Summary:
- Nvidia Corporation’s stock price has increased by 319% in one year due to the growth of large language models and AI technology.
- The company has only penetrated 3.26% of its estimated $1 trillion opportunity, indicating significant room for growth.
- It is the leading player in GPUs, data center networking, and AI software, with strong revenue growth and dominance in the market.
Justin Sullivan
What a difference a year makes. On October 13, 2022, the Nvidia Corporation (NASDAQ:NVDA) stock price hit a low for the year of $108.13, and the future for the stock looked bleak. When the company reported its second-quarter 2022 earnings, it had badly missed Wall Street analysts’ revenue guidance for the third quarter. Interest rates were still rising, and many thought a recession was likely. At the time, few were aware that everything was about to change.
In late November 2022, OpenAI released ChatGPT, one of the fastest-growing apps in internet history. The app also sparked the growth of large language models (“LLMs”), a subset of generative Artificial Intelligence (“AI”) technology. It only took a little while for many investors to figure out that Nvidia would be one of the largest beneficiaries of this new AI technology that OpenAI and Microsoft (MSFT) unleashed upon the world.
Nvidia’s closing price on October 9, 2023, almost one year later, was $452.73, up 319% from its 2022 low. The company has come a long way very rapidly, and you might wonder how much gas the stock has left when even long-time bulls have grown cautious and recommend a hold.
The answer is that it has plenty of gas. As of July 2023, the company has generated $32.681 billion of trailing 12-month (“TTM”) revenue, which, despite the company’s massive growth, has only penetrated 3.26% of an opportunity Nvidia believes is worth $1 trillion.
Nvidia second quarter FY 2024 presentation
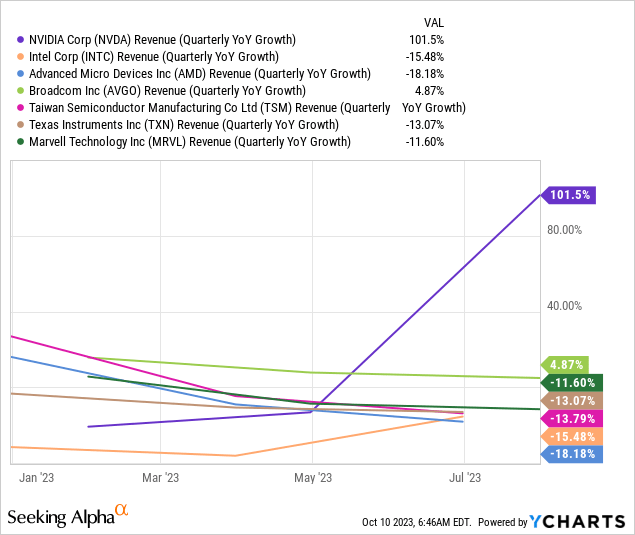
The company is a true juggernaut. It is the leading player in graphics processing units (GPUs), data center networking technologies, and AI software (CUDA software stack), all the components necessary for becoming a dominant player in building the infrastructure for accelerated computing and generative AI applications. You can see the company’s dominance in the numbers it is putting up. It recorded revenue of $13.51 billion, up 101% year over year in its second quarter fiscal year (“FY”) 2024 earnings report, beating analysts’ expectations by $2.42 billion. In contrast, its hardware peers continue to struggle during this chip industry downturn, as seen in the chart below.
Its largest segment, the data center, produced revenue of $10.32 billion, up 171% year-over-year — demand from cloud service providers and large consumer internet companies like Meta Platforms (META) is through the roof. Companies are interested in Nvidia’s HGX AI supercomputing platform, the best chipset for generative AI and LLM applications, sales of which are growing exponentially. NVIDIA’s Chief Financial Officer (“CFO”) Colette Kress said during the company’s June quarter earnings call:
Major companies, including AWS, Google Cloud, Meta, Microsoft Azure and Oracle Cloud as well as a growing number of GPU cloud providers are deploying, in volume, HGX systems based on our Hopper and Ampere architecture Tensor Core GPUs. Networking revenue almost doubled year-on-year, driven by our end-to-end InfiniBand networking platform, the gold standard for AI. There is tremendous demand for NVIDIA accelerated computing and AI platforms.
Source: Nvidia second quarter FY 2024 earnings call.
If NVIDIA does as bulls on the stock expect, it could outperform the chip industry for quite some time. Therefore, despite its high valuation and risks, this stock has become a must-have for growth investors. If you believe this company will remain the king of AI hardware and software in the long term, consider opening a position today if you don’t already own shares and consider adding if you do.
The company’s valuation and a few risks
Some investors approach investing in NVIDIA today with caution because it is far from an unknown hidden gem. Any investor familiar with technology trends has heard of this company’s dominance in AI and accelerated computing, which is why the market elevated the price-to-earnings (P/E) valuation higher than its median P/E ratio over the last ten, five, and three-year periods, as seen in the chart below.
