Summary:
- QUALCOMM is facing deteriorating revenue growth and profit margins.
- Recent stock price surge is not justified by the company’s fundamentals.
- I illustrate the trend in company’s fundamentals, discuss the challenges that face the company, and suggest an entry price based on its current valuation.
Frank Brennan
While QUALCOMM (NASDAQ:QCOM) has been a major player in wireless technology for decades since the company’s bet on Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) in late 1980s and CDMA’s adoption by the U.S. Telecommunications Industry Association as a cellular standard in 1993, it’s time for investors to reevaluate the company’s prospects amid mounting headwinds.
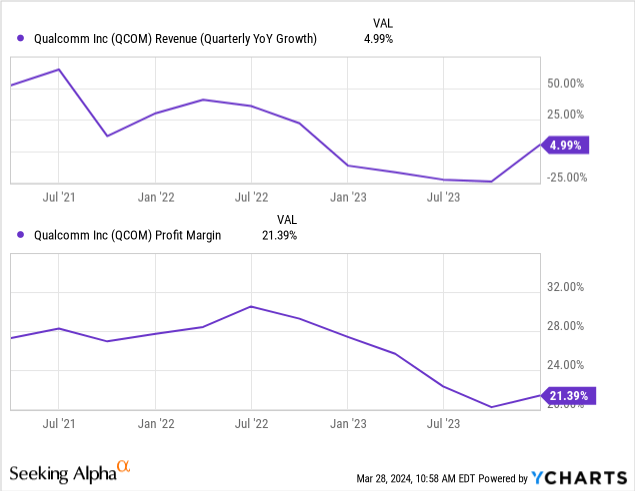
Deteriorating Revenue Growth and Margins
In recent years, Qualcomm has faced declining revenue growth rate and profit margins, as the following chart and charts later in this article illustrate:
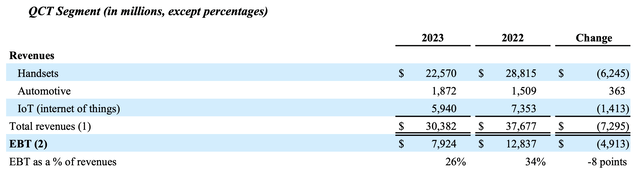
The deterioration in the company’s fundamentals is primarily due to the slowdown in the global smartphone market. Weakening consumer demand for smartphones has directly impacted sales of Qualcomm’s mobile chipsets, which have historically been a major revenue driver. The following table included in Qualcomm’s Form 10-K presents the year-over-year drop in Handsets revenues, followed by related management commentary:
Qualcomm management added in the same SEC filing that:
The decrease in QCT revenues in fiscal 2023 was primarily due to lower handset revenues, primarily driven by $7.9 billion in lower chipset shipments to certain major OEMs.
Additionally, increased competition from MediaTek, Samsung, and others has driven Qualcomm to adjust pricing strategies for Snapdragon processors, as heralded by DigiTimes’ sources at the end of 2022:
Qualcomm is likely to cut prices for its mid-range and entry-level Snapdragon mobile phone processors, including the 400 and 600 series, in 2023, according to market sources.
MediaTek’s rise is likely to continue to pressure QCOM’s pricing and margins in the coming periods, as its new Dimensity 9300 comes with respectable specs:
- High-performance 8-core CPU
- 12-core Arm Immortalis GPU for premium gaming
- Enhanced ISP for video/audio processing and noise cancellation
- Supports 4K HDR video
- Dedicated APU for Large Language Model and Generative AI support
- Integrated security processor subsystem for secure boot and OS functions
- Advanced 5G modem (Release 16) on a separate chip
- Next-generation WiFi 7 capability
While trailing behind Qualcomm’s latest Snapdragon offerings in raw power, MediaTek’s Dimensity 9300 brings advanced capabilities that position them as a challenger in the high-end smartphone market, offering smartphone OEMs an alternative for diverse market requirements and product differentiation, and likely pressuring Qualcomm’s Snapdragon pricing and margins in the future.
Even though MediaTek’s rise is a primary risk to Qualcomm investors, the magnitude and varied nature of the competitive threats to Qualcomm is not appreciated by market participants, so I dig into it further in the next section.
Intensifying Competition
The following list illustrates the intense competition Qualcomm faces across multiple business segments:
Chipset Market
- MediaTek (OTCPK:MDTTF): A major rival in the mobile chipset space, known for cost-effective solutions across mid-range and budget smartphones. They’re gaining traction even in higher-end market segments.
- Samsung (OTCPK:SSNLF): While Samsung primarily uses its in-house Exynos chips for its own phones, it also competes with Qualcomm in certain markets.
- Apple (AAPL): With the development of its A-series and M-series chips, Apple has become increasingly self-reliant on its iPhones, iPads, and Mac computers, substantially reducing its reliance on Qualcomm in recent years.
