Summary:
- Intel’s stock is undervalued, presenting a compelling investment opportunity due to its dominant market position and significant progress in manufacturing technology.
- The company’s restructuring initiatives are showing success, with improved profitability and substantial cost reductions, including a workforce reduction of 16,500 employees.
- INTC’s strong market positions in data center CPUs and PC processors, along with new product launches, underscore its growth potential and resilience.
- Government support and strategic partnerships, such as the collaboration with AWS, bolster Intel’s manufacturing capabilities and financial recovery, enhancing its long-term prospects.
tupungato
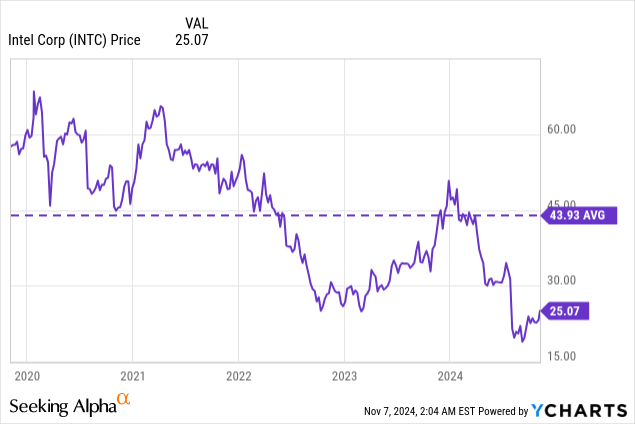
Intel Corporation (NASDAQ:INTC) stock has been in turn since April 2021, although it had a pretty good recovery in 2023. However, since January 2024, it is down more than 50%, even as the whole semiconductor and tech sector is on the bull run. Intel now stands at a pivotal moment in its history, and after hitting its 52-week lows $18.5, the stock is in a consolidation between $21.5 and $26, presenting, what I believe, is a compelling investment opportunity because now it is undervalued relative to the semiconductor sector.
Intel’s dominant market position in critical semiconductor segments. Particularly noteworthy is Intel’s commanding presence in the server CPU market, where data shows that 73% of data centers GPU-based servers utilize Intel Xeon as their CPU. This statistic is especially significant given the growing importance of AI and high-performance computing workloads, which require powerful CPU and GPU combinations.
This market leadership is now being reinforced by tangible progress in manufacturing technology. Intel’s development of its 18A node is a crucial milestone that has already attracted significant customer interest. The recent announcement of multi-billion-dollar collaboration with Amazon Web Services AWS for both Intel 3 and Intel 18A nodes serves as powerful validation of Intel’s. This partnership is particularly meaningful as it involves AWS committing to both a custom Xeon 6 chip on Intel 3 and a new AI fabric chip on Intel 18A, showing confidence in Intel’s current and future manufacturing capabilities.
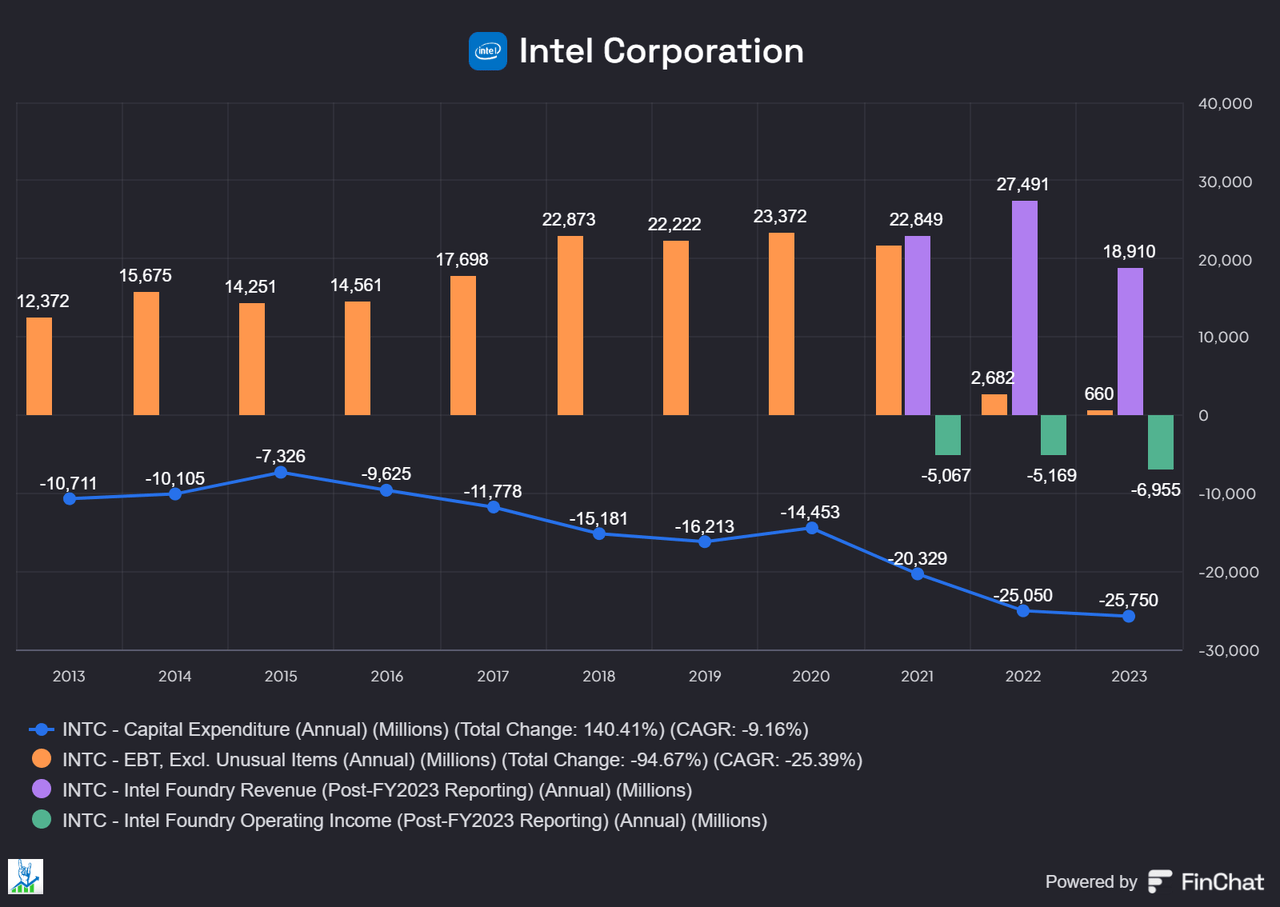
