Summary:
- There are arguments to be optimistic about a INTC turnaround, and share price rebound.
- I note that Intel has been making some smart moves in its turnaround plans, such as shedding some non-core businesses.
- With a booming AI semiconductor market, Intel is one of the few firms with a diverse enough portfolio to serve multiple needs in the AI revolution.
- I calculate an implied $188 billion FY 2025 market capitalization, or a $43/ share price target (FY 2025).
JasonDoiy
Intel’s (NASDAQ:INTC) share price has been under pressure over the past few years, due to a combination of macro headwinds, competitive pressures from both fab and foundry, as well as concerns about the company’s financials and sustainability of dividend payments. From a macro perspective, the broader semiconductor industry has been facing a downturn, which has put pressure on Intel’s topline and pricing power. In addition to macro headwinds, Intel is also facing intense competition in the compute market. Specifically, Intel faces the risk of share loss in server CPUs to AMD (AMD), Nvidia (NVDA), and tech companies’ in-house solutions.
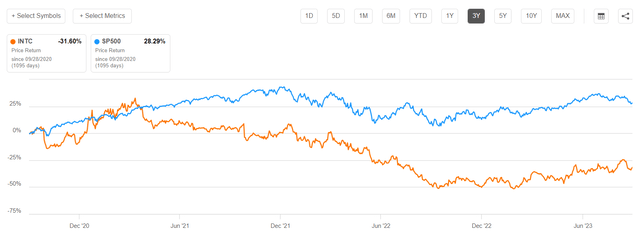
Looking at the past 3 years, INTC stock is down almost 32%, compared to a gain of 28% for the broad equity index, the S&P 500 (SP500).
However, there are arguments to be optimistic about a INTC turnaround, and share price rebound: Firstly, I point out that Intel is still one of the largest semiconductor companies in the world and holds the lion’s share of the PC and server processor markets. This gives the company a significant competitive advantage due to economies of scale, while providing a solid platform for innovation and growth; Secondly, I note that Intel has been making some smart moves in its turnaround plans, such as shedding some noncore businesses and spinning off shares of its attractive automotive business (Mobileye); Thirdly, I highlight the booming AI semiconductor market, and Intel’s position as one of the few firms with a diverse enough portfolio to serve multiple needs in the AI revolution. Finally, Intel does have a solid balance sheet, providing the company with financial flexibility to invest in new areas and pursue growth opportunities.
Turnaround Teasing Early Fruits
To address its declining financial performance in recent years, Intel has already started to execute on a comprehensive turnaround roadmap. Specifically, Intel has also been working to push for innovation, improve its manufacturing processes and reduce costs.
With reference to innovation, Intel has been investing in new growth areas such as artificial intelligence and autonomous driving. One of the key initiatives in Intel’s turnaround strategy is its IDM 2.0 strategy, which aims to transform the company into a leading integrated device manufacturer. This involves expanding Intel’s foundry business to manufacture chips for other companies, as well as investing in new technologies such as packaging and interconnects. Moreover, Intel has also been working on improving its product portfolio, with a focus on high-performance computing and data center products. The company has launched new products such as the Xeon Scalable processor and the Optane persistent memory, specifically designed for data center customers.
In addition to these initiatives, Intel has also been working on improving its financial performance. The company has been cutting costs and improving its operational efficiency to boost profitability. One of the key aspects of the turnaround has been a focus on divesting non-core businesses and streamlining operations. For example, Intel has quite successfully spun off shares of its automotive business, Mobileye (MBLY), raising almost a billion dollars.
While the turnaround progress is notable on a product and strategy perspective, Intel’s overall cash flow profile will likely need more time to recover: During the 2023/ 2024 “investment phase”, Intel’s capital intensity is likely trending around 35% of the company’s revenue, implying Intel will have roughly breakeven free cash flow in 2023/ 2024, which is consistent with management guidance.
Intel Is Betting Big On AI
Following the AI boom sparked by OpenAI’ ChatGPT, arguably all companies are pitching to investors their AI strategy — as does Intel. What makes Intel different from most players, however, are the company’s obvious AI leverage points, in my opinion.
Referencing Intel’s AI strategy, I would like to point out that through Intel’s broad portfolio encompassing both hardware (including both fab and foundry) and software, Intel is well-positioned to render artificial intelligence more accessible and pervasive across industries and all workloads, from client and edge to network and cloud. One of the key components of Intel’s AI strategy is its OpenVINO toolkit, which provides a unified development environment for creating and deploying deep learning inference solutions across a range of hardware platforms. OpenVINO includes pre-trained models optimized for integration across operating systems and different cloud solutions, making it easier for developers to get started with AI. Moreover, Intel is also developing new hardware solutions that are optimized for AI workloads, such as the Intel Nervana Neural Network Processor (NNP), a processor which is designed specifically to accelerate deep learning training and inference. Complementing this, Intel is furthermore working on new processors that combine CPU, GPU, and NPU (neural processing unit) capabilities, such as the Intel Core Ultra processor, code-named Meteor Lake. Finally, Intel is also investing in edge-native software platforms that enable developers to build, deploy, and manage distributed edge infrastructure and applications. In that context, the Project Strata stands out, which is a modular platform that brings together an ecosystem of Intel and third-party vertical applications.
