Summary:
- Google’s AI developments focus on advertising and cloud segments, with notable advancements in Search Labs, Bard, and Performance Max.
- The company’s language models, including BERT, LaMDA, and PaLM, enhance various products and services, improving speech recognition, language translation, and content creation.
- Google faces strong competition from key rivals, such as Microsoft and Amazon, who are also making significant AI advancements in search and cloud services.
400tmax
In our previous analysis of Alphabet Inc. (NASDAQ:GOOG), we explored the company’s digital ad market growth outlook and diversification efforts, particularly in Google Cloud and other segments. Despite a challenging year, Google demonstrated resilience, maintaining its market share leadership. The positive trend continued in its strong ad growth during H1 2021. We projected a strong ad revenue increase for the year and believed Google’s expansion into Google Cloud is notable despite competition from Amazon AWS (AMZN) and Microsoft Azure (MSFT). Furthermore, we determined that other revenue streams like the Play Store, YouTube Premium and smart speakers also present growth opportunities.
This analysis centers on the company’s AI advancements following its earnings briefings in the last two quarters. During these briefings, the company underscored a range of AI developments. In its most recent earnings update, the term “AI” was referenced 90 times, while in the Q1 briefing, it appeared 65 times. Our assessment delved into these AI advancements, elucidating the potential benefits for both Google and its customers. Furthermore, we scrutinized these developments across segments, identifying which areas saw the most significant AI progress. We also conducted a thorough evaluation of Google’s leading language models, dissecting each one’s capabilities. Then, we compared the company’s AI progress against its rivals, discerning any competitive advantages it might possess. Finally, we updated our revenue projections and valued the company with a DCF analysis.
Google’s AI Developments Focused on Advertising and Cloud
Based on the past 2 company’s earnings briefings in 2023, we compiled and highlighted several of its AI developments based on its segments such as Search Labs, Bard, Performance Max, Vertex AI, Duet AI, Google DeepMind and Waymo.
Google Advertising
- Google Search Labs
Google has introduced the Search Generative Experience [SGE], utilizing generative AI to offer users concise overviews of topics and recommended paths for exploration within Google Search. According to Google, this integration simplifies information retrieval, replacing manual analysis and sorting with AI-generated summaries and organized links for quicker comprehension and enhanced task efficiency. Another application of its generative AI is it enhances users’ shopping experience by offering users a concise overview of product details such as reviews, ratings, prices, and images, aiding purchase decisions through the use of the extensive Shopping Graph dataset which features over 35 bln product listings. We believe Search Labs could benefit the Google Search platform which is part of the company’s Google Advertising segment.
- Bard Conversational AI
Another AI development is Google’s conversational AI language model, Bard, which had been introduced globally and supports multimodal queries with images, expanding its capabilities in over 20 programming languages, serving as a valuable resource for developers in coding, debugging, and generating code snippets powered by Google Lens. In terms of product integration, Google highlighted future integrations with Google Maps, Sheets, Gmail and Docs Thus, we believe this could benefit its Google Cloud (Google Workspace) and Google Advertising segments which include “other Google owned and operated properties like Gmail, Google Maps, and Google Play”.
- Performance Max
According to Google, Performance Max is a streamlined campaign type in Google Ads that automates budget allocation, bidding, and creative optimization across various Google channels, enabling advertisers to drive conversions and engagement effectively while gaining insights through data-driven attribution and machine learning. Thus, we believe this could benefit its Google Advertising segment.
Google Cloud
- Vertex AI
Google’s Vertex AI enables is integrated with Google’s PaLM LLM, enabling businesses to utilize generative AI applications like chatbots and text summarization. Partnerships with companies like Behavox, Oxbotica and Lightsticks highlight the benefits of PaLM in areas such as compliance, autonomous driving, and digital media editing. Thus, we believe Google Cloud AI could benefit its Google Cloud segment.
- Duet AI
Google Workspace incorporates Duet AI, its generative AI tool, enhancing content creation and collaboration. The company highlighted the benefits to customers like Standard Industries, Lyft (LYFT), Ulta Beauty, Shopify (SHOP) and Mercedes Benz (OTCPK:MBGAF) as mentioned in its earnings briefing by improving digital experiences, search results, personalization, product launches, and cybersecurity. Thus, we believe this could benefit the company, as highlighted by management of its opportunity to upsell to 9 mln Google Workspace customers, through its Google Cloud segment which includes Google Workspace.