The company’s restructuring initiatives are showing signs of success, evidenced by the Q4 2024 guidance, which points to significant improvement in profitability. While Q3 2024 saw a non-GAAP gross margin of 18.0%, management projects this to improve substantially to 39.5% in Q4 2024. This is backed by concrete cost reduction actions, including a significant workforce reduction of 16,500 employees and a clear path to reaching a $17.5 billion operating expense target for 2025.
The market’s current valuation of Intel at 1.08x price to book value and a (forward 1y) P/E of 25.11x suggests investors remain skeptical of the turnaround story. However, I believe this skepticism creates an opportunity. The main reason I think this skepticism creates an opportunity is because Intel has the largest market share of 76% in the growing Data Center CPU market and 61.6% in the PC CPU market.
Now let me elaborate on why I see a turnaround story unfolding at Intel.
Strong Data Center Position
Intel’s Data Center and AI (DCAI) segment demonstrates resilience and growth potential in an increasingly competitive market landscape. The segment’s Q3 2024 performance, with revenue reaching $3.3 billion and marking a 9% YoY increase, underscores Intel’s enduring strength in this critical market. This growth is particularly impressive given the intense competition from both traditional rivals and new entrants in the data center space.
Intel’s dominant position in the data center market is perhaps best illustrated by its crucial role in GPU servers, where 73% of systems utilize Intel Xeon processors. This statistic is particularly significant given the growing importance of AI and machine learning workloads, which typically require powerful CPU-GPU combinations. Intel’s ability to maintain such a commanding share in these high-value configurations demonstrates the enduring strength of its Xeon platform and its deep integration within the data center ecosystem.
In the data center segment, its recent product launches and strategic initiatives. The introduction of the Xeon 6 processor with Performance-cores represents a significant advancement, doubling the performance for AI and HPC workloads compared to its predecessor. This performance improvement directly addresses the growing demand for AI computation capabilities in data centers.