- Google (GOOG): The company’s Tensor chips, used in Pixel phones, pose a growing in-house competition threat.
Automotive
- Intel/Mobileye (INTC): Intel has strong ambitions in the automotive sector with its Mobileye (MBLY) business, focusing on autonomous driving technology.
- NVIDIA (NVDA): NVIDIA’s automotive platforms and AI expertise make it a formidable competitor in connected car systems and self-driving solutions.
- NXP Semiconductors (NXPI): A major player in traditional automotive chips, NXP poses significant competition to Qualcomm in this market.
Internet of Things
- Broadcom (AVGO): Offers a variety of connectivity chips for IoT applications.
- Texas Instruments (TXN): A diverse semiconductor player with offerings in the IoT space.
- Silicon Laboratories (SLAB): Specializes in low-power wireless solutions for diverse IoT use cases.
Impact on Qualcomm’s Fundamentals
Qualcomm has seen declining profit margins in recent periods. Specifically, QCOM’s gross profit margin has declined from 60 percent to 55.5 percent in the last three-year period, its operating margin has dropped from 35 percent in Q3 2022 to 22 percent in Q4 2023, and its net profit margin has also deteriorated substantially in the same period.
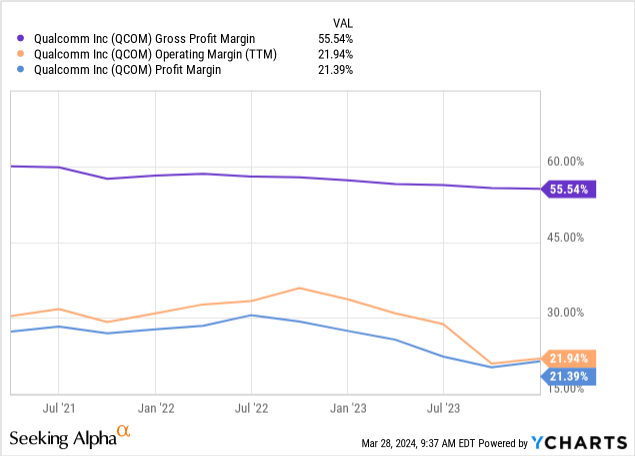
What I’d like the readers to take away from the above graph is that the deterioration in the company’s fundamentals is not contained in just one line item, but it shows up across the company’s income statement from revenue growth to all profit margins, including gross, operating, and net margins.
Pressure from intensifying competition is not the only risk facing Qualcomm in the coming periods, as I discuss the regulatory risk in the next section.
The Licensing Model Under Fire
Qualcomm derives substantial revenue from its extensive patent portfolio; however, this lucrative licensing business model attracts persistent legal challenges and regulatory scrutiny. Smartphone makers and regulators alike accuse Qualcomm of engaging in anti-competitive practices, demanding exorbitant royalties, and using its market dominance to enforce restrictive licensing deals.
Two major legal battles highlight the severity of challenges Qualcomm faces:
- The Federal Trade Commission Lawsuit: In 2017, the FTC filed suit against Qualcomm, alleging a monopoly in wireless chips. They accused Qualcomm of forcing exclusivity deals onto customers like Apple and of excessive licensing fees built on a “no license, no chips” policy. The outcome of this case resulted in a court-ordered restructuring of Qualcomm’s licensing practices.
- Apple’s Legal Battle: Apple and Qualcomm engaged in a protracted multi-year legal war over licensing agreements. In 2019, they reached a settlement including a payment from Apple to Qualcomm and a six-year licensing agreement. The settlement included a one-time payment from Apple of about $4.5 to 4.7 billion.
These high-stakes cases aren’t isolated incidents. Qualcomm has faced similar challenges across the globe, including billion-dollar fines in South Korea and the European Union. The ongoing onslaught of lawsuits creates substantial uncertainty for Qualcomm, threatening to destabilize its income stream.
Qualcomm continues to navigate a treacherous legal landscape. While the company undoubtedly possesses a substantial patent portfolio, the value of those patents diminishes if its licensing model cannot withstand ongoing antitrust scrutiny. Qualcomm’s success depends on finding a balance between fair licensing practices and maintaining profitability, a balance that antitrust regulators and industry rivals are determined to reshape across tech sector.
AI Boom May Not Benefit Qualcomm
While AI is likely to drive innovation across industries in the coming decades, Qualcomm might not be the primary beneficiary. Chip giants like NVIDIA and others specializing in AI-specific hardware hold an edge in the rapidly growing AI market, potentially leaving Qualcomm behind in this crucial race.
I believe that the Artificial Intelligence theme is making its waves through various stocks, and I’ve been covering the sector in my recent articles and have discussed the red flags I see from extreme sentiment and recent insider selling at Nvidia to low margins and intensifying competitive threats at AMD, to elevated supplier and customer credit risks at Super Micro. I recommend reading those three articles as well for a full picture of my skepticism on the theme. If you have any feedback for me or would like to ask any questions, I’m active daily in the comments sections below my articles, and I’d love to learn from you.
