Summary:
- Despite strong technological advantages and resilient and robust business growth throughout 2023, JinkSolar faces many challenges, including bearish sentiment towards the Chinese economy and renewable energy, as well as weak cash.
- Rated “Hold” with a target price of $32 per share, waiting for catalysts such as business consolidation, improvement in cash flow management, and positive macroeconomic factors.
- Key catalysts to watch for include JinkoSolar’s Q4 2023 and annual reports, potential interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve Bank, and Chinese economic data updates.
Editor’s note: Seeking Alpha is proud to welcome Long Hang Cheng as a new contributor. It’s easy to become a Seeking Alpha contributor and earn money for your best investment ideas. Active contributors also get free access to SA Premium. Click here to find out more »

zhongguo/E+ via Getty Images
Introduction
Despite impressive revenue growth and cutting-edge technology from JinkoSolar Holding Co., Ltd. (NYSE:JKS), its value is discounted due to economic headwinds in China, poor market sentiment in the renewable energy sector as well as negative cash flows. For the reasons above, I rate JinkoSolar as “Hold” with a target price of $32.
JinkoSolar Holdings Limited is a solar module manufacturer based in Shanghai, China that specializes in the design, production, and distribution of solar modules, as well as solar system integration and development. The company operates and generates sales in all major regions, such as China, Europe, Asia Pacific and the United States, displaying its global clientele. Over the past 5 years, the company’s revenues and gross profit experienced 27.1% and 28.4% compounded annual growth, establishing itself as one of the largest players in the Chinese solar module manufacturing industry and topping the charts in 2023 as it boasts the largest shipment of solar modules throughout Q1-Q3 according to Solarbe.
Despite the supposed growth of the company, the share price fails to reach a consensus as it edges down to $27.17 as of February 16th, a steep -47.80% drop from its share price one year ago. While this may be attributed to broader macroeconomic factors that play against growth in JinkoSolar’s share price, its financials tell a story that to an extent validates the uncertainty and conservatism regarding the company. I will proceed to establish the mix of positive and negative conditions and indicators that led me to the decision of rating it as “Hold”.
Solar Energy in China
Over the past 3 years, the revenue of JinkoSolar per region has seen increases across the board, achieving 76.1%, 61.7%, 5.5% compounded annual growth in China, Europe and APAC respectively, with the exception being a compounded annual decrease in the United States due to regulations imposed by the United States (US) government such as anti-dumping policies and tariffs as well as geopolitical tensions. This has led JinkoSolar to funnel its efforts into establishing its roots domestically as the company’s business in China grew from accounting for a mere 18.1% of revenue in 2020 to 41.9% in 2022.
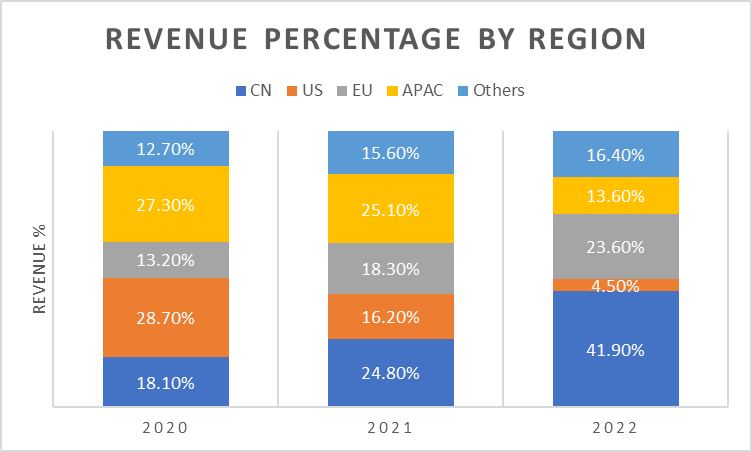
Fig 1. Author’s illustration, based on data from “JinkoSolar 2022 Annual Report”
Taking a closer look at the Chinese solar industry which accounted for 41.9% of JKS’s revenue in 2022, despite a slower-than-expected post pandemic recovery for the Chinese economy, China’s political direction is steadfast in pursuing the transition towards clean energy. With reference to the China Electricity Council’s publications, China’s solar capacity has experienced exponential growth over the past 10 years, achieving 57.4% compounded annual growth, rising from 4.2GW to 392.61GW over the specified timeframe. Additionally, according to government data and S&P Global Commodity Insights forecasts, solar energy as a component of China’s total energy generation is forecasted to experience further growth, overtaking coal in terms of installed capacity for power generation in China by 2035 and claiming up to 50% of capacity by 2050. This positions JKS for significant opportunities to capitalize on the increasing demand for solar energy solutions.
