Summary:
- OpenAI’s recent o3 breakthrough signals massive demand for Nvidia Corporation’s inference GPUs in the coming years.
- Nvidia now has two major vectors of scaling to pull demand from, which are pre-training compute and test-time compute.
- NVDA is best positioned to capitalize on growing inference GPU demand, given its state-of-the-art technology and supply chain mastery.
- Despite Nvidia’s dominance, competition is starting to ramp up significantly as hyperscalers are starting to invest heavily in the hardware arena.
J Studios
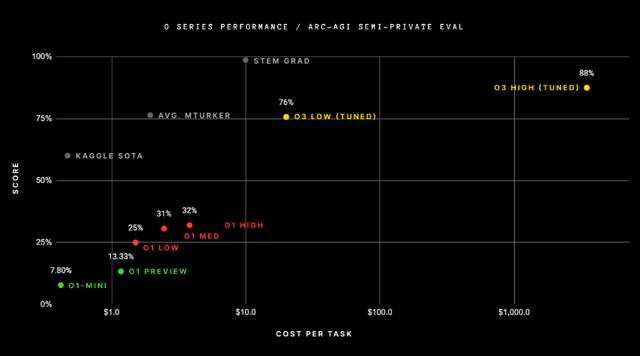
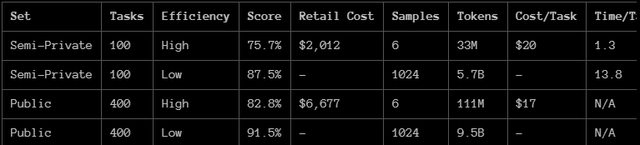
Artificial intelligence has just entered a new era. OpenAI’s reveal of the new o3 model, which delivers a shocking 75.7% score on the notorious ARC-AGI-Pub benchmark, represents a quantum leap in AI capabilities. This is not just another incremental gain, which is something we have become accustomed to after the groundbreaking release of GPT-4, but rather a revolutionary event that changes our understanding of what intelligent machines can do. For years, advanced LLMs (large language models) struggled to perform truly novel tasks. In fact, GPT-3 scored 0% on ARC-AGI’s benchmark measure of adaptability, while GPT-4 barely improved.
Almost out of nowhere, OpenAI’s o3 model shattered these assumptions and signaled that truly powerful flexible, on-the-fly reasoning is not a distant dream but a present reality. The most mind-blowing aspect of this reveal is that the o series of test-time compute models are still largely in their infancy, which means future iterations of these models will likely perform far better than even o3. However, along with this excitement comes a new challenge. o3’s breakthrough is powered by massive test-time compute.
Instead of simply training on bigger models by scaling up pre-training, o3 requires far more computational power at inference time. Each query isn’t just a quick lookup, but rather a search through enormous “program spaces,” which requires tens of millions of tokens and a staggering number of GPU cycles to solve a single complex task. This new paradigm will require exponentially more demand for inference chips and billions of dollars’ worth of additional accelerator capacity. What’s more, there is still no clear end in sight for the effectiveness of scaling test-time compute, so demand could only exponentially increase from here.
In this tectonic shift, Nvidia Corporation (NASDAQ:NVDA) emerges uniquely positioned to build the next generation of AI infrastructure. Nvidia’s GPUs have long been the gold standard for training large language models. Now, with o3 leading the charge into a future that will likely be defined by test-time compute, Nvidia’s unrivaled ability to orchestrate a complicated global AI supply chain gives it a huge strategic advantage. By delivering AI “factories” on demand, which consist of thousands of GPUs, DPUs, specialized memory, and networking gear, Nvidia has positioned itself well to supply the hardware for the unprecedented inference capacity that the o3-class models and beyond will demand.
