Summary:
- China plays a crucial role in Tesla’s success, accounting for a third of its global deliveries in the first three quarters of 2023.
- The Chinese EV market is becoming increasingly competitive; over 15 new models are set to compete with Tesla’s Model 3 and Model Y, offering competitive pricing and advanced features.
- Tesla’s market share in China is declining, and its recent Model 3 upgrade failed to significantly attract customers, highlighting the need to balance innovation with customer preferences.
- The current Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio of 77 does not seem to support a scenario of single-digit total revenue growth or a declining market share in China.
- The U.S. EV Market is growing, but not growing as fast as before.
Xiaolu Chu
Tesla’s (NASDAQ:TSLA) success hinges significantly on the Chinese market. In the first three quarters of this year, approximately 430,000 of Tesla’s deliveries were in China, accounting for a third of its total global deliveries. China’s pivotal role in the global electric vehicle (EV) landscape cannot be overstated. It serves as a dynamic and open arena where the world’s foremost EV manufacturers compete fiercely. This competitive environment is crucial for companies like Tesla, as it serves as a test for their product competitiveness. A loss in market share in this market could indicate a weakening of Tesla’s product competitive advantage. This scenario might not only affect Tesla’s standing in China but could also foreshadow a more balanced and competitive playing field in other international markets in the future.
2024: A Wave of Competitively Priced Vehicles Rivals Tesla’s Offerings
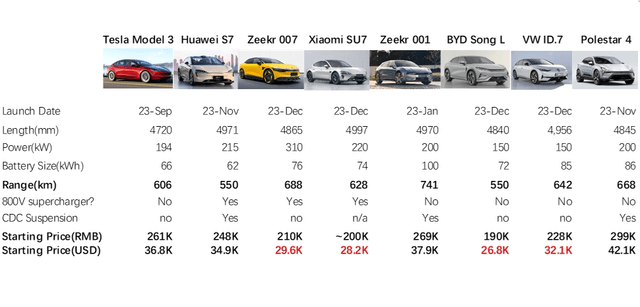
2024 is shaping up to be an unprecedentedly competitive year for EV manufacturers in China. The market entries and recent launches by key players such as Huawei, Zeekr, Xiaomi (OTCPK:XIACF), Li Auto (LI), Nio (NIO), and BYD (OTCPK:BYDDY) are significantly intensifying the competitive landscape. This surge in competition presents formidable challenges to Tesla’s established market share status, signaling a potential shift in the industry dynamics. A side-by-side comparison with Tesla’s Model 3 reveals that many of these new models excel in critical areas such as pricing, driving range, vehicle size, and advanced technological features. Notably, these competitors offer innovations like 800v fast charging, continuous damping control, and smart headlights — features that are currently not available in Tesla’s Model 3 or Model Y.
This escalation in competition marks a significant shift in the market, where features and pricing are emerging as increasingly decisive factors in consumer choice. The importance of brand reputation is diminishing in comparison to previous years, especially since none of the six brands mentioned earlier – Huawei, Zeekr, Xiaomi, Li Auto, Nio and Polestar (PSNY) – are considered weak brands. This change indicates a more level playing field where product offerings and value for money are key to consumer favor. Tesla, therefore, faces the challenge of not just maintaining its technological edge but also adapting to a market that is rapidly evolving in terms of consumer expectations in price and feature sophistications.
Over 15 models from some of the most competitive brands, including Zeekr, Xiaomi, Huawei, Li Autos, Volkswagen, Nio, Polestar and BYD are poised to challenge Tesla’s Model 3 and Model Y. Below is a summary of the most competitive models from these companies, along with their pricing, providing a snapshot of the intense competition Tesla will encounter:
- Zeekr’s aggressive pricing strategy, particularly with the Zeekr 007 priced at 210,000 RMB ($31,700), makes it a formidable competitor against Tesla’s Model 3. Its larger body size, increased battery capacity, greater range, and lower pricing collectively offer greater value. Geely Group’s diverse 2024 lineup, including six models: the upgraded Zeekr 001, Zeekr 007, Zeekr CX1E, Polestar 4 (PSNY), Lynk & Co 07 (PHEV), Lynk & Co e371 (EV). This broad range signifies a strategic approach that could notably shift EV market dynamics and pose challenges to competitors. The blend of variety and affordability in Geely’s strategy is set to potentially transform the competitive landscape.
- Xiaomi, recognized for its competitive pricing, is expected to launch its debut EV model at a starting price of 200,000 RMB ($26,800), offering a lower-cost alternative to Tesla’s offerings. Having invested $1.5 billion in R&D and assembled a 3400-strong engineering team, including designers from BMW’s IX and Z4 series, Xiaomi’s first EV boasts a larger body and longer range than the Tesla Model 3. Unlike Tesla’s minimalist design, Xiaomi retains traditional car features like physical shifters, buttons, and visible door handles. Xiaomi’s integrated ecosystem, linking phones, cars, and home appliances, could appeal significantly to its existing customer base.
