Summary:
- Apple has lagged in AI investment compared to peers, but its strong operating leverage and consistent 10% annual growth make it a hold.
- Apple’s revenue growth is limited; AI and India offer potential, but a significant impact is unlikely before 2025.
- Apple’s AI strategy focuses on integrating intelligence into devices, but it lags behind competitors and relies on third-party models like OpenAI and Google.
- Valuation aligns with current stock price; risks include losing the AI battle and supply chain dependence on China.
Wirestock
Overview
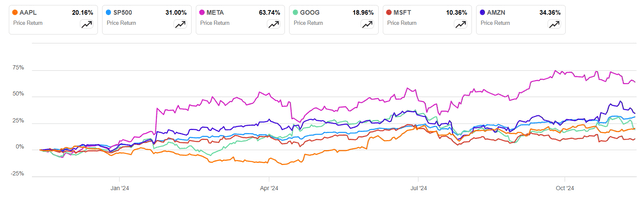
Apple Inc. (NASDAQ:AAPL) has lagged behind most tech contenders, as shown in Figure 1. Only Microsoft Corporation (MSFT) has had a lower return in one year. Warren Buffett has sold about 50% of its original stake in Apple. Most of its contenders have invested in Generative AI, and Apple has lagged.
I recommend holding on to the stock. Its capacity to grow revenue is limited in my opinion. Only AI and India can bring some lift, but their size makes it harder. Apple’s AI strategy is based on getting Generative AI intelligence to the device. Apple is unlikely to launch a radical new AI-native device that can change customer expectations for at least another year in my view. However, Apple’s strong operating leverage makes it a great business that grows at 10% year-over-year. My price target is in line with the current stock price.
Capacity to grow
Apple has been a successful company, reaching a 12-month trailing $391 billion in revenue. The problem is that to grow 5%, Apple has to find a business worth $20 billion, which is not easy. Apple can leverage its vast user base to drive growth through service offerings such as Apple Music, Apple TV+, iCloud, and Apple Arcade. In 2024, services accounted for 24% of Apple’s revenue, reaching $96 billion with a gross margin of 74%. Services segment. This business grows at 13% year-over-year and, in absolute terms, is about $10 billion, which is short to boost revenue.
Vision Pro opens a new virtual computing world, competing face-to-face with Meta’s Metaverse. It sounds like the new product line that can create a whole industry. However, it is a $3,499 gadget with no clear killer user case. While it offers impressive features and technical capabilities, consumers don’t discuss any specific practical application that could intuit mass adoption.
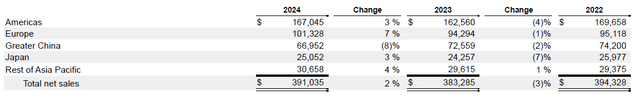
Currently, there is no geographic segment with promising growth prospects. Figure 2 illustrates that Europe is the fastest-growing market, but there, smartphone and PC adoption is high. In Europe, there is a 92% smartphone penetration.
However, Apple is advancing to conquer India’s market. Apple is growing in the premium market with a growing middle class that can reach about 580 million in a few years. Apple aims to manufacture about a quarter of its iPhones to solidify its position in the country.
AI Strategy
Apple has been implementing AI capabilities in its software and operating system since 2017. Today’s apps can use Apple AI capabilities based on the Core ML and Create ML software libraries.
However, Apple has been slow in implementing Generative AI. In my opinion, the company is behaving as always. Apple is not characterized by being the first, but as Tim Cook said in the last earnings call, “by being the best.” Anyway, I think the company is about three years late, and this is a lot of advantage left to its competitors. The company is not developing its proprietary Large Language Model (LLM) to compete. The company has reached an agreement with OpenAI to use its models, and it is negotiating with Google to incorporate the Gemini model. Apple will need to develop its own model, in my opinion, but it will require time, so it will take longer.
Anyway, Apple’s core AI strategy is to use its devices (iPhone, Mac, Apple Watch…) to integrate AI capabilities into hardware. And I think the company is not where it wants to be. I believe the recent launch of the iPhone 16 is just a quick fix. I anticipate that Apple could initiate an AI fundamental transformation no earlier than September 2025 with an iPhone with AI-integrated capabilities. That is an iPhone with integrated GPUs and AI native IOS.