Other Bets
- Waymo
Although not mentioned in its earnings briefing, Waymo, Google’s self-driving technology development utilizes AVs to provide ride-hailing services. Collaborating with car manufacturers such as Jaguar Land Rover and Volvo (OTCPK:VLVLY), Waymo has been expanding its self-driving service to multiple cities, including partnerships with companies like Uber, accumulating over 1 mln driverless miles and planning further expansion. It is included in Google’s Other Bets segment and we believe its self-driving developments could benefit this segment.
Others
- Google DeepMind
Google DeepMind is a new unit within the company that combines Google Brain and DeepMind. Their developments include…
AlphaGo, Transformers, word2vec, WaveNet, AlphaFold, sequence to sequence models, distillation, deep reinforcement learning, and distributed systems.
Following the business combination, from Q2 2023, “Google DeepMind is reported within Alphabet’s unallocated corporate costs”.
Summary
|
AI Development |
Segment |
|
Google Search Labs |
Google Advertising |
|
Bard Conversational AI |
Google Advertising and Google Cloud |
|
Performance Max |
Google Advertising |
|
Vertex AI |
Google Cloud |
|
Duet AI |
Google Cloud |
|
Waymo |
Other Bets |
|
Google DeepMind |
Others (Unallocated Corporate Costs) |
Source: Company Data, Khaveen Investments
We summarized each of Google’s 7 AI developments and its segments. We expect these AI developments to benefit based on the company’s reportable segment breakdown below.
Company Data, Khaveen Investments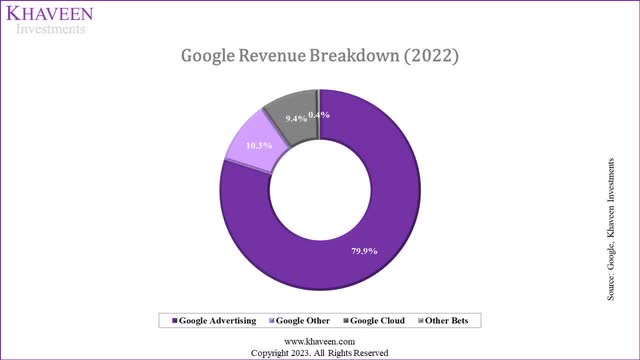
Overall, out of the 7 AI developments that we identified for Google, most of these are for Google’s Advertising and Google Cloud segments which are tied with 3 each. We believe these two segments are unsurprising as Google Advertising is its largest segment representing 80% of revenues in 2022, while Google Cloud is the third largest segment but had the fastest growth rate of 36.8%. Additionally, Google remained the top market leader in the digital advertising market and is the third largest player in the cloud infrastructure services market but had been gaining share over the past 5 years as seen in the chart below. Therefore, we expect the company’s AI developments to support its digital advertising business which could enable it to cement its market share leadership as well as support its cloud market share growth as the third largest player.
Company Data, Zenith, Khaveen Investments Synergy Research, Company Data. Khaveen Investments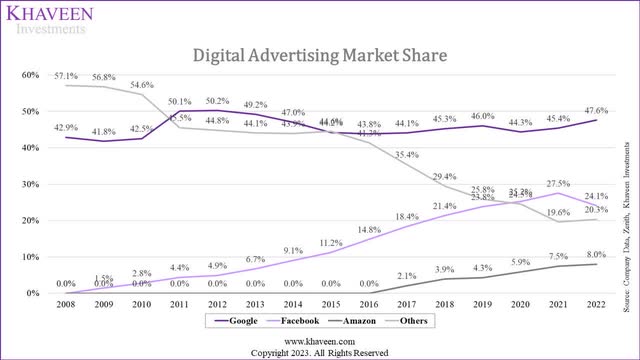
Continuous Development in Large Language Models
According to OECD, an AI language model is “a key component of natural language processing [NLP]” which is “focused on enabling computers to understand and generate human language”.
Specifically, they are…
…algorithms and models that can process, analyze and generate natural language text or speech trained on vast amounts of data using techniques ranging from rule-based approaches to statistical models and deep learning.
