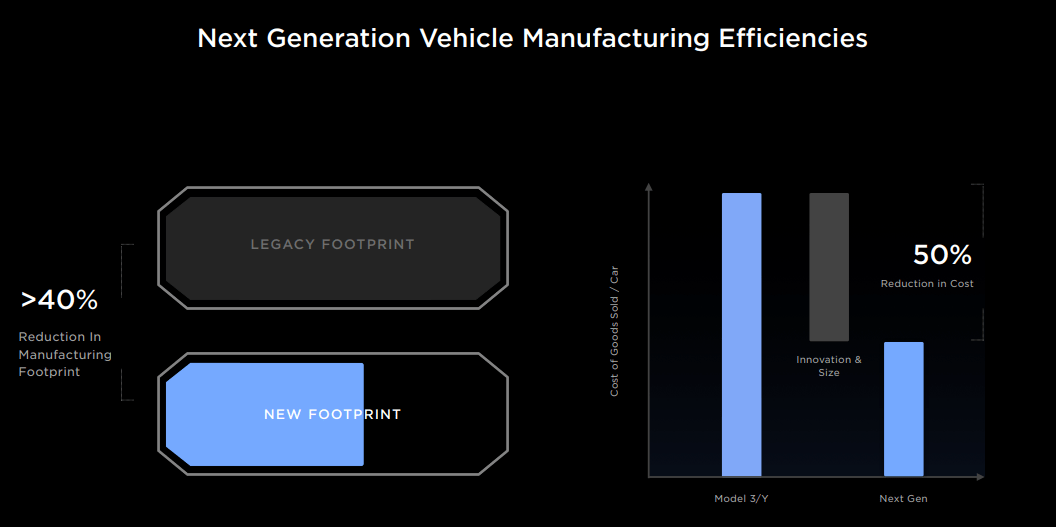
Tesla plans to develop a next-generation platform to support different vehicle types across segments and help it produce 20 million units annually. The platform is expected to deliver 50% cost savings from Tesla’s current platform, achieved through design and engineering for manufacturability and scalability, battery and powertrain improvements, and manufacturing technology improvements.
While no details were provided about the actual vehicles and pricing points, it is clear that the platform will house various models, including a more minor “Model 2” and likely a robotaxi. Tesla will utilize its newly announced Mexico plant for the next-gen platform, building on the learnings and standardizations from previous factories, including the Shanghai factory. In addition, Tom Zhu, Elon Musk’s right-hand man, has been transferred from Asia to North America to head up its assembly plants and sales operations. The company is expected to hold another vehicle unveiling day closer to the end of the year.
However, Tesla provided some numbers related to the manufacturability of its next-generation platform, indicating that it aims to achieve a 44% improvement in operator density and a 30% improvement in space-time efficiency compared to the Model 3. In addition, rather than using traditional assembly lines, the new platform would allow parallel and serial assembly, resulting in a 40% reduction in manufacturing footprint. In terms of drive units, Tesla has reduced the usage of silicon carbide by 75% and developed it to be chemistry-agnostic, resulting in a 50% reduction in factory footprint and an all-in cost reduction of $1,000 per unit.
Investor Day 2023 (Tesla)
In addition, Tesla plans to simplify and automate the manufacturing of wiring and harnesses while using 100% in-house electronic controllers on its next-generation platform to have complete control over the design and supply chain of components, resulting in a simpler and more cost-effective electronic architecture. The company’s close collaboration with suppliers during the design phase and setup of manufacturing lines enable them to use fewer components and achieve greater efficiency. The Cybertruck currently uses 85% in-sourced electronic controllers, while the Model Y uses 50–60%, but the next-generation platform will use 100%.
Furthermore, the progress made by Tesla in the automated production of dry electrodes for its 4680 battery cell production is promising. This is an area the company has been focusing on since acquiring Maxwell Technologies in 2019. At its battery day event, Tesla had set a target of reducing the cost per GWh of cells by 18% through the transition to a dry electrode process, which Elon Musk had identified as a critical factor in reducing the cost of lithium batteries. The company expects to be able to scale up this process to volume production later this year.