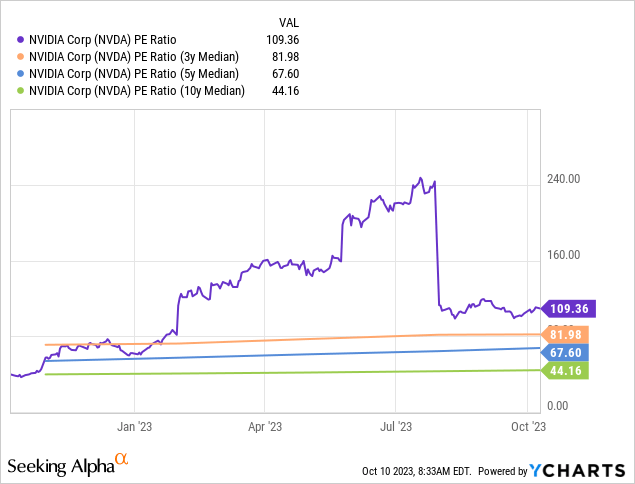
Seeking Alpha gives Nvidia an overall valuation rating of F, and the stock also grades poorly on most other valuation metrics. Considering the company’s risks, you could question its valuation and have legitimate reasons to avoid the stock.
One of the most significant concerns is supply chain risks. Specifically, Nvidia relies heavily on Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing (TSM) to produce components for its AI chips. Since most of Taiwan Semiconductor’s chip manufacturing occurs in Taiwan, Nvidia could have problems sourcing enough components from the Taiwanese company if the country has a severe conflict with China. The ensuing parts shortage would crimp its ability to manufacture AI chips, and the stock would fall like a rock from its lofty valuation. Another supply chain risk is that the demand for Nvidia’s AI chips is so high that its suppliers may be unable to provide the company with enough components to build enough AI chips to satisfy end demand.
You should also be concerned about the U.S. blocking sales of AI chips and GPUs to the Middle East and China. The company believes it could miss out on the opportunity to become an AI leader in the largest country in the world. CFO Kress said on the company’s June quarter’s earnings call:
“Over the long term, restrictions prohibiting the sale of our Data Center GPUs to China, if implemented, will result in a permanent loss and opportunity for the U.S. industry to compete and lead in one of the world’s largest markets.”
Yet, despite the risks and the stock’s perceived nosebleed valuations, investors bullish on Nvidia believe that generative AI is a long-term secular trend and that the company’s dominant position in GPUs and AI infrastructure will allow it to continue generating top and bottom-line growth above analysts’ expectations for the foreseeable future, justifying the stock’s valuation.
If you like Nvidia’s top line, you will really love its bottom line
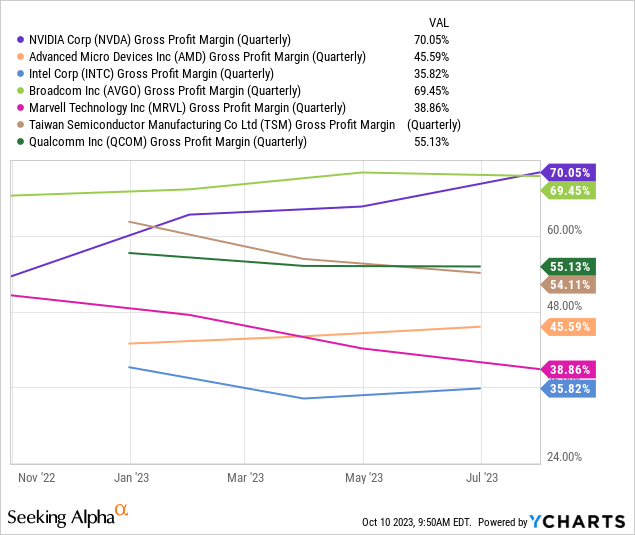
Nvidia raised its gross margins an impressive 2659 basis points from 43.5% in the June quarter of 2022 to 70.1% in the June quarter of 2023. The company credits the margin expansion to higher data center sales, driven by increased customer demand for AI and accelerated computing chips. According to Nvidia CFO Kress, these high-powered chips carry “a significant amount of software and complexity,” highlighting that chips built for AI hold a much higher value and can command higher margins than the computer chips designed for general-purpose Enterprise data center usage. The chart below shows that its 70.1% gross margin clobbers most of its chip-manufacturing peers.
Nvidia gave guidance for an increase in its gross margin to 71.5% for the third quarter. A rise in gross margin means that the company retains more capital from its sales, giving it more money and flexibility to choose between investing in growth, paying down debt, paying dividends, buying back stock, or letting the cash fall to the bottom line. In the June 2023 quarter, it chose to invest in workers by raising compensation and benefits, raising operational expenses by 6% sequentially.