Valuation Concerns
Despite these headwinds, Qualcomm’s valuation as measured by the price-to-sales ratio remains relatively high compared to recent years:
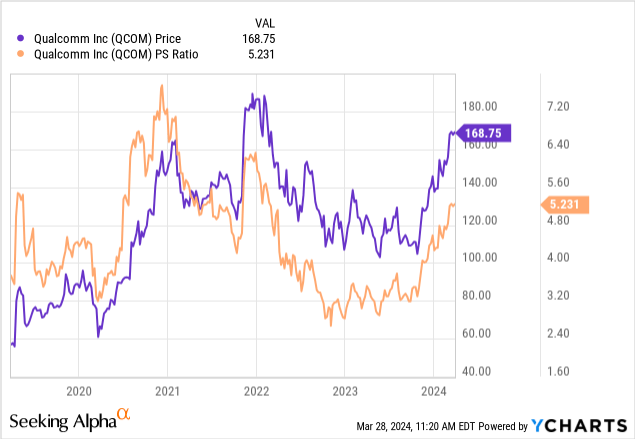
Qualcomm’s price-to-sales valuation multiple has neared the higher end of its five-year range, which could mean that market participants are pricing a potential expansion in the company’s profit margins. QCOM’s historical and forward price-to-earnings ratios are similarly at the high of historical ranges:
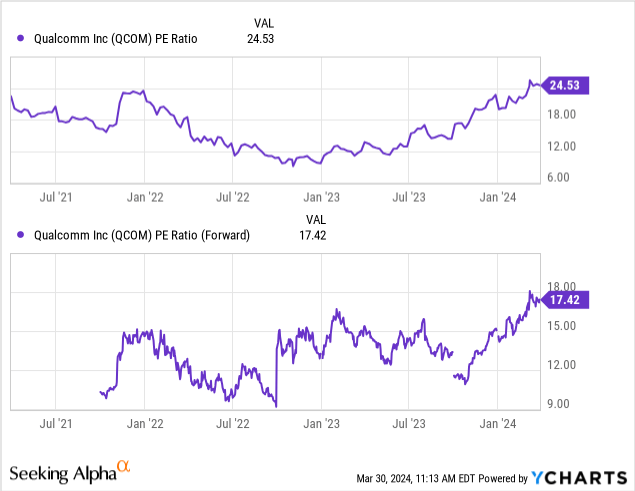
Given the significant and varied competitive threats, however, I believe that this optimism is premature. I recommend that potential investors wait for a reversion to the mean in the company’s valuation multiples that would indicate a 20 percent pullback in the stock price to $135 per share before initiating a position or adding to their existing positions, but this pullback is not large enough to justify a sale of existing positions and incurring potential taxes and fees as a result of the sale.
Risks to My Thesis
I note three reasons why QCOM could potentially outperform the stock market indices in the coming periods:
- Diversification into new growth markets: Qualcomm is actively expanding beyond its traditional smartphone chip business into promising areas. This includes automotive, the Internet of Things (IoT), and even the metaverse. Successful expansion into these markets could fuel substantial revenue growth;
- Licensing revenue potential: Qualcomm’s vast patent portfolio related to wireless technologies generates significant licensing revenues. As 5G adoption grows worldwide, this revenue stream promises to become even more lucrative with higher royalty payments connected to 5G devices;
- Rebounding smartphone market: While the smartphone market experienced a slowdown recently, Apple’s upcoming Worldwide Developers Conference this summer could refuel excitement and demand for the iPhone, which continues to use Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 5G modems.
Bottom line
While Qualcomm undoubtedly has a legacy of innovation, the mounting challenges it faces paint a worrisome picture for investors. Stagnating smartphone sales, relentless competition squeezing margins, regulatory crackdowns on its licensing revenue, and the potential to be left behind in the AI boom all converge to cast a long shadow over Qualcomm’s future. Its current valuation appears optimistic, disregarding the gravity of these threats.
While the company’s efforts to diversify into new markets may eventually yield success, these ventures are unlikely to produce substantial returns quickly enough to offset the deteriorating fundamentals in the near term.
I rate the stock HOLD and will update my analysis in future articles.
Analyst’s Disclosure: I/we have no stock, option or similar derivative position in any of the companies mentioned, and no plans to initiate any such positions within the next 72 hours. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
Seeking Alpha’s Disclosure: Past performance is no guarantee of future results. No recommendation or advice is being given as to whether any investment is suitable for a particular investor. Any views or opinions expressed above may not reflect those of Seeking Alpha as a whole. Seeking Alpha is not a licensed securities dealer, broker or US investment adviser or investment bank. Our analysts are third party authors that include both professional investors and individual investors who may not be licensed or certified by any institute or regulatory body.