Intel has launched its Gaudi 3 AI accelerator, which offers up to 20% more throughput and twice the price/performance ratio compared to Nvidia H100 for inference workloads.
The recent collaboration with IBM to deploy Intel Gaudi 3 AI accelerators on IBM Cloud demonstrates the market’s confidence in Intel’s AI acceleration technology and its potential to capture share in the rapidly growing AI infrastructure market.
Additionally, Intel has also secured important wins in the telecommunications sector, KDDI’s selection of Samsung’s vRAN 3.0 solution powered by 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable processors. This deployment shows Intel’s ability to extend its data center leadership into adjacent markets like 5G infrastructure and network transformation.
Dominant PC Market Share
Intel’s commanding position in the PC processor market continues to serve as a bedrock of its business, even amid intense competition and market challenges. The Client Computing Group (CCG) performance in Q3 2024 tells a nuanced story, with revenue reaching $7.3 billion. While this represents a 7% YoY decline, let’s dig a little bit deeper. The underlying trends suggest Intel’s market leadership remains intact. Here is Why.
The evidence of Intel’s market strength comes from the notebook segment, which has shown remarkable resilience and growth. Notebook revenue reached $4.88 billion in Q3 2024, marking a significant increase from $4.5 billion in Q3 2023. This growth is particularly noteworthy given the broader market context. Jefferies analysts estimate overall CPU shipments (including Intel, AMD, and ARM) at approximately 292 million units for calendar year 2024, compared to a total market size of around 270 million units.
In Q3 2024, Intel’s notebook shipments, which include mobile workstations, reached 53.5 million units globally. Intel’s ability to grow notebook revenue in this environment speaks to its competitive advantages and strong OEM relationships.
Intel’s PC market position appears poised for further strengthening with the introduction of the Intel Core Ultra 200V series processors and the upcoming Intel Core Ultra 200S processors. These new products are specifically designed to capitalize on the growing AI PC market, with Intel projecting to ship more than 100 million AI PCs by the end of 2025. The Core Ultra 200V series code-named Lunar Lake, delivers significant improvements in battery life and performance gains while the Core Ultra 200S processors, code-named Arrow Lake expanded AI capabilities to desktop platforms and also launched AI desktop PCs.
18A Node Technology
Intel foundry business is in decline from its peak of 2022, Intel’s path to industry leadership fundamentally hinges on its manufacturing technology capabilities. The company’s recent Intel 18A node development represents what could be a defining moment in semiconductor manufacturing history potentially returning Intel to process leadership after years of trailing competitors.
The progress of Intel 18A node development has emerged as a powerful validation of the company’s manufacturing capabilities. This node represents Intel’s fifth major process technology advance in just four years. The practical implications of this technology are already materializing, the most notable validation comes from Amazon Web Services (AWS), which has committed to a multi-year, multi-billion-dollar collaboration with Intel. This agreement includes two major components: a custom Xeon 6 chip to be produced on Intel 3 and a new AI fabric chip to be manufactured on Intel 18A.
The development progress of lead products for Intel 18A provides further evidence of the technology’s maturity. Both Panther Lake for client computing and Clearwater Forest for servers have met their early milestones ahead of next year’s planned launches. This achievement is particularly noteworthy given Intel’s historical challenges with new process node transitions in recent years. The fact that both client and server products are tracking ahead of schedule suggests broad applicability of the 18A node across different product segments.
Intel has already begun exploring the potential for designs to be produced on Intel 18A and subsequent nodes, including Intel 18AP and Intel 14A. The company expects these advanced nodes to be produced in its Ohio facilities in the United States. It signals Intel’s potential return to its historical position as the world’s leading semiconductor manufacturer. I think Intel is poised to regain its manufacturing leadership position by 2025 with a turnaround from its recent manufacturing challenges.
$3 Billion Under The CHIPS Act
In Q3 2024 with the Biden-Harris Administration’s award of $3 billion in direct funding under the CHIPS and Science Act for Intel’s Secure Enclave program to expand the supply of advanced semiconductors and microelectronics for the Department of Defense. Intel already worked with the Department of Defense through initiatives like the Rapid Assured Microelectronics Prototypes, Commercial (RAMP-C) and State of the Art Heterogeneous Integration Prototype (SHIP) programs. Intel’s unique position as the only American company that both designs and manufactures logic chips makes it a valuable partner in enhancing the resilience of U.S. technological systems.