In Figure 3, you can see Apple’s position among its competitors in AI. Comparison is not precise; Amazon invests enormous amounts of CAPEX in its logistics business. However, it can give you a hint about its position in this race. Amazon.com, Inc. (AMZN) is the least comparable company in terms of its multiple businesses, but I clearly position it as a leader in investing. Alphabet Inc. (GOOG) (GOOGL), Meta Platforms, Inc. (META), and Microsoft Corporation (MSFT) are in second position. And we could consider Apple to be in a lower position, especially in CAPEX investing. And that is a key point: it’s all about investing in cloud computing for AI or not. Apple has decided in the short term not to do it; its strength is to bring intelligence to the device. It will outsource cloud AI to the main providers (OpenAI, Google…), which is the main differentiation from its competitors. Will it succeed?
Figure 3: Author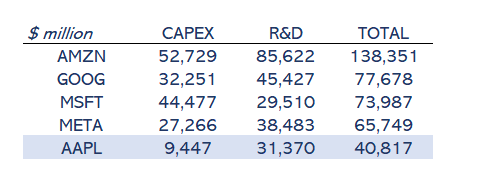
It is hard to answer the question; there are no facts to support it, just the magic of Apple’s innovation. I believe that, nowadays, they are working to transform all the product lines from iPhone to Mac, including Vision Pro and Apple Watch. They will be AI natives who will lead the AI device market, which, I think, is the next battle for the AI revolution. That will increase revenue significantly in most of its products, especially the iPhone.
I assume that the AI push will cause at least 75% of active devices to buy another device, accelerating growth. Currently, all devices are new within 6 years. That means in 2026, I think the growth rate will be 21%, 25% in 2027, and 20% in 2028. Later, it will return to the current 2-3% revenue growth
Operating leverage
I see that it won’t be easy to lift revenue growth. I assign a 70% probability of AI success. One reason this business is strong is its ability to use operating leverage. That is how its operations are much more efficient in converting cash collected to cash available for shareholders, which is free cash flow.
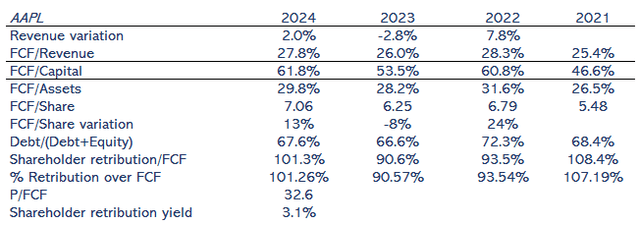
The Free Cash Flow (FCF) as a percentage of revenue in 2024 was 27.8%, up from 26.0% in 2023. This indicates that despite slow revenue growth, Apple was able to convert a larger portion of its revenue into cash flow. The FCF to capital ratio was 61.8% in 2024, up from 53.5% in 2023. This indicates that Apple effectively utilized its capital to generate free cash flow, reflecting higher efficiency in managing its capital base.
FCF per share was $7.06 in 2024, +13% higher than $6.25 in 2023. It was $6.79 in 2022 and $5.48 in 2021, demonstrating strong growth over the years. That is an increase of 10% over the last four years. It is not within my range of 15%-30% but is much more than 2-3% of revenue growth. FCFC per value is the direct indicator of shareholder value.
How does it achieve this operating leverage? Its gross profit margin has increased from 44.2% to 46.2%, and its EBITDA ratio has risen from 32.8% to 34.4%. Apple becomes more efficient each year, and a dollar gains more value.
The shareholder’s compensation as a percentage of FCF increased to 101.3% in 2024 from 90.6% in 2023. This indicates that Apple returned all its free cash flow and more to shareholders through dividends and buybacks.
In the end, the business can convert a high proportion of its revenue into compensation to the shareholder. In three years, even when the company has grown 2% annually, free cash flow per share has grown 10%.
Valuation
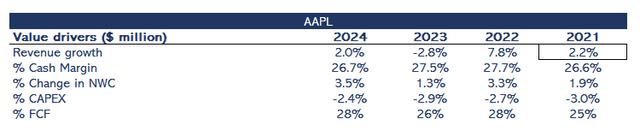
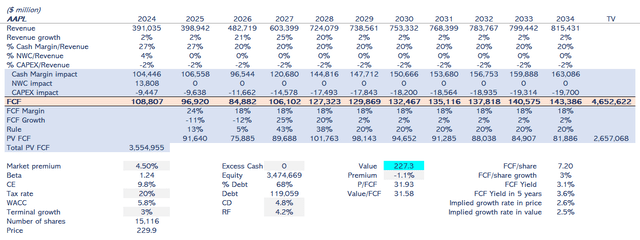
Figure 5 shows the company’s value drivers, considering a year as the last four quarters to capture the latest information. Regarding margins, I utilize a measure I call Cash Margin, which involves adjusting net income for non-cash items such as amortization and depreciation, stock-based compensation, and deferred income tax.