According to TechTarget,
A large language model (LLM) is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm that uses deep learning techniques and massively large data sets to understand, summarize, generate and predict new content.
Some of Google’s notable AI language models include BERT, which was introduced in 2018, LaMDA in 2021 and PaLM in 2022 with its updated version released in 2023. Moreover, the company highlighted that it is developing its next AI model named Gemini with multimodal capabilities. We compared these LLMs in the table below.
|
Google Language Models |
BERT |
LaMDA |
PaLM2 |
|
Year Launched |
2018 |
2020 |
2023 (2022 PaLM) |
|
Model Maximum Parameters |
340 mln parameters (BERT-Large) |
137 bln parameters |
340 bln parameters |
|
Training Data Set |
Pre-trained on vast amounts of unlabeled text data, fine-tuned on specific labeled data tasks |
A blend of data called Infiniset |
Large corpus of textual data |
|
Use Cases |
Search Engine Understanding, Language Translation, Question Answering |
Dialogue-based applications |
Automated content creation, chatbot responses, text completion |
|
Key Features |
Bi-directional Context Understanding |
Improved understanding of conversational context |
Large Model Size |
|
|
|
|
|
Strengths |
|
|
|
|
Weaknesses |
|
|
|
Source: Our World in Data, TopBots, Tech Target, Google, Search Engine Journal, Khaveen Investments
In the table above, we compared BERT, PaLM2 and LaMDA based on their year launched, model parameters, training dataset, use cases, key features, strengths, and weaknesses.
- BERT is a language model that uses cases that include search engine understanding, language translation, and question answering. It stands out for its contextual understanding and pre-trained language representation. Its key feature is Bi-directional contextual understanding which means that AI takes account of the surrounding words on both the left and right sides, allowing it to capture the context and meaning of words more effectively. However, BERT’s lack of incremental learning capabilities and performance relative to newer Google models are weaknesses of the model.
- LaMDA is developed with a specific focus on dialogue-based applications. It demonstrates strengths in improved understanding of conversational context and nuanced language comprehension. However, its weaknesses include data bias.
- PaLM2 is one of Google’s largest language models with a 340 bln trained dataset (540 bln for PaLM) and is known for its content generation capabilities. With its large size and ability to process extensive textual data, PaLM is suitable for automated content creation, chatbot responses, and text completion tasks. The model’s training in dialogue data enables it to understand conversational nuances and generate contextually appropriate responses. However, the substantial computational demands of PaLM and potential bias inherited from its training data are limitations of the model.
Google benefits from its language models in several ways, leveraging them across its products and services as well as for new product development.
- Firstly, Google integrates its language models into multiple NLP applications like Google Assistant, Translate, and Smart Reply, leading to improved speech recognition, language translation, and automated responses. These models also enhance services like Smart Compose and Autocorrect by predicting and suggesting contextually relevant text, thereby increasing writing efficiency.
- Furthermore, Google’s language models enhance voice recognition technology, improving the accuracy and reliability of voice searches and commands. These models enable a better understanding of spoken language, facilitating voice-based interactions across devices and enabling features like grammar suggestions, spell-checking and formatting recommendations to aid users in effective content creation and editing.
- Google offers access to its language models to external entities through Google Cloud. This enables developers, researchers, and businesses to incorporate Google’s language models into their applications and services. The Google Cloud Natural Language API includes features such as sentiment analysis, entity recognition, and content classification, enabling external parties to integrate Google’s language model capabilities into their projects. Additionally, Google enables businesses and developers to utilize its AI language models to build customized chatbots and other applications.
Overall, Google has developed various AI language models such as BERT, LaMDA and PaLM. We believe its continuous development in language models highlights Google’s improvements in language models with each new model being more powerful as the trained datasets of each model are larger than the previous one with PaLM as its most powerful model compared to LaMDA and BERT. We believe this could allow Google to continue benefiting from its language models by integrating them into various applications and services like Google Assistant, Google Translate, and Smart Reply and enhance features such as Smart Compose and Autocorrect, providing context-based suggestions while composing content. Additionally, the language models contribute to voice recognition technology, making voice search and command more accurate, and supporting grammar suggestions and spell checking. We also expect its language models to benefit Google Cloud’s growth as it allows external developers and businesses to utilize their capabilities in applications and services, including sentiment analysis, entity recognition, and content classification.
