Summary:
- Intel is a multinational technology company and one of the leaders in the semiconductor industry, founded in 1968 by Gordon Moore and Robert Noyce.
- The company’s share price has grown by 16.93% since the beginning of 2023, outperforming major competitors like Analog Devices and QUALCOMM Incorporated.
- Despite challenges in the PC market and macroeconomic environment, Intel’s revenue is expected to grow in the second quarter of 2023 compared to the previous quarter.
- To regain lost share in the semiconductor industry, the company plans to launch the 5th generation Emerald Rapids server processors belonging to the Xeon family and the 14th generation Meteor Lake processors in the coming year.
- We initiate our coverage of Intel with a “hold” rating for the next 12 months.
recep-bg/E+ via Getty Images
Intel (NASDAQ:INTC) is a multinational technology company and one of the leaders in the semiconductor industry, founded in 1968 by Gordon Moore and Robert Noyce and continues to play a key role in driving the digital revolution.
Despite a sharp drop in the company’s net income in recent quarters, reflected in a decrease in dividend payments, Intel management continues developing new chips and technologies to regain lost share in the global semiconductor market. So, in the coming year, the company plans to launch the 5th generation Emerald Rapids server processors belonging to the Xeon family and the 14th generation Meteor Lake processors in the coming year. In addition, Intel will receive subsidies from the US, German and Israeli governments to build chip factories needed to reduce dependence on Asian suppliers.
The company’s central processing units have become widely used in personal computers, servers, and data centers around the world, allowing millions of customers to experience powerful computing capabilities that can process vast amounts of data, perform various simulations and develop complex machine learning and artificial intelligence algorithms that will ultimately improve the quality of life of hundreds of millions of people. In addition to microprocessors, the company’s product portfolio consists of GPUs, SSDs, networking products, artificial intelligence solutions, integrated circuits, and more. The company’s core operating segments are Data Center and AI (DCAI) and Client Computing (CCG), collectively accounting for about 80.9% of Intel’s total revenue in Q1 2023.
Author’s elaboration, based on 10-Q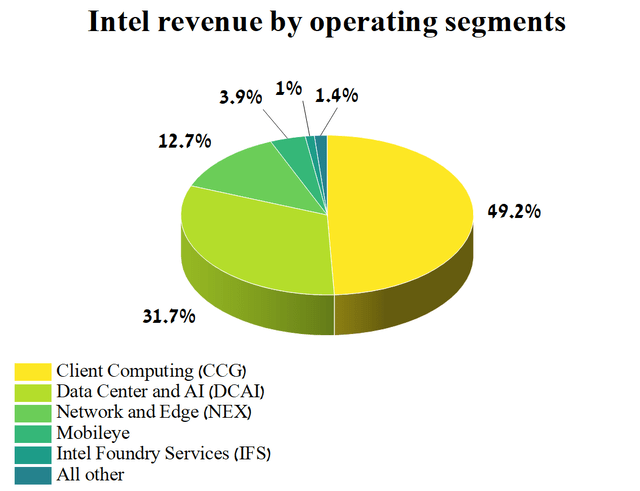
On April 27, 2023, Intel published financial results for the first three months of 2023, which, despite beating analysts’ expectations for revenue, showed a decrease in sales in all major business segments of the company, except for Mobileye, due to the ongoing crisis in the personal computer industry and the slow recovery of the Chinese economy. Despite all the difficulties the company is experiencing, since the beginning of 2023, Intel’s share price has shown growth of about 16.93%, outperforming such major competitors in the technology sector as Analog Devices (ADI) and QUALCOMM Incorporated (QCOM), but at the same time significantly lagging behind Micron Technology (MU) and AMD (AMD).
Author’s elaboration, based on Seeking Alpha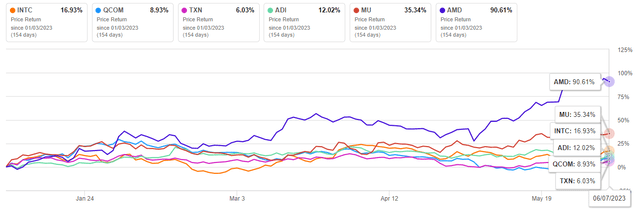
We initiate our coverage of Intel with a “hold” rating for the next 12 months.