As expected, the event focused on Elon Musk’s Master Plan 3, which aims to achieve a sustainable energy future for Earth with the core strategy of scaling up the company’s operations. Tesla plans to grow significantly in vehicle sales and non-auto ventures such as battery storage, leveraging its software DNA, vertical integration, cost reduction, manufacturability, and continuous improvement. While there are concerns about the feasibility of the ambitious growth plan, the investor day showcased Tesla’s superiority over traditional automakers in the global adoption of electric and software-defined vehicles.
Overall, Tesla’s unwavering commitment to achieving a sustainable energy future for Earth With a focus on scaling up its operations and leveraging its strengths in software and manufacturing, Tesla is poised to leave traditional automakers in the dust and pave the way for a cleaner, greener tomorrow.
NIO’s Ambitious New Models Face Operational Challenges & Margin Pressures
During NIO’s Q3 2022 earnings call in November 2022, the company announced it would release five new models in the first half of 2023. Further details regarding the new models and their expected timelines were provided during the Q4 2022 earnings call. In addition, NIO confirmed that the delivery of the EC7, its latest flagship coupe SUV, and the new ES8, its largest six-seat SUV, will begin in May and June, respectively, as previously announced in December 2022.
The ES6 and EC6 models will also receive upgrades, and the new ES6 is expected to be delivered in Q2 of 2023 without specifying the exact month, but it is expected around June. In addition, management has confirmed that NIO will release a new model, likely a station wagon converted from the ET5, but no expected delivery date was provided.
NIO
Even after removing one-time items worth RMB 985 million from its cost, NIO’s vehicle margin has decreased to 13.5%, the lowest reported since the company went public. Management has attributed the soft gross margin to a shift in product mix toward lower-margin ET5s and elevated battery prices, which may have reached their peak.
In the first quarter of 2023, these factors will continue affecting NIO’s vehicle margin. Additionally, the company will face further challenges, such as promotional activities related to clearance sales of old EC6, ES6, and ES8 models and scheduled factory upgrades for new model releases, which may reduce production efficiency and push down NIO’s vehicle margin even further. However, the company remains confident that its vehicle margin will recover from 18% to 20% by Q4 2023 due to the lowering raw material costs for battery packs and new battery partnerships.
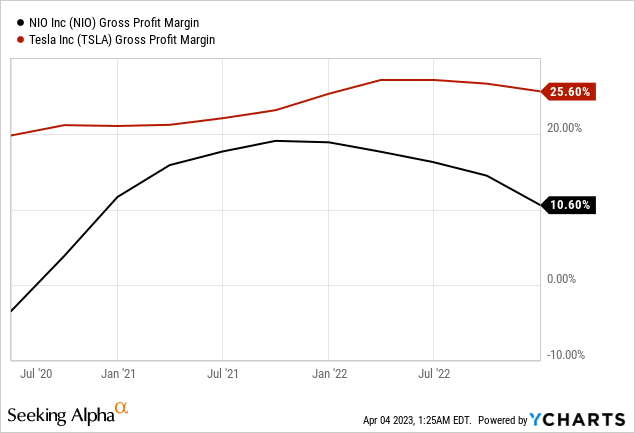
Moreover, NIO’s operating expenses have been rising rapidly, with R&D and SG&A expenses in Q4 2022 being the highest since the company went public. Higher payroll expenses drove this increase as NIO takes on multiple projects simultaneously. During the earnings call, management acknowledged that cost control is crucial for NIO in 2023.
Still, instead of improving efficiency at the company level, which often involves job and project cuts, NIO will focus on increasing efficiency per person. This approach may result in slower top-line growth for NIO, as evidenced by management’s comments in January regarding lower-than-expected demand for the ES7 and ET7 and elevated expenses.
Furthermore, NIO’s recent guidance cut is a cause for concern as the company has faced several challenges in the past few quarters, including issues with metal casting parts, EDS assembly, silicon carbide supply, and delivery logistics, resulting in lower-than-expected deliveries. These issues have raised concerns about management’s ability to execute, primarily as they aim to launch two other auto brands and expand into Europe.