- Huawei has rapidly become a mainstream car brand. The Huawei AITO M7 impressively garnered 50,000 orders in just 50 days, and it now boasts around 5,000 weekly deliveries. Its latest models, the M9 and S7, have each achieved over 20,000 orders within 10 days post-launch. The forthcoming upgraded M5 is positioned to rival Tesla’s Model Y, with a more affordable starting price. Notable features of Huawei’s EVs include their own Continuous Adaptive Control (CDC), autonomous driving technology, smart headlights, and an in-house operating system. Similar to Xiaomi, Huawei’s integrated ecosystem of phones, cars, and home appliances could effectively appeal to its existing customer base.
- Volkswagen faced a decline in China in 2023, with VW Shanghai sales dropping about 16% in the first half of the year, and even more concerning was an 81% decline in profit. Volkswagen’s ID.7 is its strategic response to regain market share in China, adopting an ultra-low pricing strategy. Despite its size of 4900mm and a battery capacity of 85kWh, both indicative of higher production costs, the ID.7 is priced at only $32,000.
- Li Auto plans to launch its most affordable SUV in the first half of 2024, the L6, likely priced at around 270,000 RMB (or $38,000), which is the same starting price as Tesla’s Model Y. Additionally, Li Auto is set to launch its EV model M7 in 2024, which could also compete with Model Y.
- Nio is gearing up to launch two models under its secondary brand, aiming to price these vehicles at approximately 250,000 RMB and 180,000 RMB respectively. These models will feature 800v fast charging and battery swap technology, with batteries that are expected to be thinner than those in current Nio models. The first of these models is estimated for release around June of 2024.
Table 1 – Tesla Model 3 vs. China’s Latest EV Competitors
Decline in Upgraded Tesla Model 3 Sales and Tesla’s Shrinking Market Share in China
When Tesla launched its upgraded Model 3 in October, expectations were high. However, recent sales data from China in the weeks following the late October 2023 launch, paints a less optimistic picture. Since the week of November 5, 2023, the Model 3’s sales have been on a downward trajectory(as it is shown in the chart below). This decline is noteworthy, especially since this upgrade was the first major one. Yet, it failed to significantly surprise or attract customers, leading to stagnant sales growth.
One key reason for customer reluctance towards the new Model 3 is the absence of traditional features like a physical gear shifter or blinker. This shift, though innovative, may have inadvertently distanced a portion of Tesla’s customer base. Such a scenario underscores a pivotal challenge in the automotive sector: the need to balance groundbreaking innovation with the expectations and preferences of customers.
Compounding this issue is the Model 3’s pricing, which is approximately 20,000 RMB higher than what many customers anticipated. This price point reveals a significant aspect of the Chinese market: its sensitivity to price.
Figure 1: Tesla’s Weekly Deliveries in China
China Passenger Car Association (CPCA) 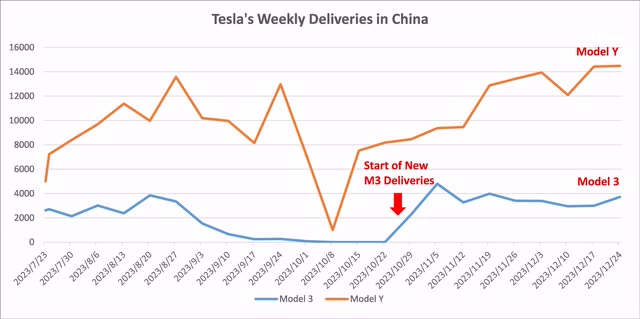
Tesla does not have as strong a moat as Apple, as demonstrated by its market share in China. Apple holds a 14.2% share in the Chinese smartphone market as of Q3 2023, whereas Tesla has approximately an 8% share in new energy vehicles (EVs and plug-in hybrids combined) in the first three weeks of December 2023, per the data from China Passenger Car Association. This is partly because cars rely less on an ecosystem of an operating system, and there are a larger number of competitors. Notably, Tesla’s market share has declined from 10% in the first half of 2023, peaking at 14% in March, to 8% in November or the first three weeks of December. This trend is a significant concern for Tesla investors.
