Summary:
- Apple reported a 1.4% decline in revenue on a year-on-year basis in the recent quarter.
- However, its net income increased by 2% while EPS increased by 5% which might look like margin expansion for the company.
- Digging deeper, we can see that most of the net income growth is due to a decline in provision for income tax and EPS growth is due to buybacks.
- Apple is showing increase in R&D expense and decline in margins for Services which can hurt the profitability in the next few quarters.
- The forward estimates for both revenue and earnings are negative which makes the stock very expensive with a PE of over 30 or twice its historical average.
Nikada/iStock Unreleased via Getty Images
Apple (NASDAQ:AAPL) reported another quarter of revenue decline on a YoY basis. The 1.4% decline in revenue was already priced in. However, Apple’s CFO Luca Maestri warned that this decline could persist in the next quarter also. Despite this decline, some bullish analysts noted the improvement in net income and EPS. Apple’s net income increased by 2%. It is important to dig deeper into this metric to look at the exact reason for net income growth. Apple’s income before taxes in this quarter was $22.73 billion while in the year-ago quarter, it was $23.06 billion which shows a 1.5% decline in the recent quarter. Hence, the income before taxes declined at a faster pace compared to the revenue. Apple’s provision for income taxes declined by $800 million in the recent quarter which helped push the net income in positive territory.
In my previous article, “Apple: Let the dust settle before making a move”, it was mentioned that the company is already facing an uphill battle in products like Vision Pro. The bill of materials of Vision Pro is a staggering $1500. It also requires massive R&D investment which is reflected in the rapid growth of this metric. Apple’s margin and net income could fall as the revenue stagnates over the next few quarters.
One of the reasons behind a decline in Apple’s income before taxes is due to an increase in R&D expenses. The R&D bill in the recent quarter was $7.44 billion compared to $6.8 billion in the year-ago quarter which is close to a 10% jump. Another reason for the decline in Apple’s margin is a dip in the gross margin of Services segment. The gross margin of Services segment reduced from 71.5% in the year-ago quarter to 70.5% in the recent quarter.
Apple does not show potential for strong net income growth in the next few quarters. Declining revenue and net income could lead Wall Street to question the historically high valuation multiple given to Apple making the stock more likely to show a correction.
Net income growth is a mirage
Apple’s headline metric showed a 2% growth in net income on a YoY basis which seems a good number when we consider that the revenue base declined by 1.4% in this period. However, looking closely at the numbers shows that most of the gain in net income is due to a decline in the provision for income tax. Income before provision for income tax actually declined by 1.5% which is higher than the revenue decline and shows a margin decline.
Company Filings
Figure 1: Comparison of net income and taxes reported by Apple in the recent quarter and the year-ago quarter. Source: Company Filings.
The tailwind due to the decline in provision for income tax is unlikely to happen consistently. Hence, we could see Apple report a decline in net income over the next few quarters which will increase the doubts over the long-term earnings growth potential of the company.
It should be noted that the company is already getting close to a cash-neutral position. Hence, any dip in net income will directly impact the buybacks and the ability of the management to give good dividend growth.
Reasons behind income decline
One of the reasons behind the decline in income before taxes is the rapid growth in R&D expense. Most investors accept that a higher R&D bill is required for a company to be innovative in the tech field. However, Apple’s R&D bill has steadily grown faster than revenue which has impacted the company’s margin.
Company filings
Figure 2: Apple’s R&D expense compared to year-ago quarter. Source: Company Filings.
Apple’s R&D bill increased by 9.6% in the recent quarter compared to the year-ago quarter.
YCharts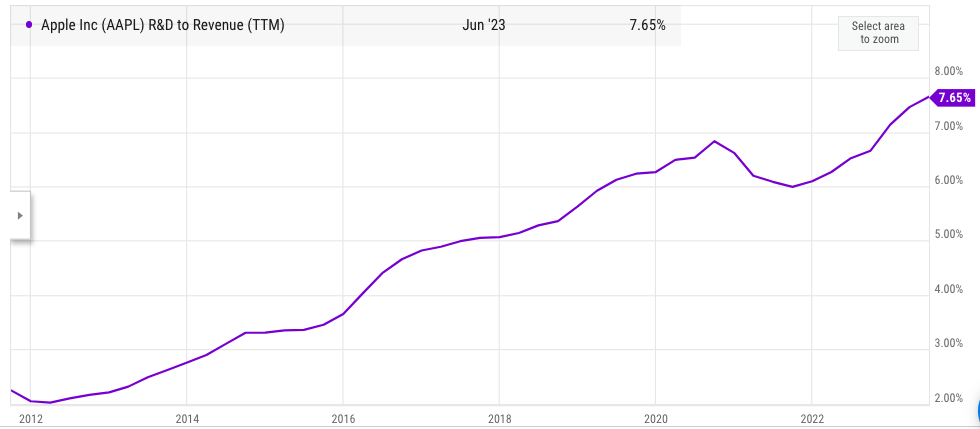
Figure 3: Apple’s R&D to revenue metric in the last ten years. Source: YCharts.