The o3 model has absolutely shattered the previous record on the ARC benchmark.
o3: Paradigm Shift in AI Reasoning
For years, large language models have impressed us with truly advanced pattern recognition, but have performed abysmally on questions requiring true novelty. For instance, GPT-4 and other equivalent foundation models like Claude or Gemini have been able to achieve world-class results on known tasks and benchmarks, but have struggled to perform genuinely new challenges. The assumption that “bigger and bigger models” would keep translating to vastly smarter models has hit a wall.
OpenAI’s o series of models have promised that a different approach, one that involves intense test-time search, reasoning chains, and adaptive solution generation, could break through this wall. While o1’s results have been promising, it has not truly shattered expectations in the way o3’s results have. However, this new breakthrough means that inference will no longer be cheap and trivial but intensive and exploratory. Instead of running a static, prebaked model quickly at inference, OpenAI’s o3 can now orchestrate complex reasoning processes that consume a huge amount of GPU cycles per query. This implies that there will need to be increasingly large inference cluster sizes that are tuned for the “search on-the-fly” workloads.
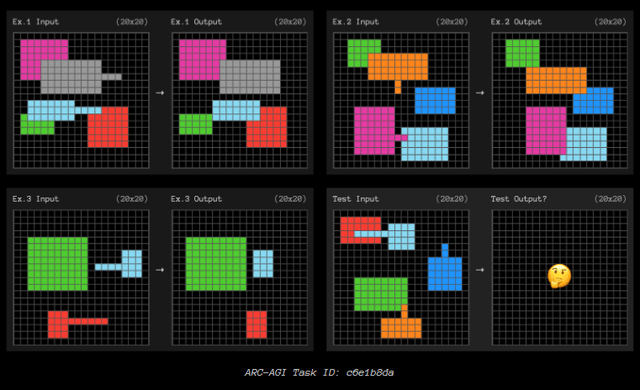
Here are some tasks in the ARC test.
Why Test-Time Scaling Matters
AI’s growth in hardware demand was historically driven by training larger language models. Once trained, these foundation models’ inference costs were relatively predictable and stable. However, o3’s success reveals that test-time compute is poised to explode. Imagine a world where every complex question triggers an incredibly elaborate and sophisticated token search spanning billions and eventually trillions of parameters. As AI gets increasingly embedded into enterprise workflows, consumer services, and even sovereign data centers, the number of such queries will likely soar exponentially.
This new paradigm has a vital component that investors should understand: test-time scaling has no obvious ceiling yet. This means that as long as users want smarter, more context-aware AI with reasoning capabilities that rival even human experts, the computational intensity for inference will keep climbing exponentially. Each generation of new models will almost certainly push this even further, thus demanding even more GPUs.
o3 was actually able to perform even better than the aforementioned 75.7% when given a longer time to “think.”
Nvidia: The End-to-End Supplier
Nvidia is currently the only company capable of meeting the explosive inference demand given its reach, relationships, and supply chain mastery. To serve this evolving landscape, it is no longer enough just to create a GPU. Rather, a company must have control of a global pipeline delivering advanced memory, high-speed networking, specialized connectors, DPUs, racks, cooling systems, and a software stack that connects all these pieces. Nvidia’s decades of ecosystem building, along with its deep supplier partnerships, give it a large strategic edge over competitors like Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). Nvidia’s strong relationship with suppliers like Micron, InfiniBand, Spectrum-X, etc., is a large reason for its supply chain advantage.
Under the test-time compute paradigm, where inference is no longer a lightweight activity, cloud providers, AI companies, and enterprises will likely race to deploy agentic AI and foundation models that rely heavily on Nvidia. They will need massive GPU clusters to handle the continuous, adaptive inference loads. Nvidia’s supply chain dominance ensures that it can stand up these data centers rapidly, at scale, and with optimal configurations. In fact, Nvidia has recently popularized the term “AI factory” to describe its ability to deliver prepackaged AI data centers. Even if Nvidia is unable to fully meet demand, it will likely still have a massive edge over competitors.