Google’s AI Comparison
In this section, we examine whether Google has an advantage in terms of its AI developments such as its Bard Conversational AI tool Bard, Search Labs and Google Cloud AI.
Comparison of Conversational AI Tools
|
Conversational AI Models |
ChatGPT |
Bing Chat |
Bard |
|
AI Language Model |
Supports GPT-4 |
Supports GPT-4 |
PaLM2 |
|
Model Parameters |
Reported to be 1 tln parameters |
Reported to be 1 tln parameters |
340 bln parameters |
|
Pricing |
$20/month (ChatGPT Plus) |
Free |
Free (Experimental Phase) |
|
Number of Active Users |
100+ mln users |
Up to 100 mln (Total Bing Users) |
143 mln users (May 2023) |
|
Word Limitation |
3,000 words |
4,000 characters (Around 800 words) |
4,000 characters (Around 800 words) |
|
Data Prompt Format |
Text-based (Expected to Support Images in the Future) |
Text and Image |
Text and Image |
|
Data Source |
Trained on a vast dataset until 2021. ChatGPT Plus introduced the capability to conduct web searches using Bing search |
Constantly gathers data from the internet to stay up-to-date |
Trained a dataset containing Common Crawl, Wikipedia, documents, and web conversations. Bard’s real-time web search capability ensures access to the latest answers and research findings |
|
Coding Ability |
ChatGPT outperforms Bard in areas like code generation, problem-solving, third-party plugins & UI extensions, and user experience |
Believed to be similar to ChatGPT using the same GPT-4 model |
Bard surpasses ChatGPT in terms of refactoring code, debugging assistance and cost. |
|
Creative Text formation |
Excels as a summarizer, translator, and in various text-related tasks |
Create sophisticated and grammatically accurate creative text formats, yet there can be instances of repetition and inaccuracies in the generated text |
Might not match ChatGPT’s fluency, engagement, and versatility in generating various text formats. |
|
Word Limitation |
3,000 words |
4,000 characters (Around 800 words) |
4,000 characters (Around 800 words) |
|
Data Prompt Format |
Text-based (Expected to Support Images in the Future) |
Text and Image |
Text and Image |
Source: Mlyearning.org, The Decoder, SimilarWeb, Plural Insights, Zappier, Khaveen Investments
In the table above, we compared the 3 conversational AI models which are ChatGPT, Bing and Bard. ChatGPT is powered by GPT-4 which was reported to be trained with over 1 tln parameters and its data set includes Common Crawl, Wikipedia, books and articles. It is offered for a subscription cost of $20 per month for ChatGPT Plus. Bing is also based on GPT-4. Bard is powered by Google’s PaLM2 (340 bln parameters).
In a comparison of users, ChatGPT was reported to have over 100 mln users. In addition, Bing Chat is free to over 100 mln Bing users. Despite its recent launch, Bard has an estimated number of users of 143 mln in May 2023 according to SimilarWeb. Furthermore, ChatGPT has an advantage over Bing and Bard with higher word limitations. Though, Bing and Bard both support text and images for prompts compared to ChatGPT. However, image formats are expected to be introduced in the future.
In terms of coding ability, in a study by Plural Insights, ChatGPT outperforms Bard in code generation, problem-solving, third-party plugins, and user experience. On the other hand, Bard surpasses ChatGPT in refactoring code, debugging assistance, and user cost. For text generation, ChatGPT is considered the better writer, offering summarization, translation, and other textual tasks. Bing can generate creative and grammatically correct text but may be repetitive or factually inaccurate. Bard can generate factual and informative text but may not be as fluent or engaging as ChatGPT and may have limitations in generating text in different formats.
Overall, we believe that Bard is at a disadvantage compared to other conversational AI like ChatGPT and Bing which are based on OpenAI’s more powerful GPT-4 compared to PaLM2. Furthermore, we believe ChatGPT’s better coding and creative text capabilities reflect its strengths compared to Google’s Bard.