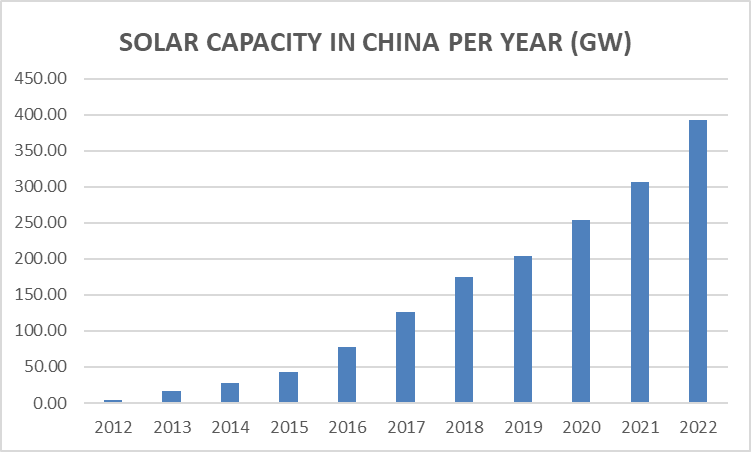
Fig 2. Author’s own illustration, based on data from China’s National Energy Administration
Technological Position
According to research conducted by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL)’s latest publication “Best Research-Cell Efficiency Chart (Version 63)”, JinkSolar leads the market in the research-cell efficiency of multicrystalline silicon cells, reaching record heights of 23.3% with its competitors Canadian Solar as well as Trina Solar both being at approximately 21.2%. Despite leading research in multicrystalline silicon cells, LONGi Group’s conversion efficiency in silicon heterostructure cells as well as perovskite/silicon tandem looms over at 26.8% and 33.9% respectively. It is worth noting that perovskite solar cells have exceptionally high-energy conversion due to its chemical properties but comes at the cost of containing toxic materials that may raise problems during disposal. Until a solution for the disposal of perovskite solar cells emerges, it is not likely that the hyper-efficient cell will become mainstream.
With strong competition in the form of LONGi Group as well as Trina Solar and Canadian Solar, JinkoSolar differentiates itself from its competition due to having in-house research and development (R&D) over the entire value chain instead of outsourcing intermediate production to third-party firms. This means the company innovates their research findings for each stage of production, from ingot to wafer to cell and finally to module. This complete ownership ensures that each component’s function fully contributes to the efficiency and overall technological direction of their final product, resulting in market-leading conversion efficiency and thus cutting itself a technological edge.
Moreover, the strategic in-housing of their value chain carried a significant role in their product transformation from p-type to the superior n-type solar cells, with the latter being more resistant to light-induced degradation as well as costing less than the former. In-house supply enables agile changes as well as tighter coordination between departments, leading to a swifter implementation of technological advancements derived from R&D. JinkoSolar’s focus on n-type TOPCon technology is expected to continue driving its market share and dominance in the coming years.
Market Sentiment Towards Renewable Energy
In 2023, the S&P Global Clean Energy Index fell by more than 30%, revealing a broadly negative sentiment towards the renewable energy sector. Given the Federal Reserve Bank’s interest rate hikes from 2022-2023 as a means to cool down inflation in the United States, capital heavy industries such as solar module manufacturers (as well as renewable energy in general) took the brunt of an increasing cost of capital. Such narratives led bearish speculation towards the entire solar module manufacturing industry as the share price of JinkoSolar and their competitors edged downwards over the 2023 calendar year.
Economic Headwinds
Headquartered in China, it comes to no surprise that JinkoSolar suffers from economic headwinds faced by the broader post-COVID Chinese economy. As the annual growth of real GDP grinded to a slow 3% in 2022, it has climbed its way back up to 5.2% in 2023, a slower than expected recovery. This is in part due to the series of credit default risks by large property developers in China, namely Evergrande and Country Gardens, with the former undergoing liquidation in January 2024. Consequently, Chinese consumers with their life savings held in property experienced a drastic reduction in accumulated wealth, fostering a cautious environment for consumption and thus slowing the recovery.