The financial position of Intel and its prospects
Intel’s revenue for the first three months of 2023 was $11.72 billion, down 16.5% from the previous quarter and 36.1% from the first quarter of 2022.
Despite the persistence of a challenging macroeconomic environment, including the high-interest rate of the Fed, Intel’s actual revenue has beaten analysts’ consensus estimates in seven of the last nine quarters. And the company was able to significantly exceed Wall Street’s expectations for the first quarter of 2023. This is despite the fact that the elevated interest rate has led to a crisis in the PC market and strengthening in the US dollar against foreign currencies. At the same time, Intel’s P/S [TTM] is 2.41x, which is 13.38% less than the average for the sector and 14.52% less than the average over the past five years.
Author’s elaboration, based on Seeking Alpha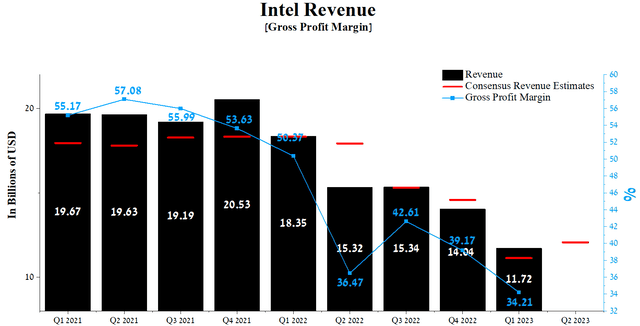
The most significant impact on the company’s financial position comes from the Client Computing segment, whose revenue was about $5.77 billion, down 38.1% year-on-year. However, the drop in sales in this segment did not surprise investors due to the Gartner report, which published preliminary estimates for the shipment of personal computers by vendors two weeks before the publication of Intel’s financial results for the first quarter of 2023. Thus, according to Gartner, the volume of shipments by the leading companies in the global PC market continues to decline yearly, but this pace is starting to slow down. We estimate that PC sales will begin to recover at the end of the third quarter of 2023, thus stabilizing the price of Intel shares, which are under pressure from short sellers.
Author’s elaboration, based on Gartner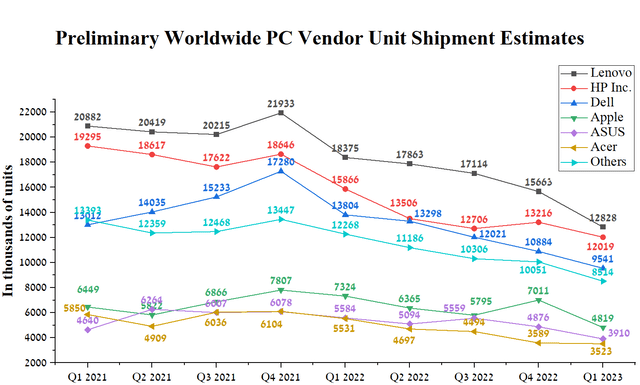
Intel’s revenue for Q2 2023 is expected to be $11.99-12.51 billion, up 8.6% from analysts’ expectations for the first three months of 2023. We believe that numerous factors will provide a gradual increase in revenue.
The first is government subsidies for constructing the company’s factories in countries such as the US, Germany, Poland, and Israel. An essential chipmaker support program that will directly boost Intel’s revenue is the $52.7 billion CHIPS and Science Act approved in 2022, allowing the company to secure funding to build four factories in Arizona and Ohio. This bill signed by President Biden, aims to reduce dependence on the supply of chips from Asia and create jobs in the US, which is especially important for him in the run-up to the 2024 presidential election.
Germany will invest 9.9 billion euros in Magdeburg to build a factory worth more than 30 billion euros. Negotiations were also recently completed for a subsidy from the Israeli government to build a chip factory in Kiryat Gat, due to open in 2027. In general, Israel has long been one of the most important countries for Intel, in which, historically, some discoveries changed the company’s history for the better.
To regain lost share in the semiconductor industry, the company plans to launch the 5th generation Emerald Rapids server processors belonging to the Xeon family and the 14th generation Meteor Lake processors in the coming year.