Comparison of Generative AI Integration in Search Engines
In this section, we compared the company’s AI development in its search engine which is significant for the company as Google Search accounted for 72% of Google’s Advertising segment revenues in 2022. We compared the company’s Search Labs development with Microsoft’s Bing Chat AI integration as Microsoft is the second company behind Google in the search engine market.
|
Features |
Google Search Labs |
Bing AI |
|
AI Language Model |
PaLM2 |
GPT-4 |
|
Generative AI Capabilities |
Yes (SGE offers query responses, recommendations, and a conversational interface for search queries) |
Yes (Capability to generate diverse content like images, essays, code, and text) |
|
Coding Ability |
Yes (Coding Tips) |
Yes (Noteworthy for its ability to identify and rectify code errors effectively) |
|
Productivity Software Integration |
Yes (Google Workspace) |
N/A |
|
AI Shopping Tools |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Travel Planning |
Yes |
Yes |
Source: Company Data, Google, BeeBom, ZDNet, TechCrunch, Khaveen Investments
Based on the table, Google’s Search Labs leverage generative AI with its Search Generative Experience (‘SGE’) powered by PaLM 2. This feature allows it to respond to queries, make recommendations, and provide a conversational interface for search queries. On the other hand, Bing also has generative AI capabilities, enabling it to generate new content such as images, essays, code, and text. Additionally, Bing Chat serves as a conversational web search engine powered by GPT-4.
Both Search Labs and Bing provide coding support. Search Labs offers coding tips, while Bing AI Chat is capable of finding errors in code and providing solutions. Regarding productivity software integration, Search Labs allows users to add generated content directly to Google Sheets or other Google Workspace applications. On the other hand, we could not identify similar features between Bing AI Chat with the Google Workspace integrations.
Both Search Labs and Bing incorporate AI shopping tools and travel planning features into their search engines. Search Labs uses AI-powered snapshots to display noteworthy factors related to shopping to enhance the shopping experience. SGE leverages Google’s database of 200 mln places in the world and 35 bln product listings. Similarly, Bing also integrates AI-powered shopping tools to provide users with improved shopping assistance. Bing also has a feature allowing users to create personalized travel itineraries.
Overall, in search engines, Google’s AI developments with SGE are fairly similar to Microsoft’s Bing Chat AI integration with common features such as generative AI capabilities, coding abilities and support, AI shopping tools and travel planning features. However, we believe Google’s productivity software integration provides it with a slight advantage over Microsoft in terms of features. Though, Microsoft’s Bing Chat is powered by GPT-4 which is a more powerful language model compared to PaLM2.
Comparison of Cloud AI
Gartner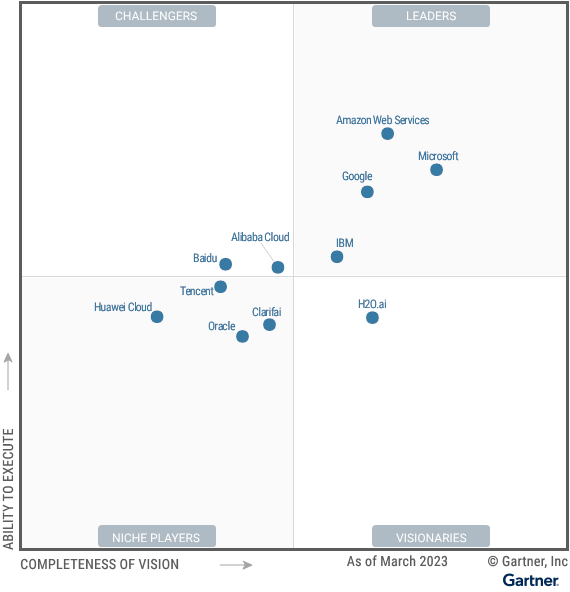
According to Gartner, Google is a Leader in the 2023 AI Cloud Service Developer Magic Quadrant. Gartner highlighted Google Vertex AI. Furthermore, Google’s strengths include its market responsiveness through the enhancement of its services such as more low-code tools which “makes the platform easier for non-data-scientists to use”.
Moreover, another strength of Google is its extensive resources and it has…
…built out one of the strongest portfolios of language, vision, structured data and autoML services. Google offers individual prebuilt autoML services for language, structured data and vision, including both image and video.