Paired with 4 consecutive months of sub-50 PMI, popular economic indicators illustrate a Chinese economy with weak demand and contracting factory activity, which undoubtedly raises negative sentiment indiscriminately towards Chinese companies and JinkoSolar is no exception. However, it is important to note that the January PMI may not be wholly indicative of China’s production activity as workers return to their hometown to prepare for Chinese New Year celebrations that occur in February this year.
Financials
Starting off with quarterly reports, JinkoSolar has undoubtedly demonstrated strong revenue growth over the three currently reported quarters of 2023. Total revenues for the third quarter of 2023 were RMB31.83 billion (US$4.36 billion), representing a 3.7% increase from the previous quarter and a 63.1% increase from the same period in 2022. Gross profit for the third quarter of 2023 was RMB6.13 billion (US$840.6 million), with a gross margin of 19.3%. This marked an increase from the previous quarter and the same period in 2022. The company also reported basic and diluted earnings per ordinary share of RMB6.42 (US$0.88) and RMB4.61 (US$0.63), respectively, for the third quarter of 2023. This translates into basic and diluted earnings per ADS of RMB25.66 (US$3.52) and RMB18.46 (US$2.53), respectively, beating out expectations by a significant margin. However, as JinkoSolar’s quarterly reports only provide their income statement and balance sheet, we need its cash flow statement to complete the full picture, which leads us to their annual reports.
Looking at JinkoSolar’s net changes in cash over the past 10 years, its performance shows a mix of both positive and negative fluctuations in the company’s cash position. Shortening the timeframe to the past 5 years, JinkoSolar has consistently seen net cash inflows each year which seem rosy, yet this is not the complete reality.
Breaking down JinkoSolar’s cash from operating, investing and financing, we see a different story. Over 2012-2022, JinkoSolar’s cash flow from operating and investing has shown a downward trend, with this trend spiking further downward in the past 2 years. Both items reached a 10-year low in 2022 at a net cash outflow of RMB5.8 billion and RMB12.3 billion, respectively. The final piece of the story that ties it together is an increasing trend in cash inflows from financing that also spiked within the last two years to RMB12.0 billion in 2021 and RMB20.0 billion in 2022, both covering the sum of cash outflows from operating and investing in their respective year.
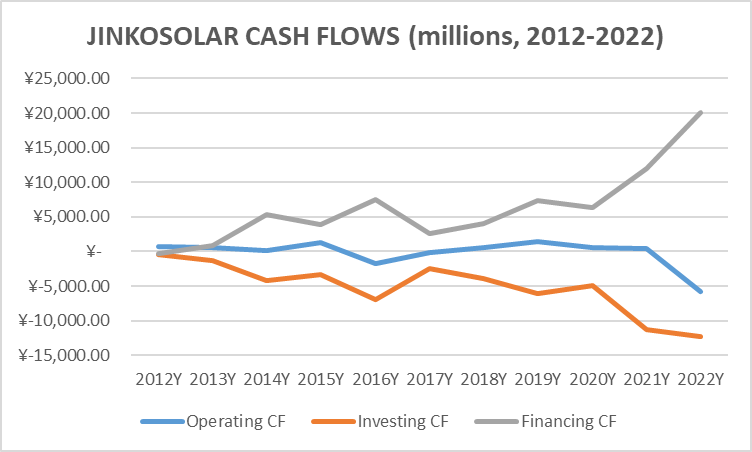
Fig 3. Author’s own illustration, based on data from “JinkoSolar 2012(-2022) Annual Report”
Via the financials of JinkoSolar, it is evident that the business is pursuing growth in sales and investment and thus economies of scale. However, this comes at the cost of taking on vast amounts of financing in the form of liabilities and equity, with the former possibly determining the survival of the business. With reference to the balance sheet, JinkoSolar has begun stabilizing its current ratio from below 1 to approximately 1, which brings a hint of confidence in their liquidity and stability.