We are evolving into a world where data centers are starting to evolve into what Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang likes to call “AI factories,” or dedicated infrastructures that continuously produce and refine intelligence. Nvidia aims to be the de facto supply of these factories, which makes sense given the company’s full-stack approach. This is where its GPUs, DPUs, NVLink, Grace CPUs, software frameworks, and partner ecosystems, allow for turnkey AI factories designed to handle high compute loads like those present in o3-level test-time scaling. While competitors may be able to match individual specs of different components, none can integrate all the parts of an AI data center like NVIDIA can.
Here is a visual representation of what an “AI factory” would look like.
Riding the Scaling Curve
Key to Nvidia’s future success is the notion that scaling still has a way to go. While pre-training scaling is hitting a soft wall due to the data limit, test-time compute scaling is still in its early stages. As reasoning-centric models proliferate, there is no intrinsic reason why we won’t keep pushing for more complex reasoning per query. The productivity gains made from true reasoning models will justify the large costs associated with running such queries.
With every new model that tests the boundaries of reasoning, Nvidia is in a perfect position to supply even larger compute clusters, faster networking, and more advanced orchestration software. Even the coding layer is dominated by Nvidia’s CUDA framework, which again puts the company at a huge advantage compared to competitors.
Financial Strength Allows for Strategic Agility
Nvidia’s recent financial results were already spectacular, with the company reporting $35.1 billion in revenue during Q3 FY2025. This represents a staggering 94% YOY growth, which is unheard of for a company of its size. The test-time compute revolution, driven home by the performance of o3, will only supercharge Nvidia’s growth by expanding its total addressable market significantly. As costs per inference soar initially, Nvidia’s scale and operational prowess enable it to negotiate for better prices and continuously improve system efficiency.
Nvidia’s immense cash generation, along with the company’s liquidity and leverage in the supply chain, will allow the company to weather geopolitical storms, invest in new architectures, build data center prototypes, etc. All these activities require tens of billions of dollars and will be unreachable for the vast majority of Nvidia’s competitors, especially the smaller startups.
Major Risks Remain
Despite the positive outlook on Nvidia, the company faces some major risks moving forward. Not only is Nvidia facing far more fierce competition from traditional accelerator vendors like AMD and Intel (INTC), but also from hyperscalers like Amazon (AMZN), Google (GOOG), and Microsoft (MSFT). These cloud giants are desperately trying to get out from under the control of Nvidia, which makes sense given how much of their AI businesses are reliant on Nvidia’s GPUs. As a result, Nvidia basically has all the major tech giants and traditional accelerator vendors, putting downward pressure on its margins.
Nvidia also faces uncertain research directions. While the current trends suggest that there is no end to inference scaling, revolutionary new approaches, like more efficient model architectures or hybrid quantum-classical systems, could reduce compute intensity. If researchers find ways to drastically cut down on inference costs while maintaining o3-level capabilities, the appetite for Nvidia’s hardware could see a major downturn.
Conclusion
As o3 ushers in an era of unbounded inference scaling, the implications for Nvidia are profound. Already boasting a market capitalization of $3.2 trillion, Nvidia Corporation is poised to see even more upside as a result of the test-time compute revolution brought about by OpenAI’s new class of models. For investors, Nvidia’s role in this new paradigm is clear; no other company is better positioned than Nvidia to capture the demand growth of this revolution, as no other company has the holistic approach and state-of-the-art technologies that Nvidia possesses.
Analyst’s Disclosure: I/we have no stock, option or similar derivative position in any of the companies mentioned, and no plans to initiate any such positions within the next 72 hours. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
Seeking Alpha’s Disclosure: Past performance is no guarantee of future results. No recommendation or advice is being given as to whether any investment is suitable for a particular investor. Any views or opinions expressed above may not reflect those of Seeking Alpha as a whole. Seeking Alpha is not a licensed securities dealer, broker or US investment adviser or investment bank. Our analysts are third party authors that include both professional investors and individual investors who may not be licensed or certified by any institute or regulatory body.