Figure 2: Comparison of Tesla and Total New Energy Vehicles Monthly Deliveries in China
China Passenger Car Association (CPCA) 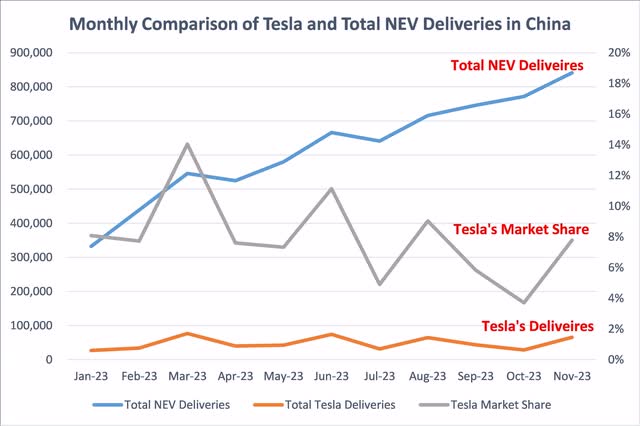
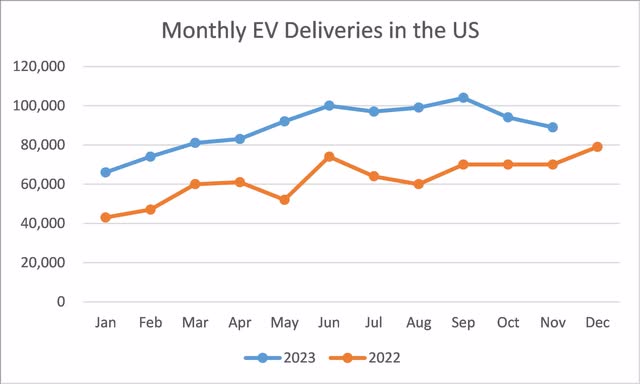
The U.S. Market is Growing, but Not Growing as Fast as Before
While the total market deliveries for electric vehicles continue to rise, there has been a noticeable deceleration in this growth over the recent two-month period. This slowing momentum can be attributed to a confluence of factors, including product fatigue as consumers become accustomed to existing models without significant new innovations to stimulate demand. Additionally, a downturn in oil prices has made traditional fuel-powered vehicles more economically attractive to some consumers, which may also be tempering the growth trajectory of EV sales.
Figure 3: Monthly EV Deliveries in the US
What Is The Risk of Tesla’s Short Thesis
The short thesis for Tesla centers on heightened competition and a declining growth trend, as well as high valuation. However, there are risks to shorting Tesla, notably its potential expansion into new areas leveraging its chip-making and AI capabilities. Tesla might excel in future segments like robotics and smartphones, although their release or official launch is uncertain for 2024.
- Expansion into Robotics: Tesla’s confirmed development of the Optimus Robot represents a significant potential expansion of its technology portfolio. The robot, designed to perform a variety of tasks, could open new revenue streams in automation and artificial intelligence. It is said that the Tesla Optimus Gen-2 is expected to arrive between 2025 and 2027.
- Expansion into Smartphones: Tesla’s prowess for innovation has led to rumors about its potential expansion into consumer electronics with a Tesla-branded smartphone. Although the company has not confirmed these rumors and they have not been addressed in earnings calls, the persistent buzz underscores the market’s curiosity about Tesla’s brand extension capabilities. It is noteworthy that other EV makers, including NIO and Geely, have confirmed their ventures into smartphone production to improve user experience with their vehicles.
Tesla’s Valuation of 77 P/E Is Not Supported
Tesla’s position in the ‘Magnificent 7’ emphasizes its unique market challenge in China’s EV sector, with a 9% market share that contrasts sharply with other industry leaders. This situation reflects the EV market’s fragmented nature, similar to the broader automotive industry, where even leaders like Toyota only hold a modest global share. Despite Tesla’s potential in emerging areas like robotics or smartphones, no confirmed product launches in these segments are planned for 2024.
From a quantitative perspective, Tesla is trading at a P/E ratio of approximately 77, experiencing single-digit revenue growth and negative adjusted income growth in the previous quarter. The company also failed to meet Wall Street expectations, with earnings reported at 66 cents per share adjusted, versus the expected 73 cents, and revenue at $23.35 billion against the anticipated $24.1 billion. Such stretched valuations could pose a risk to its stock price if the weakening growth trend continues into 2024, which, according to previous analysis, is very likely.
In summary, this short thesis for Tesla posits that the company’s challenges in the highly competitive Chinese EV market, combined with its stretched valuation and slowing growth, present significant risks for investors. Tesla’s declining market share in China, in the face of formidable competitors offering more advanced and affordable models in 2024, indicates potential difficulties in maintaining its competitive edge. Additionally, high investor expectations reflected in Tesla’s P/E ratio are at odds with its current financial performance, suggesting a possible overvaluation and making it a potential short target for investors wary of these emerging market dynamics.
Analyst’s Disclosure: I/we have a beneficial short position in the shares of TSLA either through stock ownership, options, or other derivatives. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
Seeking Alpha’s Disclosure: Past performance is no guarantee of future results. No recommendation or advice is being given as to whether any investment is suitable for a particular investor. Any views or opinions expressed above may not reflect those of Seeking Alpha as a whole. Seeking Alpha is not a licensed securities dealer, broker or US investment adviser or investment bank. Our analysts are third party authors that include both professional investors and individual investors who may not be licensed or certified by any institute or regulatory body.