Over the last 10 years, both JinkoSolar increased their debt and equity financing significantly but stabilized their debt to equity ratio of around 3. Relative to their competitors, JinkoSolar is on the upper end of debt to equity financing, implying higher financial risk due to debt obligations, cost of capital, financial flexibility as well as increased interest expense. Though, this may not be the case in the future, as the debt to equity ratio of JinkoSolar and their competition are on track to converge at around 2.1.
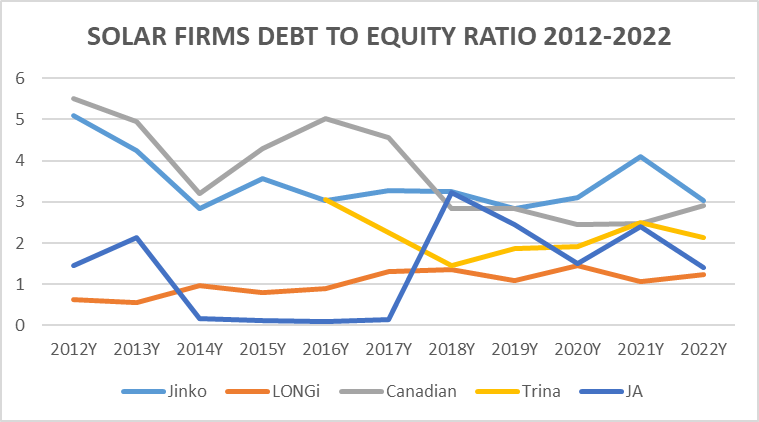
Fig 4. Author’s own illustration, based on data from annual reports of mentioned firms
Given JinkoSolar’s impressive business growth, it isn’t a stretch to say that they are leveraging debt and equity harder than competitors to gain an edge in technology through capital expenditure. Yet whether these expenditures are fully justified remains to be seen as the broader renewable energy market remains sluggish despite JinkoSolar’s business growth. Personally, I have faith and do look forward to a strong comeback from the renewable energy sector, yet broader investor sentiment seems to disagree with my wishes.
Valuation
(All of the data within this subheading are from Bloomberg Terminal, retrieved on 16/2/2024)
Since JinkoSolar as well as the company’s competitors have widely negative FCF, it is quite tricky to value these companies based on DCF. Given the industry’s average current blended forward (BF) P/E of 6.4, JinkoSolar’s -19% 2-year historical average premium to competitors, we can do an equity relative valuation. Taking the industry BF P/E and discounting it by JinkoSolar’s negative premium, we have an implied multiple of 6.4*(1-19%) = 5.2.
Multiplying that by its BF EPS of 6.16, it is easy to price JinkoSolar at $32 per share, given some margin of error. To an extent, this negative premium is justified as most of the company’s financial ratios are below the industry mean, illustrated in the table below.
| BF P/E | BF EV/EBITDA | BF EV/EBIT | BF EV/Revenue | |
| JinkoSolar | 4.4 | 6.3 | 10.3 | 0.5 |
| Mean | 6.4 | 10.9 | 8.7 | 1.4 |
Table 1. Author’s Compilation, based on data from Bloomberg Terminal
Given that the blended forward estimates for all these ratios come from the aggregation of estimates from different sources, such as sell-side analysts, independent research firms, or internal projection, it seems that there isn’t much of a narrative for exponential growth in share price to match its growth in revenue. Conservatively speaking, I would agree with the implied price of $32 within the foreseeable future until further information is released. For short-term investors, JinkoSolar sits at $27.17 per share as of 16/2. This could mean a modest upside of 17.8% in 2024, but it lacks the punch to beat out the market.
Risks
Given an overview of the industry landscape as well as JinkoSolar’s company specifics, it is crucial to look into certain risks that may lead to uncertainty in the company’s future revenue and FCF.
A glaring downside risk that some may observe would be geopolitical risks as seen by the US government’s anti-dumping policies and tariffs, yet I believe that JinkoSolar has strategically insulated themselves from such risk by shifting the bulk of their business to their domestic (Chinese) market as well as Europe and to a lesser degree the APAC region. However, given that 41.9% of JinkoSolar’s revenue in 2022 (Fig 1.) originates from domestic demand, this presents risk in the form of “putting all your eggs in one basket”. As the Chinese and Eurozone economies face a slow recovery and an economic slowdown respectively, the company’s revenue growth is resilient yet plagued with doubt and skepticism. Major deciding factors in whether JinkoSolar’s business growth persists would include the regions’ commitment towards developing renewable energy despite being on the weaker ends of the business cycle.