My base case considers Apple’s success in its AI strategy. As I have outlined in the AI section, revenue growth in 2026 will be 21%, 25% for 2027, and 20% for 2028. Later, revenue growth will be 2%.
If Apple integrates AI models natively into its devices, it will position the intelligence into the device, but it will always have to infer queries from the Cloud. It doesn’t matter if Apple uses the OpenAI model, Google’s model, or even develops its proprietary model. I consider Apple to use a third-party AI model in my model, which impacts the cash margin. From the current 27%, it will decrease to 20%. If Apple develops its proprietary model, it will impact CAPEX at the same level, as I assume model costs will be the same in one model or the other. So, I consider a 2% CAPEX over revenue along the ten-year analysis.
Cash flows will be discounted at a 5.8% WACC because the beta is 1.24. The risk-free rate is 4.2%. The company’s leverage is 68% of total capital. Perpetual growth rate is set at 3%.
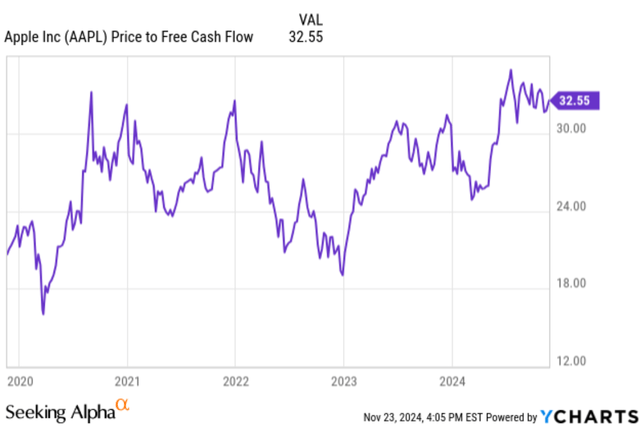
As shown in Figure 6, my value estimate is $227 per share, a 1.1% discount over its current stock price. The company is reasonably priced by the market. My implied multiple Price to Free Cash Flow is 32, slightly higher than the historical levels (Figure 7). My valuation supports the core idea that Apple will be one of the leaders in the AI market with its device-oriented AI.
Risks
Apple’s main risk is losing the AI battle against Google and its flagship operating system, Android. This translates into losing market share in device sales. Losing ten percentage points of market share will translate into a 16% decrease in share value. I assign a 30% chance of being in this situation.
Apple’s supply chain depends extensively on China. 90% of Apple’s products are manufactured and assembled by partners like Foxconn, Pegatron, and Luxshare in Chinese factories. Apple’s cost advantages are due to its ability to outsource to China, which has been optimized over decades to support large-scale production. Even when India is growing to diversify its supply chain, any disruption or political arbitrariness could damage its costs and customer experience.
On the market side, China is an important segment, accounting for about 20% of total revenue. The company’s success in China is based on its ability to position itself as a premium brand in contrast to competition from domestic companies like Xiaomi, Huawei, and Oppo. Lately, Huawei has developed a portfolio of premium smartphones that has attracted attention and gained market share with Apple. With that, the government has recommended that public employees refrain from using iPhones, weakening Apple’s position in the market.
Conclusion
The company’s valuation matches the current stock price. It is based on increased revenue growth from AI native devices, which will increase over the next three years from 2026. At the same time, the cash margin will decrease from 27% to 20% from AI transformation and will last until the tenth year of my model. This margin deterioration is due to outsourcing Generative AI services to a third-party model owner such as OpenAI or Google.
Analyst’s Disclosure: I/we have a beneficial long position in the shares of AAPL either through stock ownership, options, or other derivatives. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
Seeking Alpha’s Disclosure: Past performance is no guarantee of future results. No recommendation or advice is being given as to whether any investment is suitable for a particular investor. Any views or opinions expressed above may not reflect those of Seeking Alpha as a whole. Seeking Alpha is not a licensed securities dealer, broker or US investment adviser or investment bank. Our analysts are third party authors that include both professional investors and individual investors who may not be licensed or certified by any institute or regulatory body.