In the Tim Cook era, Apple’s R&D to revenue has increased from 2% to 7.6%. We could easily see this metric reach 10% by the end of this decade as Apple needs to invest heavily in new products, services, AI, and other features. It will continue to be a headwind for future earnings growth for the company.
Another major headwind has been the decline in margin within the Services segment. The gross margin of Services segment declined from 71.5% in the year-ago quarter to 70.5% in the recent quarter.
Company Filings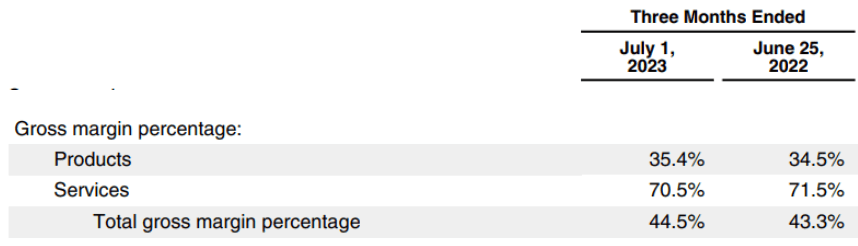
Figure 4: Decline in Services gross margin. Source: Company Filings.
Apple’s Services business includes a wide range of revenue streams. Some are very high margins like the licensing revenue and App Store commissions. However, other revenue streams like Apple TV+ and Apple Music are very low-margin business. Growth in these businesses is likely to pull down the overall margins in the Services segment. This trend is likely to accelerate as Apple makes heavier investments in Apple TV+ which is a big money pit.
Forward estimates for earnings
It is likely that we will see earnings decline over the near term as Apple tries to find future high-growth services. The consensus revenue estimate for next year and 2025 show that the company’s revenue could still grow at 5-6% annually. However, a recent statement by CFO Luca Maestri has forecasted another quarter of revenue decline.
YCharts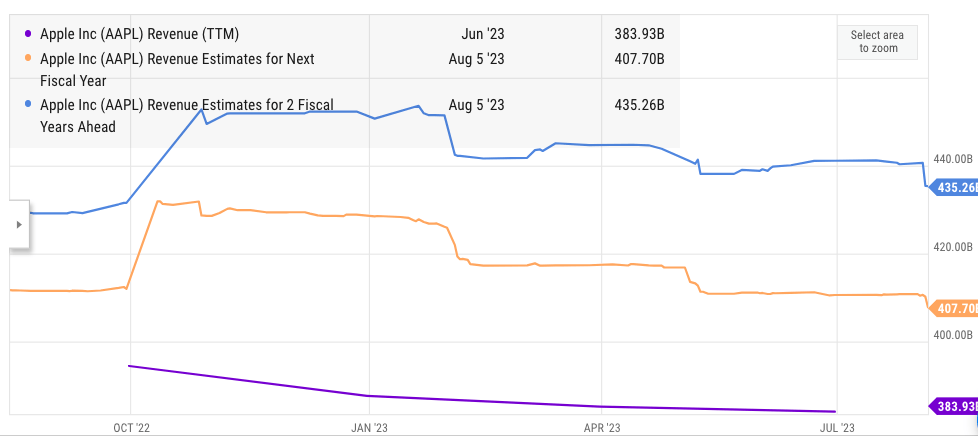
Figure 5: Comparison of Apple’s revenue for next year and the year after that. Source: YCharts.
It is likely that Wall Street will eventually reduce the forward revenue estimate for the company in the next quarter. This can cause a major bearish sentiment toward the stock. The earnings growth is also unlikely besides the 3-4% increase due to buybacks. Apple spent $17.5 billion on stock buybacks in the recent quarter. This pace might also decline as the company reaches cash neutral position and more investment is required in Apple TV+ and other services.