In addition, it gave back around $3.4 billion to shareholders through share repurchases and cash dividends. The remaining cash fell to the bottom line, resulting in $6.88 billion in net income and $2.48 earnings per share (“EPS”), smashing Wall Street analyst EPS estimates by $0.75. As seen in the chart below, as of the June quarter, bottom-line earnings growth has accelerated significantly faster than its +100% top line revenue growth — a beautiful stock for growth investors.
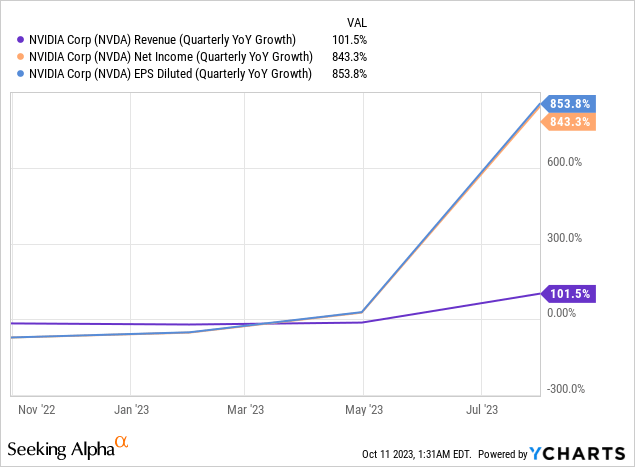
The company has a solid balance sheet, with $16.02 billion in cash and short-term investments and $9.70 billion in long-term debt. Nvidia has a high capacity to stay afloat during tough times. Last but not least, the company’s free cash flow (“FCF”) has jumped significantly since this time last year. The chart below shows that quarterly FCF jumped from around $0 last year to $6.06 billion in the June quarter this year.
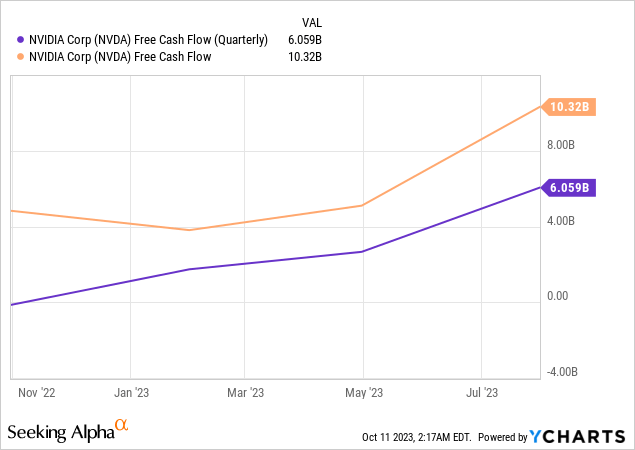
Have you ever wondered why Nvidia became one of the best-performing stocks in the S&P 500 this year? It’s because it is rare to see companies with a +$1 trillion market capitalization display triple-digit revenue and profit growth like this company has this year. Nvidia forecasts third-quarter FY 2024 revenue of $16.00 billion, implying revenue growth of 170% year-on-year if it hits its mark — utterly amazing numbers.
How long can Nvidia continue this performance?
The market has already spoken about which company has emerged as the AI infrastructure king. Its two main competitors, Intel (INTC) and Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), have data center sales that lag significantly behind Nvidia. The website Visual Capitalist cites the New York Times for estimating that Nvidia holds 70% of the market for AI chips.
Nvidia’s fundamentals and stock outperformance are directly related to its dominance in AI chips and corporate demand for AI chips. Whether the company can remain the king of AI chips and whether generative AI and other forms of AI remain in high demand or become a fad will determine whether the company can continue to put up these incredible numbers we have seen in its second quarter.
First, let’s address whether competitors can quickly remove the King’s AI infrastructure crown. While other hardware manufacturers will eventually eat away at its 70% market share in AI chips, investors should remember that Nvidia has a substantial “first mover” advantage in developing AI technology. Before Alphabet (GOOGL), then named Google, fascinated people with Alpha Go beating a human Go player in 2015, Nvidia held a GPU Technology Conference (“GTC”) in 2014 where Chief Executive Officer Jensen Huang first started talking about the importance of CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture). This computing language allows Central Processing Units (CPUs) to work in harmony with GPUs. He also discussed how companies were beginning to use GPUs for Machine Learning, Big Data Analytics, and Computer Vision. Huang’s vision for GPUs and CUDA in 2014 seems prescient today. CUDA has become a competitive advantage for the company’s GPU hardware and AI capabilities.