In addition to Google, Microsoft, AWS and IBM (IBM) are also ranked as Leaders in the AI Cloud Service Developer Magic Quadrant by Gartner. Amazon’s Cloud AI services…
…includes Amazon SageMaker and other popular language and vision services, is designed to automate the full AI and ML cycle from development to operations”.
Additionally, Microsoft Azure…
has a comprehensive offering for all three use cases: language, vision and autoML.
Finally, IBM’s cloud AI developer services strength includes its robust products according to Gartner,
Watson Discovery and Watson Natural Language Understanding provide strong capabilities for answering questions and generating narratives. IBM’s vision services are competitive, especially its video content analysis capabilities. Maximo Visual Inspection includes deep-learning models that learn to analyze video streams for classification and to detect objects, actions and anomalies.
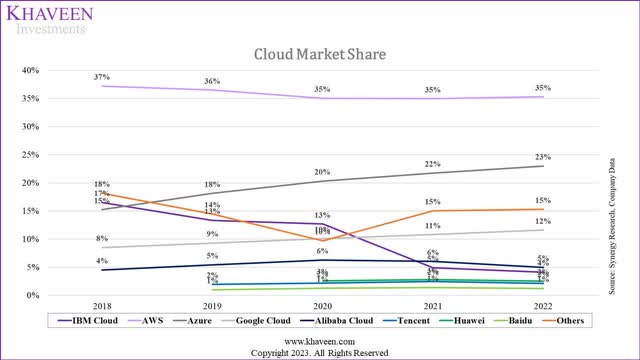
Overall, we believe Google Cloud’s ranking by Gartner highlights its strong position in the cloud service AI but is surpassed by AWS and Microsoft Azure. We believe this is unsurprising as we previously determined that not only are AWS and Microsoft Azure larger than Google in terms of market share but these companies have an advantage over Google in terms of the breadth of their cloud service product offerings with Azure having the highest of 288 followed by AWS (227) and then Google (220).
Summary
To conclude, we compared Google’s AI developments in key segments such as search and cloud. Despite Bard being powered by Google’s most powerful model, PaLM, we believe ChatGPT still has the advantage over it as it is powered by a more powerful and larger language model (GPT-4). In relation, we believe in search engines, Bing Chat could have an advantage over Google’s AI development with SGE as it is powered by the more powerful GPT-4. Whereas in the cloud, we expect Amazon and Microsoft to remain to have the edge over Google due to their larger market position and cloud service product breadth.
Risk: AI Developments from Key Competitors
We believe one of the risks to the company is strong AI developments from key competitors which we believe are Microsoft (search and cloud) and Amazon (cloud). In our previous analysis, we highlighted several AI developments by Microsoft in Search such as Bing AI and its Intelligent Cloud. According to Microsoft,
Bing has grown to exceed 100 million daily active users and daily installs of the Bing mobile app have increased 4X since launch.
…which we believe highlights the increasing competition to Google. Specifically, we believe Google could face tough competition, especially from Microsoft due to its partnership with OpenAI which had developed the largest LLM with GPT-4 currently. That said, Microsoft had confirmed its development of its next LLM called Gemini which could build on its capabilities and compete stronger with GPT-4.
Valuation
|
Google Revenue Breakdown ($ mln) |
2021 |
2022 |
2023F |
2024F |
2025F |
|
Google Advertising |
189,497 |
224,473 |
260,041 |
310,244 |
363,180 |
|
Growth % |
28.1% |
18.5% |
15.8% |
19.3% |
17.1% |
|
Google Other |
28,032 |
29,055 |
35,244 |
42,574 |
51,302 |
|
Growth % |
29.1% |
3.6% |
21.3% |
20.8% |
20.5% |
|
Google Cloud |
19,206 |
26,280 |
35,079 |
48,601 |
67,335 |
|
Growth % |
47.1% |
36.8% |
33.5% |
38.5% |
38.5% |
|
Other Bets |
753 |
1,068 |
1,268 |
1,505 |
1,787 |
|
Growth % |
14.6% |
41.8% |
18.7% |
18.7% |
18.7% |
|
Hedging gains (losses) |
149 |
1,960 |
1,960 |
1,960 |
1,960 |
|
Growth % |
-15.3% |
1215.4% |
0.0% |
0.0% |
0.0% |
|
Total Revenue |
237,637 |
282,836 |
333,591 |
404,885 |
485,565 |
|
Growth % |
29.5% |
19.0% |
17.9% |
21.4% |
19.9% |
Source: Company Data, Khaveen Investments
We updated our revenue projections from our previous analysis based on its segments. For the Google Advertising segment, we updated our digital advertising market projections with the company’s full-year 2022 revenues and updated our market share growth assumption based on its 3-year average of 1.17% but tapered down by 0.5% per year to derive a 3-year average of 17.4% for its Google Advertising segment growth. For Google Other, we updated its 2022 revenues and retain our previous projection on its Google Other segment. Whereas for Google Cloud, we updated our revenue forecasts for the segment based on our cloud market projections from previous analyses. In total, we forecasted Google’s revenues at a 3-year growth rate of 19.7% on average compared to its past 5-year average of 21.1%.