The company’s success in these government partnerships is evidenced by concrete achievements. In 2023, Intel successfully delivered the first multi-chip package prototypes under the SHIP program, a significant milestone in ensuring access to cutting-edge microelectronics packaging for the Department of Defense. This is the reason Intel is focusing on domestic manufacturing and its ongoing development of the New semiconductor manufacturing facility in Ohio. The strategic importance of this facility is underscored by AWS’s planned $7.8 billion investment to expand its data center operations in Central Ohio, adding to the $10.3 billion it has invested in the state since 2015. This convergence of private sector investment alongside government support creates a powerful ecosystem for semiconductor manufacturing in the region.
The company is also working with defense industrial base (DIB) through the RAMP-C program, which has been equally impressive. Intel has successfully onboarded several critical DIB customers including Boeing, Northrop Grumman, Microsoft, IBM, and Nvidia, and has made significant progress in developing early DIB product prototypes. This success showcases the readiness of Intel’s 18A process technology and ecosystem solutions for high-volume manufacturing of sensitive defense related components.
This robust government support provides Intel with significant advantages as it executes its manufacturing strategy. Beyond the direct financial benefits, government backing helps de-risk major capital investments. As geopolitical tensions increase, the U.S. is pushing for more secure domestic semiconductor manufacturing.
Restructuring Progress And Financial Recovery
Intel’s financial turnaround is gaining meaningful traction through its comprehensive restructuring initiatives, with Q3 2024 results and Q4 guidance providing tangible evidence of progress. The company’s aggressive approach to cost reduction and operational efficiency is just the beginning, setting the stage for improved profitability and sustainable growth.
Most notably, Intel’s ambitious $10 billion cost reduction plan, which aims to drive operational efficiency and agility while creating capacity for ongoing strategic investments in technology and manufacturing leadership. A crucial component of this plan is the significant workforce reduction of 16,500 employees, representing more than 15% of Intel’s core workforce by year-end. This will give Intel a little bit of room to breathe because they have been talking about layoffs since 2022, but now it looks like it is imminent.
Operating expense management shows clear progress toward the company’s targets. Intel has provided specific guidance for full year 2024 Research, Development, and Marketing, General and Administrative (R&D and MG&A) expenses of approximately $20 billion on a GAAP basis. When adjusted for acquisition related charges of $0.1 billion and share-based compensation of $2.4 billion, this translates to non-GAAP R&D and MG&A expenses of $17.5 billion, aligned with the company’s cost reduction goals.
Revenue guidance for Q4 2024 of $13.3-14.3 billion, coupled with expected non-GAAP earnings per share of $0.12, indicates that Intel’s core business remains intact even as it undergoes significant transformation. This positive earnings outlook represents a meaningful improvement from the Q3 2024 non-GAAP loss per share of $0.46, suggesting that the worst of the restructuring impact may be behind the company.
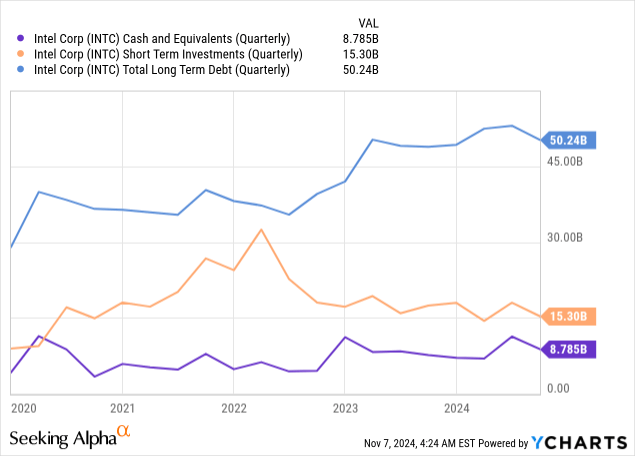
The strength of Intel’s cash generation capabilities remains intact despite the restructuring charges, with the company generating $4.1 billion in operating cash flow during Q3 2024. This substantial cash flow provides crucial flexibility to fund both the restructuring initiatives and ongoing strategic investments. The company maintained a strong liquidity position with $8.78 billion in cash and cash equivalents and $15.3 billion in short-term investments as of Q3 2024, ensuring adequate resources to complete its transformation.