NIO’s recent operational issues are due to the company’s overly aggressive deployment of new manufacturing processes technology, such as highly automated assembly lines and mega casting, without enough focus on mitigating supply chain risks. It’s unclear if this is a structural issue. Still, the management has been taking steps to mitigate and address bottlenecks, such as qualifying additional casting suppliers to eliminate capacity constraints for the ET7 and adding assembly lines to support ET5 volumes.
Finally, as NIO navigates these obstacles, management addresses bottlenecks and mitigates supply chain risks. Whether these efforts keep NIO on track remains to be seen, but the company is undoubtedly revving for an exciting ride.
NIO Has A More Attractive Risk/Reward Profile
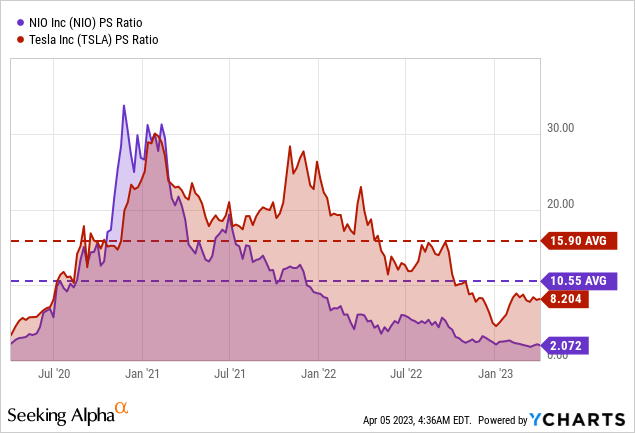
It may be reasonable to believe that Tesla’s stock price is around its fair value, but the recent sell-off has created another good entry point for TSLA. As a result, the stock trades below its 3-year average Price/Sale multiple of 15.9x, and with a current P/S of 8.2x, a potential rerating is underway as soon as the market gains more visibility in the company’s production and deliveries.
Despite the plunge in NIO’s market value to multi-year lows, the company’s outlook appears to be improving in light of China’s zero-Covid policy relaxation and China’s 11-year high purchasing managers index (a measure of factory activity). NIO has a market worth of over $15.4 billion and a P/S ratio significantly lower than its EV peers at about 2.1x. Despite the high uncertainty, following the brutal selloff in 2022, risk-seeking investors might consider building a position in the stock as the market outlook improves in the second half of the year.
Takeaway
In conclusion, NIO and Tesla face significant operational and margin pressures as they navigate the highly competitive and rapidly evolving EV market. NIO’s ambitious new models, recent operational challenges, and Tesla’s focus on manufacturing efficiency and cost reduction through its next-generation platform highlight the intense pressures that companies in the EV space face. However, both companies remain focused on innovation and growth, and it remains to be seen how they will fare in the highly competitive EV market in the years ahead.
Editor’s Note: This article discusses one or more securities that do not trade on a major U.S. exchange. Please be aware of the risks associated with these stocks.
Analyst’s Disclosure: I/we have a beneficial long position in the shares of TSLA either through stock ownership, options, or other derivatives. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
Seeking Alpha’s Disclosure: Past performance is no guarantee of future results. No recommendation or advice is being given as to whether any investment is suitable for a particular investor. Any views or opinions expressed above may not reflect those of Seeking Alpha as a whole. Seeking Alpha is not a licensed securities dealer, broker or US investment adviser or investment bank. Our analysts are third party authors that include both professional investors and individual investors who may not be licensed or certified by any institute or regulatory body.
Author of Yiazou Capital Research
Unlock your investment potential through deep business analysis.
I am the founder of Yiazou Capital Research, a stock-market research platform designed to elevate your due diligence process through in-depth analysis of businesses.
I have previously worked for Deloitte and KPMG in external auditing, internal auditing, and consulting.
I am a Chartered Certified Accountant and an ACCA Global member, and I hold BSc and MSc degrees from leading UK business schools.
In addition to my research platform, I am also the founder of a private business.