The company does not plan to stop there and continues to actively develop chips for AI, which is of particular interest from Wall Street in the current period of enormous excitement and the introduction of this technology into people’s lives.
Data Center and AI Investor Webinar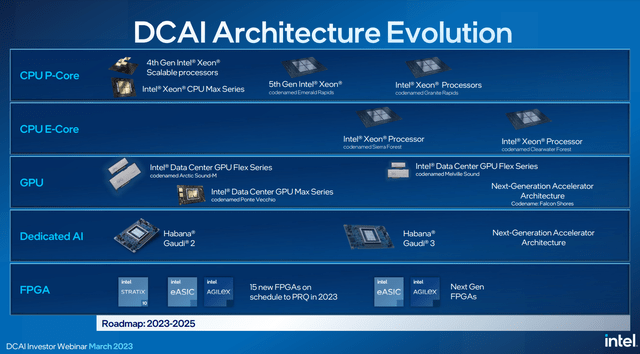
The key risk for Intel is that it will continue to be significantly technically behind Taiwan Semiconductor and Samsung. So these companies are at the final stage of developing and preparing for mass production of next-generation chips using the 2-nanometer process technology, while Intel is just beginning this journey.
In addition, a problematic situation with high levels of customer stocks remains, likely to improve only in the second half of 2023. As a result, this not only puts downward pressure on the semiconductor industry, but also reduces its attractiveness in the eyes of investors unwilling to invest in high-risk assets during elevated interest rates.
So, at the Q1 2023 earnings call, Intel’s management stated the following.
In addition, the recovery in end market demand from channels reopening is also lower than our expectation. Therefore, the fabless semiconductor inventory adjustment in first half ’23 is taking longer than our prior expectation. It may extend into third quarter this year before rebalancing to a healthier level.
Intel’s Q1 2023 operating income margin was -11.98%, down significantly from the prior year while maintaining its downward trend quarter-on-quarter. Moreover, this financial figure is not only substantially lower than that of the technology sector but also that of competitors such as Analog Devices, QUALCOMM Incorporated, and Texas Instruments, which is another factor that discourages investors from choosing Intel as a long-term investment.
We forecast that Intel’s operating income margin will reach 1% by 2023 and rise to 4.5% by 2024, driven by a slow recovery in global semiconductor market share, lower inflation, and subsidies to build chip factories.
The company’s earnings per share (EPS) for the first three months of 2023 was -$0.66, up 312.5% quarter-on-quarter, with only six of the last nine quarters beating analyst consensus estimates. Moreover, Intel’s Q2 EPS is expected to be between -$0.07 and -$0.09, up 95.4% from the consensus estimate for Q1 2023.
On the other hand, Intel’s Non-GAAP P/E [FWD] of 79.33x is 258.34% higher than the sector average and 393.12% higher than the average over the past five years, which is one of the factors indicating that Wall Street overvalues the company in the current period of lower inflation and tougher competition in the industry.
Author’s elaboration, based on Seeking Alpha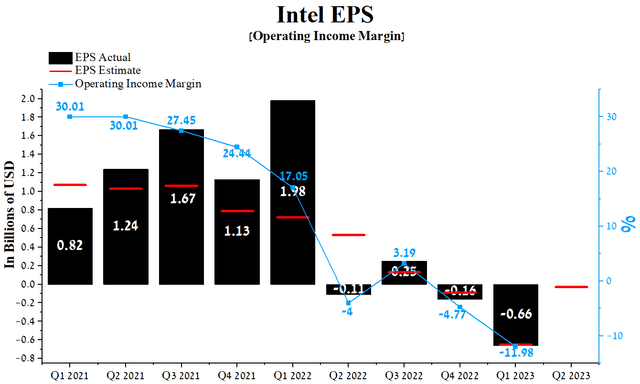
As Intel’s financial position deteriorated, the company stopped repurchasing outstanding shares in Q3 2021. We do not expect the company to start pursuing a share repurchase policy in the next two years, and, as a result, the total shares outstanding will continue to grow by an average of 16m QoQ, which will put additional pressure on the stock.