Financially, a major risk lies in the credibility of JinkoSolar’s clients. Despite strong growth in revenue, we have analyzed that a significant portion of its sales come in the form of receivables than cash, thus resulting in low or even negative CF from operations relative to CF from financing over the past 10 years (Fig. 3). A possible narrative for the downward spike in CF from operations in 2022 could be JinkoSolar extending credit to buyers in times of economic slowdown in order to maintain sales growth. And as the recovery of the Chinese economy isn’t the V-shaped rebound some were or are still looking for, there lies risk of clients defaulting, converting the receivables into bad debt, thus skimming future cash inflows from the projected FCF.
Lastly, JinkoSolar is subject to all kinds of systematic risk, ranging from interest rates, currency risk or regulatory risk. As inflation in the US cools down to ~3%, edging closer to the US’s inflation rate target of 2% it isn’t likely that significant interest rate hikes will occur, with many even expecting interest rate cuts later this year. On the flip side, if the pundits’ predictions of a rate cut materializes, this could result in a relative depreciation of the USD against the RMB, which may lead to an increase in the reported revenue of the company. As for regulatory risks, China is known for its swiftness in implementing regulations at the drop of a hat, as seen in its enforcement of gaming regulations which evaporated nearly $80 billion in market value from China’s two biggest gaming companies in December 2023. However, as the Chinese government mostly slaps tight regulations on sectors it deems harmful to the development of their country (such as gaming), we believe that the Chinese government will not impose draconic restrictions on the solar market due to their consistent support the sector’s growth unless certain developments pose safety hazards.
Conclusion
Despite incredibly strong business growth, growing market share, technological advantages and a positive outlook for solar energy in China based on China’s policy direction, JinkoSolar is held back by both systematic and unsystematic risk. This comes in the form of bearish sentiment towards the Chinese economy and renewable energy held by the market, as well as weak cash flow management and FCF from JinkoSolar’s operations. Acknowledging JinkoSolar’s identity as a solar module manufacturer aiming to expand its business and thus market share before the renewable energy becomes fully developed, it is understandable for the business to incur large amounts of fixed cost in the form of investment in PPE as well as drastic increases in accounts receivables to secure business transactions during times of economic slowdown for its clients. This results in significant cash outflow in the short term. However, these practices are not sustainable in the long run and certainly reduce FCF, thus shareholder value. Thus giving JinkoSolar its rating- “Hold” with a target price of $32 per share.
As an investor and supporter of renewable energy, the major catalysts I would look for that may warrant a “Buy” rating would include the following. Being company-specific, I would want to see signs of JinkoSolar shifting their emphasis on consolidating their position in the market while maintaining reasonable and competitive growth as well as reductions in accounts and notes receivable which increase their FCF. Thus, I look forward to their 2023 Q4 report and 2023 annual report to receive further insight on their business direction. From a macro and industry-wide perspective, investors should also look forward to interest rate cuts from the Federal Reserve Bank and Chinese economic data updates, as both are possible macroeconomic catalysts for upward movement in JinkoSolar’s share price. Lastly but not least, investors should pay attention to global policies, trends and publications that signal health in the global or at least Chinese renewable energy market as that would justify JinkoSolar’s substantial investments in PPE and financing by increasing the certainty that there is, in fact, robust demand for their supply. If a combination of the mentioned catalysts emerges, I strongly believe that JinkoSolar possesses significant deep value, but we shall wait and see.
Analyst’s Disclosure: I/we have no stock, option or similar derivative position in any of the companies mentioned, and no plans to initiate any such positions within the next 72 hours. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
Seeking Alpha’s Disclosure: Past performance is no guarantee of future results. No recommendation or advice is being given as to whether any investment is suitable for a particular investor. Any views or opinions expressed above may not reflect those of Seeking Alpha as a whole. Seeking Alpha is not a licensed securities dealer, broker or US investment adviser or investment bank. Our analysts are third party authors that include both professional investors and individual investors who may not be licensed or certified by any institute or regulatory body.