Looking ahead to 2025, Intel has provided clear targets for capital expenditures, projecting $20-23 billion in spending compared to approximately $25-27 billion expected in 2024.
These comprehensive restructuring efforts supported by improving financial metrics and clear forward guidance indicate that Intel’s financial recovery is gaining momentum. While challenges remain, the company’s decisive action on cost reduction coupled with improving margins and maintaining strategic investments suggests a path to sustainable financial performance improvement in the quarters ahead.
Valuation Analysis
Intel’s current valuation metrics tell an interesting story about market expectations. Trading at 1.08x price to book value, compared to the semiconductor sector median of 9.45x, Intel’s shares reflect significant skepticism about the company’s ability to generate returns on its substantial asset base.
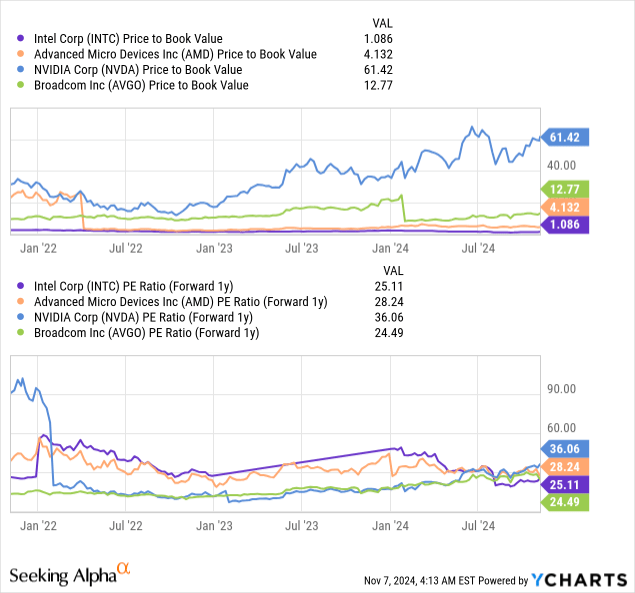
Looking at earnings-based metrics, Intel’s (forward 1y)P/E ratio of 25.11x appears reasonable given the company’s growth potential and market position when compared to its peers like Nvidia (36.06x) and AMD (28.24x).
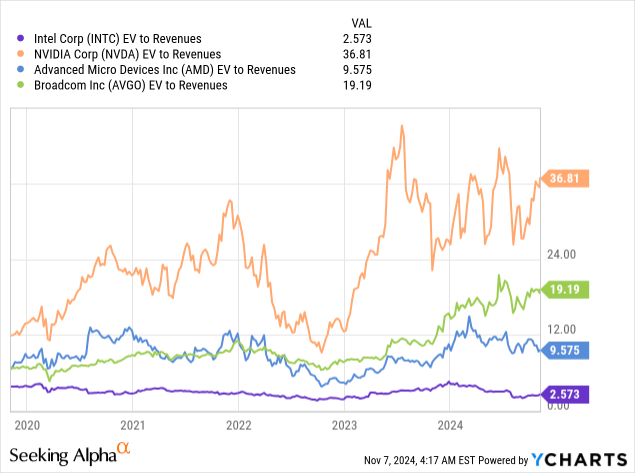
The company’s EV/Sales ratio of 2.57x is way below its peer, below Intel’s own five-year average of 2.92x. This metric is particularly interesting given Intel’s revenue stability and potential growth catalysts in AI PCs and foundry services.
These valuation metrics must be considered in the context of Intel’s improving fundamental picture. The Q3 2024 results, while showing some expected pressure with revenue of $13.3 billion (down 6% YoY), demonstrated progress in key areas. The Q4 2024 guidance is particularly encouraging, projecting non-GAAP gross margin improvement to 39.5% from 18.0% in Q3, suggesting the worst of the margin pressure may be behind the company.
Despite Intel’s recent removal from the Dow Jones Industrial Average, its stock has shown resilience, rebounding from its 52-week low of $18 to around $26. This recovery suggests that investors may see potential in Intel’s turnaround strategy, despite the initial shock of the Dow exit.