Author’s elaboration, based on Seeking Alpha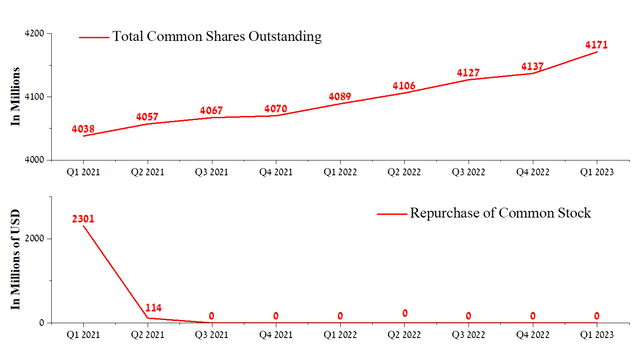
At the end of March 2023, Intel’s total debt stood at about $50.27 billion, a significant increase from 2021 due to the need to invest billions of dollars in chip development to close the gap with TSMC and Samsung. At the same time, due to a sharp and significant drop in EBITDA in recent quarters, the total debt/EBITDA ratio increased from 1.13x to a record high of 5.1x for Intel.
Author’s elaboration, based on Seeking Alpha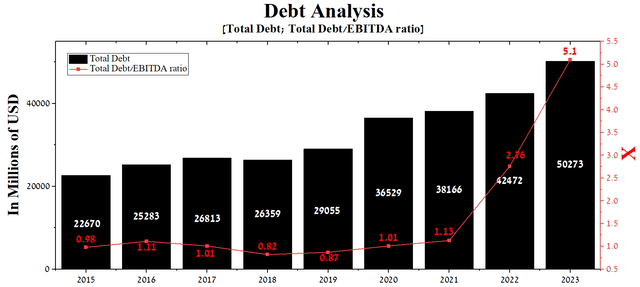
Given the maturity dates of the senior notes and negative cash flow, we expect Intel to resort to refinancing part of the debt to reduce financial risks and continue to pursue an active R&D policy.
Conclusion
Intel is a multinational technology company and one of the leaders in the semiconductor industry, founded in 1968 by Gordon Moore and Robert Noyce and it continues to play a key role in driving the digital revolution.
The most significant impact on the company’s financial position comes from the Client Computing segment, whose revenue was about $5.77 billion, down 38.1% year-on-year. However, the drop in sales in this segment did not surprise Wall Street because of the Gartner report, which shows a volume of shipments by the leading companies in the global PC market.
Despite a sharp drop in the company’s net income in recent quarters, reflected in a decrease in dividend payments, Intel management continues developing new chips and technologies to regain lost share in the global semiconductor market. So, in the coming year, the company plans to launch the 5th generation Emerald Rapids server processors belonging to the Xeon family and the 14th generation Meteor Lake processors. The company does not plan to stop there and continues to actively develop chips for AI, which is of particular interest from Wall Street in the current period of enormous excitement and the introduction of this technology into people’s lives. In addition, Intel will receive subsidies from the US, German and Israeli governments to build chip factories needed to reduce dependence on Asian suppliers.
Given the reduced hype around AI and the likelihood of a Fed rate hike in 2023, we expect the company’s share price to correct to a strong support zone around $29.50-$30.20 in the next two months. We initiate our coverage of Intel with a “hold” rating for the next 12 months.
Analyst’s Disclosure: I/we have no stock, option or similar derivative position in any of the companies mentioned, and no plans to initiate any such positions within the next 72 hours. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
This article may not take into account all the risks and catalysts for the stocks described in it. Any part of this analytical article is provided for informational purposes only, does not constitute an individual investment recommendation, investment idea, advice, offer to buy or sell securities, or other financial instruments. The completeness and accuracy of the information in the analytical article are not guaranteed. If any fundamental criteria or events change in the future, I do not assume any obligation to update this article.
Seeking Alpha’s Disclosure: Past performance is no guarantee of future results. No recommendation or advice is being given as to whether any investment is suitable for a particular investor. Any views or opinions expressed above may not reflect those of Seeking Alpha as a whole. Seeking Alpha is not a licensed securities dealer, broker or US investment adviser or investment bank. Our analysts are third party authors that include both professional investors and individual investors who may not be licensed or certified by any institute or regulatory body.