Intel’s recently held innovation day for 2023 strengthened my expectations that Intel is building its future on the importance of AI. For the majority of the event, Intel discussed AI capabilities for its client roadmap as well as within x86 servers. One of the key highlights of Intel’s AI strategy relates to Gaudi AI accelerators. Intel discussed the implied value of a large AI supercomputer that will be built on Intel Xeon processors and Intel Gaudi 2 AI hardware accelerators. In terms of AI-specific products, Intel has been developing a range of solutions for different use cases and has made progress in AI edge, which refers to AI processing that takes place on devices rather than in the cloud. This is important because it allows for faster processing and lower latency, which is critical for applications such as autonomous vehicles. Intel has also been developing a range of edge AI solutions, including the Intel Movidius Myriad X VPU, which is a vision processing unit.
Financials
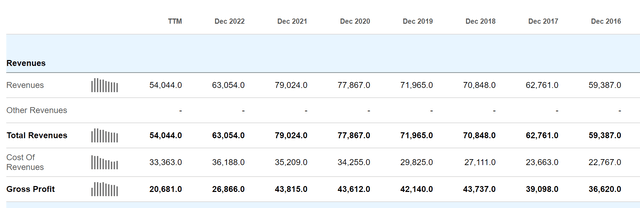
Intel’s fundamentals have started to recover only recently, and still remain strongly depressed versus pre-COVID benchmarks. For the trailing twelve months, Intel generated $54 billion in sales, which is $72 billion from cyclically adjusted pre-Covid levels, a CAGR of negative 7.3%).
Over the same period, Intel’s operating income crashed from $22.4 billion, to negative ($2.4 billion). To be fair, the loss of operating income was also influenced by higher R&D expenses, which expanded by $3.6 billion during the discussed period. However, the R&D effect is only very minor compared to the $22.4 billion operating income benchmark for 2019. The major part of Intel’s profitability loss was carried by a contraction in gross operating margin.
Seeking Alpha
As of Intel’s latest financial report, Q2 2023, quarterly group revenue was $12.9 billion, which actually exceeded consensus expectations; Intel’s gross margin for the quarter was 39.8%, which was also better than expected, reflecting continued efficient cost management; and Intel highlighted that it reduced operating expenses by 14% year-over-year. With that said, operating cash flow turned positive again, coming in at $2.8 billion. Intel closed the quarter with more than $24 billion of cash and cash equivalents, and thus felt comfortable paying a $500 million dividend to investors, despite an adjusted free cash flow of negative $2.7 billion.
Performance To Improve Again in Q3
For Q3 2023, Intel anticipates a strengthening PC market (Intel’s Client Computing Group or CCP). In the earnings call with analysts, CEO Pat Gelsinger noted that the inventories held by major clients and buyers have returned to more typical levels, indicating that customers are starting to re-enter a re-stocking phase. As a result, Intel foresees a sustained recovery during the latter half of 2023.
Notably, for Q3 management anticipates revenue to fall within the range of $12.9 billion to $13.9 billion. Even at the lower end of this guidance, this suggests an expansion in the company’s top line compared to the previous quarter. Furthermore, the non-GAAP gross margin is projected to be approximately 43%, an increase of nearly 300 basis points compared to the second quarter.
What Intel Could Be Worth?
Valuing Intel is shaky, because valuation in general is shaky, and there are many approaches that might result in a different estimate. The fact that Intel is in a turnaround process certainly doesn’t help here.
That said, I think it is fair to assume that after the restructuring, Intel will likely balance its profitability at 16-18% EBIT margin (by 2025), which would be slightly below the company’s historical performance. Now, if we apply this profitability estimate to consensus sales expectations for FY 2025 of $69 billion, according to Refinitiv, we can calculate Intel’s operating profitability for FY 2025 at $11.7 billion. This number, multiplied by a reasonable 18x EV/EBIT margin (the industry benchmark), results in a $211 billion enterprise value.
Adjusting the enterprise value with Intel’s net debt position equal to $23.3 billion would result in an implied $188 billion FY 2025 market capitalization, or a $43/ share price target (FY 2025).
Conclusion
There are arguments to be optimistic about an INTC turnaround, and share price rebound. Specifically, I note that Intel has been making some smart moves in its turnaround plans, cutting costs, and shedding some noncore businesses. Moreover, with a booming AI semiconductor market, Intel is one of the few firms with a diverse enough portfolio to serve multiple needs in the AI revolution. I calculate an implied $188 billion FY 2025 market capitalization, or a $43/ share price target (FY 2025).
Analyst’s Disclosure: I/we have no stock, option or similar derivative position in any of the companies mentioned, and no plans to initiate any such positions within the next 72 hours. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
Seeking Alpha’s Disclosure: Past performance is no guarantee of future results. No recommendation or advice is being given as to whether any investment is suitable for a particular investor. Any views or opinions expressed above may not reflect those of Seeking Alpha as a whole. Seeking Alpha is not a licensed securities dealer, broker or US investment adviser or investment bank. Our analysts are third party authors that include both professional investors and individual investors who may not be licensed or certified by any institute or regulatory body.