For Intel, the path forward hinges on its ability to deliver on its ambitious technology roadmap and manage costs effectively. However, execution risks in manufacturing and competition from Nvidia and AMD remain key obstacle
Intel’s strong market positions provide a solid foundation for value creation. The company maintains a 73% share in GPU-accelerated server CPUs, while showing growth in both notebook volumes (up 6% YoY) and data center revenue (up 9%). These dominant positions in core markets generate substantial cash flow, providing resources to fund the company’s transformation while maintaining financial flexibility.
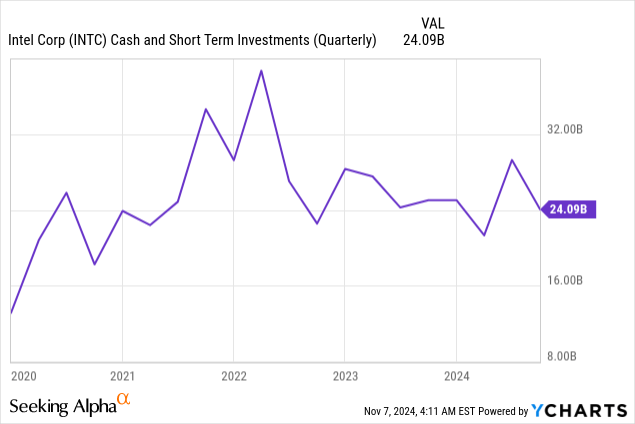
The balance sheet remains solid with $24.09 billion in total cash and short-term investments, providing ample liquidity to fund strategic initiatives while maintaining financial flexibility. This strong financial position helps limit downside risk while providing resources for strategic investments.
The Hurdles Ahead
While Intel’s turnaround strategy shows promising signs, it faces several risks and challenges that need consideration.
The execution risk in Intel’s manufacturing technology transition the company’s ambitious goal of delivering five nodes in four years while early indicators are positive, with Intel 18A development proceeding on schedule and lead products like Panther Lake and Clearwater Forest meeting initial milestones Intel’s previous challenges with node transitions, particularly with 10nm demonstrate how manufacturing delays can significantly impact financial performance and competitive position.
Intel’s current margin structure and transition costs are a problem. The Q3 2024 results showed significant margin pressure, with non-GAAP gross margin falling to 18.0% from 45.8% a year earlier. While Q4 2024 guidance suggests improvement to 39.5%, this remains below historical levels and reflects ongoing pressure from manufacturing investments and competitive dynamics. The company’s $50.24 billion in total debt as of Q3 2024 adds another layer of financial risk, requiring careful balance sheet management during this period of heavy investment.
While these challenges are significant, they should be viewed in the context of Intel’s substantial resources including $24.09 billion in total cash and short-term investments, strong government support and demonstrated ability to generate operating cash flow ($4.1 billion in Q3 2024).
My Takeaway
When considering all these factors, strong market positions, improving execution, multiple growth catalysts and government support. Intel presents a compelling risk-reward proposition for long-term investors. While risks remain, including execution challenges and competitive pressures, the current valuation appears to more than account for these risks while providing an upside potential if the company’s turnaround strategy continues to gain traction.
The Q3 2024 results and Q4 guidance suggest this turnaround is indeed progressing, making current price levels an attractive entry point before potential broader market recognition of Intel’s improving trajectory. For investors willing to take a longer-term view, Intel offers an opportunity to invest in an industry leader embarking on a significant transformation at a valuation that provides meaningful upside potential with relatively limited downside risk given the company’s strong market positions and improving fundamental picture.
Analyst’s Disclosure: I/we have a beneficial long position in the shares of INTC either through stock ownership, options, or other derivatives. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
Seeking Alpha’s Disclosure: Past performance is no guarantee of future results. No recommendation or advice is being given as to whether any investment is suitable for a particular investor. Any views or opinions expressed above may not reflect those of Seeking Alpha as a whole. Seeking Alpha is not a licensed securities dealer, broker or US investment adviser or investment bank. Our analysts are third party authors that include both professional investors and individual investors who may not be licensed or certified by any institute or regulatory body.