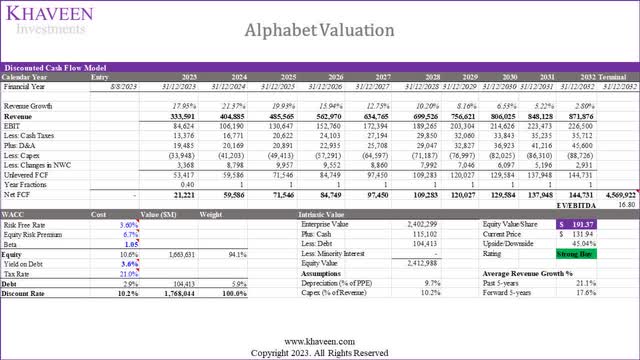
We valued the company with a DCF analysis and the terminal value based on selected digital advertising companies’ average EV/EBITDA of 16.8x which is fairly in line with the company’s 5-year average of 17.94x. Based on a discount rate of 10.2% (Company’s WACC), our model shows its shares are undervalued by 45%.
Verdict
All in all, Google’s AI developments encompassed seven areas, with three related to Google Advertising and three associated with Google Cloud. These segments align with expectations, as Google Advertising constitutes the majority of revenues (80% in 2022), while Google Cloud experienced rapid growth at 36.8%. We believe its AI developments could benefit the company and provide it with opportunities to cement its digital advertising market share leadership and enhance its competitiveness in the cloud where it has been gaining share as the third largest player behind Amazon and Microsoft. Notably, Google has made significant progress in language models, including BERT, LaMDA, and PaLM. Each new model surpasses its predecessor in power and size, with PaLM as the most powerful. We believe the integration of these language models enhances Google’s applications like Google Assistant, Google Translate, Smart Reply, Smart Compose, and Autocorrect.
Furthermore, we believe Google Cloud benefits from these language models, providing capabilities for sentiment analysis, entity recognition, and content classification. However, compared with Bing Chat, we believe ChatGPT holds an advantage over Google’s Bard due to its use of the larger and more powerful GPT-4 language model. Also, in the cloud segment, we believe Amazon and Microsoft maintain an edge over Google due to their larger market presence and wider range of cloud services.
Based on a DCF valuation, we obtained a price target of $191.37 which is lower compared to our previous price target in 2023 based on a P/S valuation of $225.79 as we forecasted a lower 5-year average growth rate of 17.6% compared to 21.2% previously. We maintain our rating of the company as a Strong Buy with an upside of 45%.
Analyst’s Disclosure: I/we have no stock, option or similar derivative position in any of the companies mentioned, and no plans to initiate any such positions within the next 72 hours. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
No information in this publication is intended as investment, tax, accounting, or legal advice, or as an offer/solicitation to sell or buy. Material provided in this publication is for educational purposes only, and was prepared from sources and data believed to be reliable, but we do not guarantee its accuracy or completeness.
Seeking Alpha’s Disclosure: Past performance is no guarantee of future results. No recommendation or advice is being given as to whether any investment is suitable for a particular investor. Any views or opinions expressed above may not reflect those of Seeking Alpha as a whole. Seeking Alpha is not a licensed securities dealer, broker or US investment adviser or investment bank. Our analysts are third party authors that include both professional investors and individual investors who may not be licensed or certified by any institute or regulatory body.