A counterargument to this thesis
Bullish analysts will point to the current correction and say that it gives a better entry point for long-term investors. The brand strength of the company is still strong, and it has a stable upgrade cycle which will deliver healthy free cash flow in the near term. The walled garden made by the company around its App Store is very difficult to breach and will force customers to stay with Apple and add new products even if they are a bit pricey.
Investors will need to gauge if the long-term prospects are good enough to overcome the near-term challenges. It is very likely that Apple will report low single digits or even negative revenue for the next few quarters because a large number of upgrades got pushed ahead during the pandemic. We could see the current headwinds stay till early 2025. Investors with a longer-term horizon could wait for the current correction to play out before adding more Apple stock to their portfolio.
Wait for correction
Apple is still trading at over 30 times the forward P/E. This is the highest ratio among Big Tech peers like Alphabet (GOOG) (GOOGL), Microsoft (MSFT), and Meta (META). On the other hand, the YoY revenue growth of Apple has been the lowest among the tech giants. The forward revenue estimates are also not very optimistic. Hence, it is likely that Wall Street could give another 15%-20% correction in Apple stock over the next few weeks.
YCharts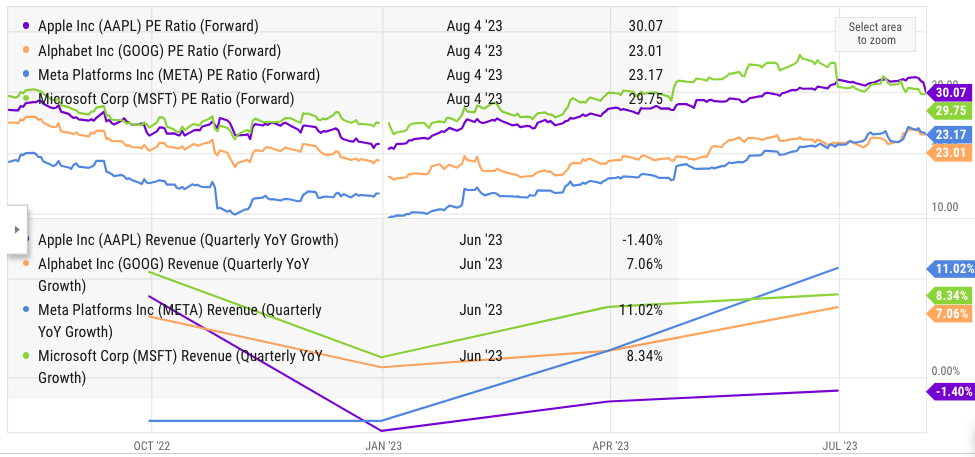
Figure 6: Comparison of Apple, Microsoft, Meta, and Alphabet. Source: YCharts.
Investors looking to make a long-term bet could wait for the current correction to complete before adding to their position. However, it is also important to look at the margin headwinds from a longer perspective. It is unlikely that Services margin will regain the earlier high as most of the new services have wafer-thin margins. The tailwind from buybacks will also reduce as the company reaches a cash neutral position. Prior to the pandemic, Apple stock traded at an average PE of 15. If the current decline in revenue and income persists for another quarter or two, we could see Apple stock show a bigger decline and get closer to the historical average PE ratio.
Investor Takeaway
Apple reported a net income growth of 2% on a YoY basis. However, income before provision for taxes actually declined by 1.5% which is higher than the revenue decline. Apple is seeing margin headwinds within the Services segment and is also showing rapid increase in R&D expense. Both these headwinds are likely to persist which can further push down the margins.
Apple is still trading at a forward P/E ratio of over 30 which is the highest among big tech peers. This valuation multiple is despite the lowest YoY revenue growth of the company in this group. We could see a strong correction in the stock over the next quarter as the key metrics like revenue and net income remain stagnant or decline.
Analyst’s Disclosure: I/we have no stock, option or similar derivative position in any of the companies mentioned, and no plans to initiate any such positions within the next 72 hours. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
Seeking Alpha’s Disclosure: Past performance is no guarantee of future results. No recommendation or advice is being given as to whether any investment is suitable for a particular investor. Any views or opinions expressed above may not reflect those of Seeking Alpha as a whole. Seeking Alpha is not a licensed securities dealer, broker or US investment adviser or investment bank. Our analysts are third party authors that include both professional investors and individual investors who may not be licensed or certified by any institute or regulatory body.