Even before the introduction of generative AI, analysts like John Vinh of KeyBanc argued that Nvidia deserved premium valuation because its software gave it an “impenetrable position in machine learning/AI computing.” Although there are competitors to CUDA like OpenCL, TensorFlow, PyTorch, and AMD open-sourced GPUFORT in 2021, they have yet to make substantial progress in breaching Nvidia’s moat. What makes it so hard to breach CUDA’s moat? Well, at the Goldman Sachs Communacopia & Technology Conference, NVIDIA’s Vice President of Enterprise Computing Manuvir Das made an interesting comment that points out why many hardware companies face challenges dislodging CUDA:
I had my first conversation with Jensen, who is the CEO of a chip company, and all he would talk to me about was developers. And I really didn’t get it. And then I watched his keynote at GTC Conference from the previous year. And here’s the CEO spending 3 hours talking about use case after use case of accelerated computing that developers can embrace and build applications for. And it was an eye-opening thing for me. And I guess what I realized was — at the time was this company had this vision that there’s a new form of computing coming, accelerated computing, but it’s not a free thing. You don’t just take applications and move it to accelerated computing. You have to work on it one domain at a time. And that means you need developers to embrace it.
Source: Goldman Sachs Communacopia & Technology Conference.
Das went on to say, “It’s not about the chips, it’s about the whole [technology] stack.” Nvidia puts just as much time into software as its hardware and builds to the needs of its primary customer, the developer. Today, Nvidia has a strong developer community of at least four million, providing a networking effect moat for CUDA and its GPU hardware that is difficult to breach. The company doesn’t just rest on its laurels either. It constantly updates CUDA with new features. It released its last major update, CUDA 12.0, in December of 2022, which includes extensive support for its latest chips.
In addition, the company’s hardware is nothing to sneeze at, either. When the online publication tom’s Hardware compared Intel, AMD, and Nvidia’s AI solutions side by side in January of 2023 to determine which GPU offered the fastest AI, Nvidia destroyed the competition. Its intense focus on solving developer problems, instead of only trying to sell a piece of hardware or software, makes the company difficult to compete against. While competitors may eventually breach its moat, provide a competitive solution, and take market share away from Nvidia, it is hard to argue that will occur any time soon.
Another fascinating factoid is that although cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform manufacture hardware for their internal use, they are buying Nvidia H100 Tensor Core GPUs like hotcakes. The website Tom’s Hardware cites an article by the Financial Times that the demand for the H100 is so high that they are sold out deep into 2024 and that Nvidia plans to triple production next year to keep up with the demand. This insane demand for AI chips brings up the second factor in Nvidia’s ability to continue its tremendous performance.
Suppose generative AI proves much less beneficial for companies than the hype suggests; demand for Nvidia’s AI chips could drop like a rock — a terrible scenario for those who choose to invest in this company. However, while it’s still early and still in the testing phase, the evidence so far suggests that companies are finding generative AI helpful. According to a CNBC survey, “47% of top technology officers across the economy say that artificial intelligence is their number one budget item over the next year.” Statista is bold enough to predict generative AI will grow at a compound annual growth rate of 24.40% between 2023 and 2030. If the demand for AI remains that high or even accelerates and Nvidia remains the king of AI infrastructure, it could move up from its position as the fifth highest market cap to challenge Microsoft and Apple (AAPL) for the top position.
Don’t miss this fantastic opportunity
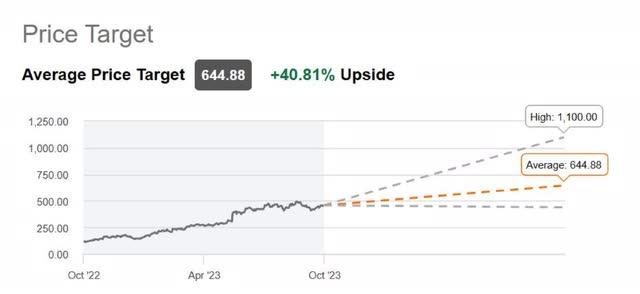
Although Seeking Alpha analysts have collectively placed a Hold on the stock due to its high valuation and risks, Wall Street analysts think differently and maintain a Strong Buy. As of October 10, 2023, the average Wall Street price target was $644.88, implying a 40.81% upside.
If you are a growth investor not scared off by stocks with high valuations, you should take the time to do your due diligence on Nvidia and consider buying this stock today.
Analyst’s Disclosure: I/we have no stock, option or similar derivative position in any of the companies mentioned, but may initiate a beneficial Long position through a purchase of the stock, or the purchase of call options or similar derivatives in NVDA over the next 72 hours. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
Seeking Alpha’s Disclosure: Past performance is no guarantee of future results. No recommendation or advice is being given as to whether any investment is suitable for a particular investor. Any views or opinions expressed above may not reflect those of Seeking Alpha as a whole. Seeking Alpha is not a licensed securities dealer, broker or US investment adviser or investment bank. Our analysts are third party authors that include both professional investors and individual investors who may not be licensed or certified by any institute or regulatory body.